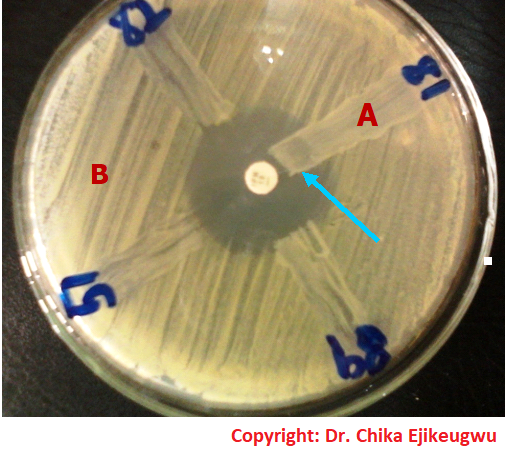
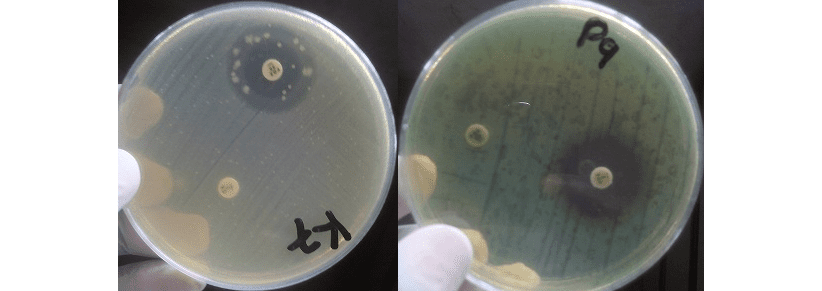
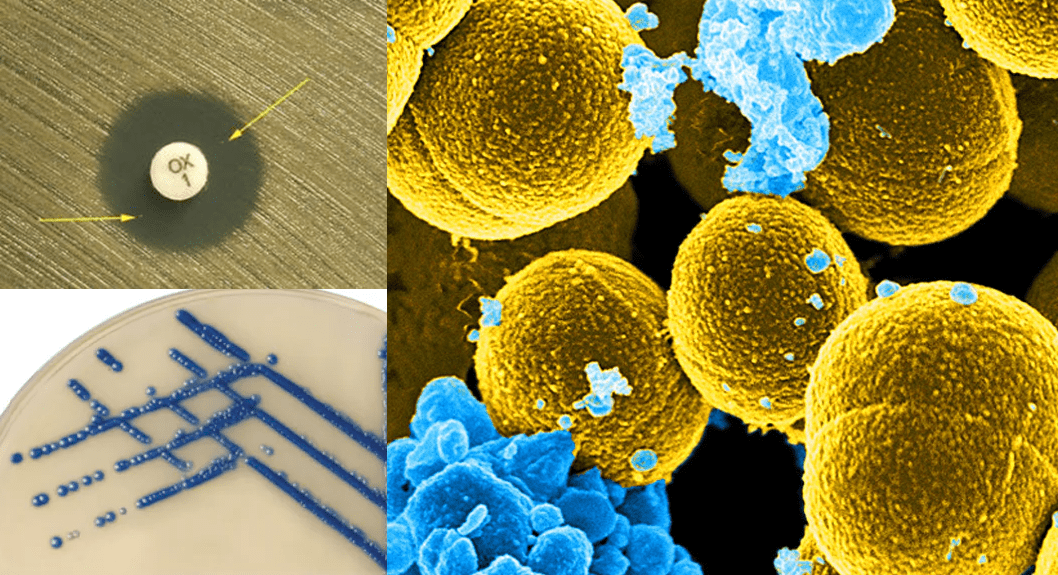
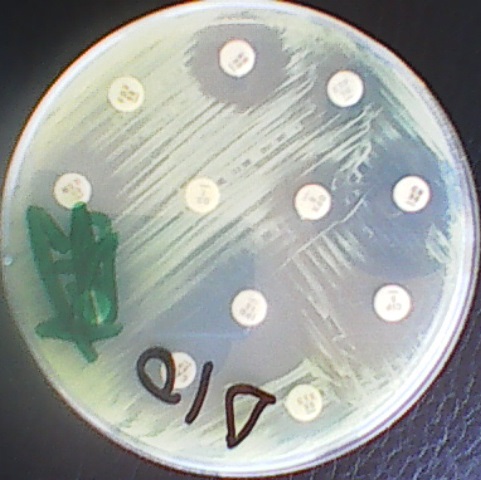
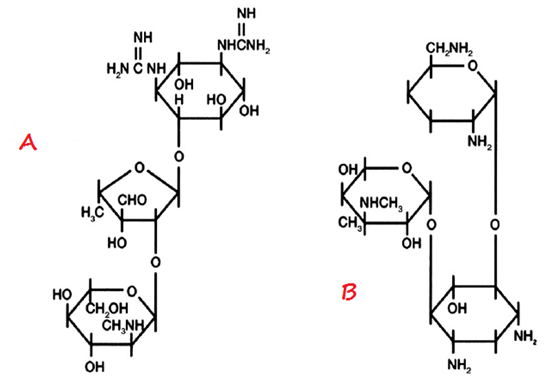
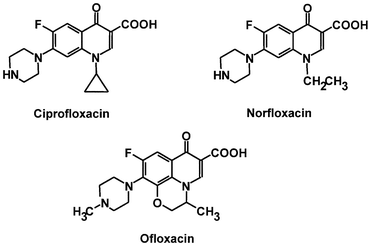
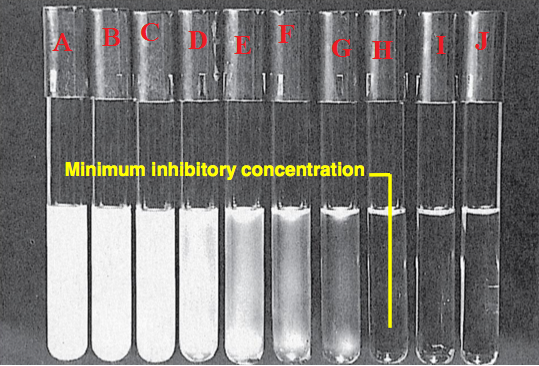
Antibiotics remain one of the most important discoveries in medical science, serving as a cornerstone […]
Category: Pharmaceutical Microbiology
AmpC ENZYMES
AmpC β-lactamases are a class of enzymes produced by certain bacteria that confer resistance to […]
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): A Global Health Threat
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a type of bacterium that has become resistant to many […]
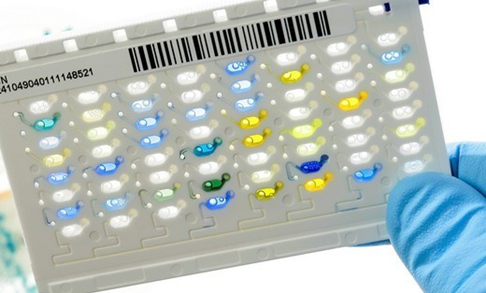
AUTOMATED SYSTEMS FOR BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION AND ANTIBIOGRAM: VITEK 2 AUTOMATED COMPACT SYSTEM & MALDI-TOF
AUTOMATED SYSTEMS FOR BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION AND ANTIBIOGRAM: VITEK 2 AUTOMATED COMPACT SYSTEM & MALDI-TOF There […]
Clinical and pharmacological significance of synergism, antagonism and additive effects of drugs or pharmacological compounds
The terms synergistic effect (synergism), antagonistic effect (antagonism) and additive effect are all clinical and […]
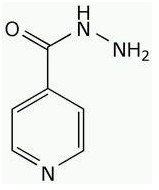
ISONIAZID – anti-tuberculosis (TB) drug
Isoniazid or isonicotinyl hydrazine (INH) is a first-line antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis […]
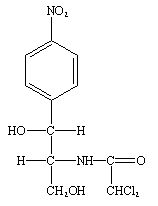
CHLORAMPHENICOL
Chloramphenicol is a protein synthesis inhibitor but the antibiotic unlike other drugs that interfere with […]
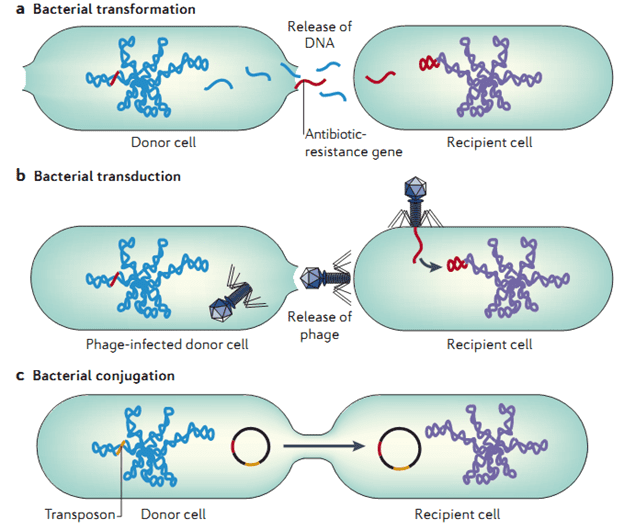
MECHANISMS OF TRANSFER OF RESISTANCE GENES IN BACTERIA
Below are some of the major ways through which bacteria pass on their antibiotic […]
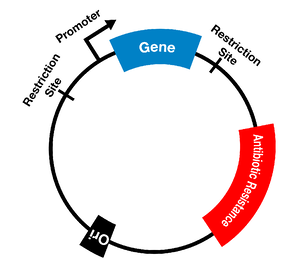
GENETIC BASIS OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Genetic resistance of microbes to antibiotics is due to a chromosomal mutation in the bacterial […]
UNDERSTANDING MBL MICROBIOLOGY
Metallo-beta-lactamases (MBLs) are beta-lactamase enzymes produced by pathogenic bacteria, and which hydrolyzes the carbapenems (e.g. […]
ESBL Positive – Understanding Extended spectrum beta-lactamases tests
