Nycodenz: application and properties
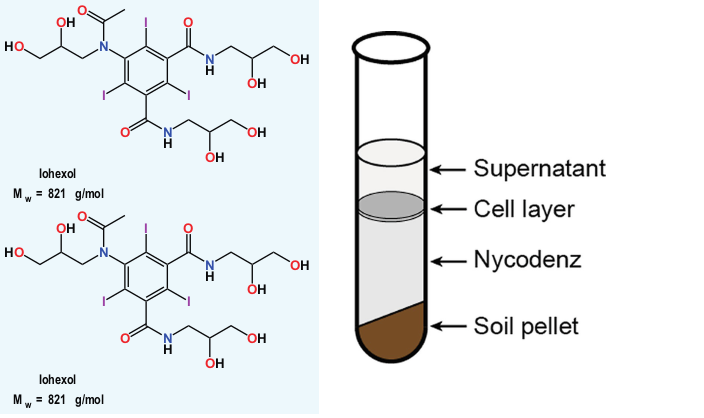
What is Nycodenz Nycodenz is a non-ionic, triiodinated radiopaque substance used primarily in molecular biology and biochemistry for density gradient centrifugation. Its chemical formula is C_19H_26I_3N_3O_9. Nycodenz creates gradients that are used to separate cells, viruses, organelles, and other biological particles based on their density. Nycodenz is a brand name for a non-ionic, iso-osmotic density […]
Nycodenz: application and properties Read More »
Environmental & Soil Microbiology, Microbe Lab, Techniques in Microbiology Lab