ADENOVIRIDAE FAMILY
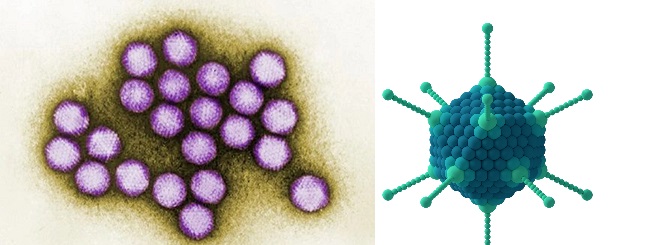
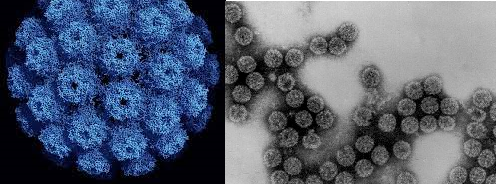
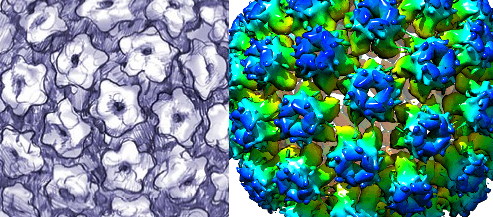
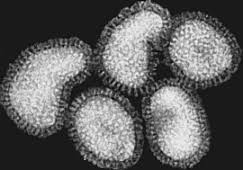
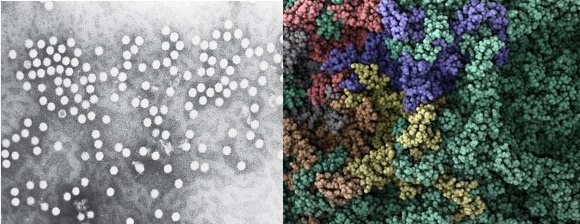
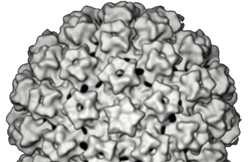
Adenoviridae family is made up of two viral genera which are Mastadenoviridae (which contain viruses that infect humans and other mammals)and Aviadenovirus (which contain viruses that infect birds). Adenoviruses are one of the major viruses in this family; and they have a worldwide distribution. Adenoviruses have an icosahedral shape, and they have no envelope. They […]
ADENOVIRIDAE FAMILY Read More »
Virology