What does it mean to be ESBL positive? Learn how to detect these antibiotic-resistant bacteria […]
ANTIMICROBIAL PROPERTIES OF LICHEN SECONDARY METABOLITES
Lichens possess varying antimicrobial properties; and they have been shown to be active against a […]
Materials from the iAMR team for teaching & illustrating AMR
Are you looking for more information about Antibiotic Resistance or antimicrobial resistance (AMR)? Do you […]
BETA-LACTAMASE: an important resistance mechanism in bacteria
Beta-lactamases are enzymes secreted by both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria, and which have […]
MULTIDRUG RESISTANT BACTERIA (MDRB)
The introduction of antibiotics into clinical medicine for the treatment of infectious diseases heralded an […]
GENTAMICIN
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic. Aminoglycosides are antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis like the tetracyclines, […]
CIPROFLOXACIN
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic that is derived from the earlier quinolones. Nalidixic acid is […]
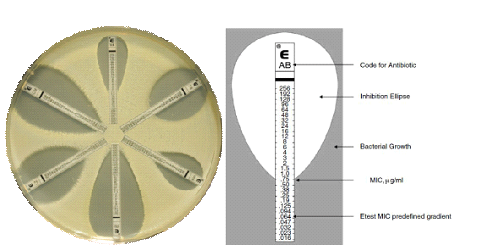
MINIMUM INHIBITORY CONCENTRATION INTERPRETATION: Guidelines for accurate testing
This definitive guide unlocks the secrets of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration interpretation with clear explanations of […]
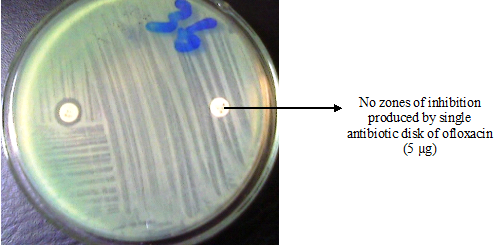
MEASUREMENT OF ANTIMICROBIAL EFFICACY/ACTIVITY
The determination of the antimicrobial susceptibility of a given pathogen to a particular antimicrobial agent […]
GENOTYPIC DETECTION OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANT MICROBES
The genotypic detection and characterization of antibiotic resistant genes in pathogenic bacteria is more specific […]
FEATURES OF THE VITEK 2 AUTOMATED COMPACT SYSTEM FOR BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION AND ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY TEST (AST)
Helping the physician select the best treatment at a much faster pace based on the […]
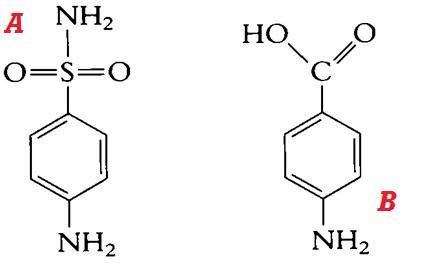
SULPHONAMIDES
Sulphonamides or sulpha drugs are generally known as folate synthesis inhibitors because they inhibit […]
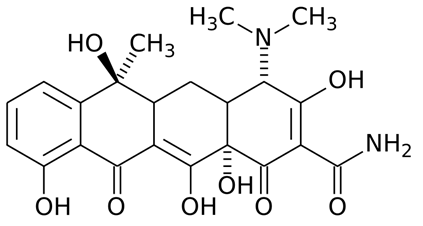
TETRACYCLINES
Tetracyclines are general purpose antibiotics used for a variety of clinical applications, and they include […]
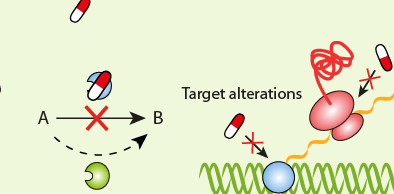
TYPES OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Bacteria have evolved to survive in diverse environments. They survive exposure to harsh chemicals including […]
BRIEF HISTORY OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Antimicrobial agents, particularly antibiotics are the most significant class of pharmaceuticals and are one of […]
Sterile & Non-Sterile Pharmaceutical Products
Sterile pharmaceutical products are defined as sensitive pharmaceutical products that should be free from living micro-organisms, […]
CONTROL OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Antibiotic resistance knows no border of any country since there is free movement of both […]
IMPACT AND COST OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE ON PUBLIC HEALTH AND THE ECONOMY OF A NATION
Antimicrobial agents (antibiotics in particular) have helped countless numbers of people worldwide owing to their […]
FACTORS THAT CONTRIBUTE TO ANTIBIOTIC (ANTIMICROBIAL) RESISTANCE
Antibiotic resistance is a global health problem that bedevils our health sector and threatens our […]
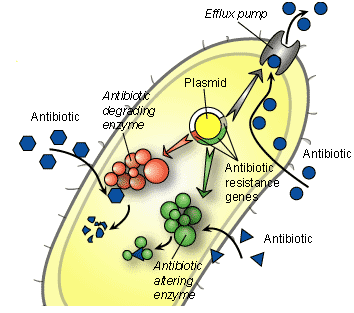
SPECIFIC MECHANISMS OF ACQUIRING RESISTANCE BY BACTERIA/MICROBIAL PATHOGENS
An antibiotic has to go through a number of steps in order to exert its […]
MODE (MECHANISMS) OF TRANSFER OF RESISTANCE GENES
Antibiotic resistant bacteria owe their drug insensitivity and ingenuity in developing resistance against our therapeutic […]
ANTIMICROBIAL (ANTIBIOTIC) RESISTANCE: definition, selective pressure and clonal selection
Antibiotic or antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a phenomenon that occurs when bacteria are not killed […]
TYPES OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
The resistance of a microbial cell to the potent action of antimicrobial agents or antibiotics […]
Chromatic Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci (VRE) agar
Chromatic VRE is a selective and differential chromogenic medium used for the qualitative and presumptive detection […]
HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP): Building Effective Food Safety Control Systems for Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) is an internationally recognized, science-based food safety management […]
INDICATOR ORGANISMS
Indicator organisms are microorganisms that signify the possible contamination of food or food products as […]
HISTORY OF ANTIBIOTICS – a synopsis on how it all started
Over the past 70 years, antibiotics have saved countless number of lives across the globe […]
NITROCEFIN TEST FOR BETA-LACTAMASE PRODUCTION
The production of beta-lactamase enzymes by Gram negative bacteria including E. coli, P. aeruginosa and […]
Vancomycin resistance in Enterococci
Enterococcus (plural: Enterococci) is a group of bacteria that is normally found in the intestines […]
What are ESBLs?
ESBLs (extended spectrum beta-lactamases) are enzymes that mediate resistance to extended-spectrum (third generation) cephalosporins (e.g., […]
WHO Global Principles for the Containment of Antimicrobial Resistance in Animals Intended for Food
Purpose: To minimize the negative public health impact of the use of antimicrobial agents in […]
Differences between Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) & Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Laboratory Testing Regulations
People are often confused by differences between Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) regulations and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) […]
CEFTAZIDIME-IMIPENEM ANTAGONISM TEST (CIAT)
Ceftazidime-imipenem antagonism test (CIAT) is one of the phenotypic confirmation tests that can be used […]
Fusidic acid
Fusidic acid is a bacteriostatic antimicrobial agent and/or antibiotic that is derived from the fungus, […]
ROUTES OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION
Therapeutic drugs are administered in various ways, and these include parenteral and oral administration. Other […]
PHARMACOKINETICS & PHARMACODYNAMICS
Pharmacokinetics is simply the study of how the body reacts to therapeutic agents or drugs […]
DRUG INTERACTION
To be clinically effective for the treatment of infectious diseases, every drug must reach a […]
MONITORING OF WATER QUALITY
Water quality is defined as the suitability of water to sustain various uses or processes […]
ACTIVE AIR MONITORING
Active air monitoring also involve the use of settle plates or sedimentation culture plates (as […]
PASSIVE AIR MONITORING
Passive air monitoring is usually done using special type of Petri dish plates known as […]