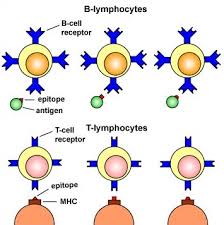
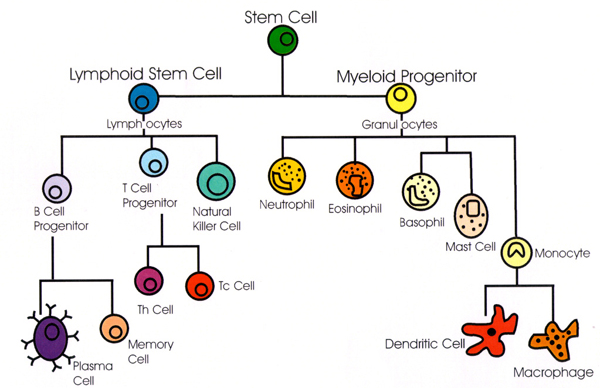
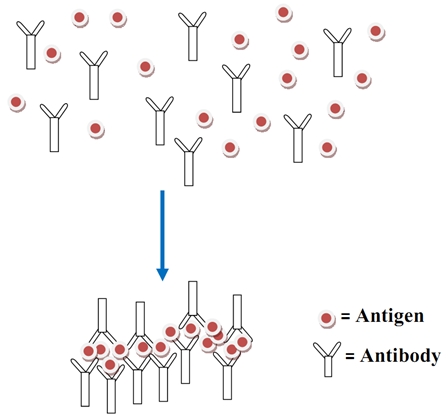
INNATE IMMUNITY
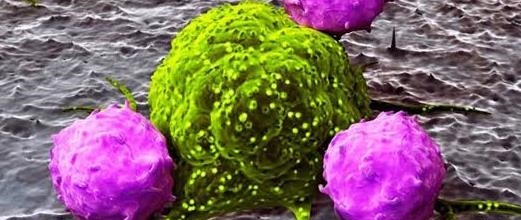
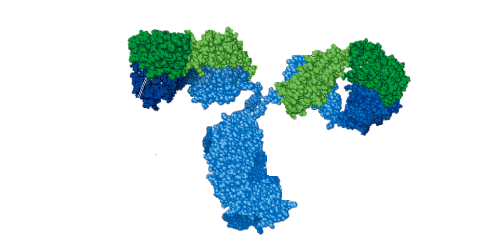
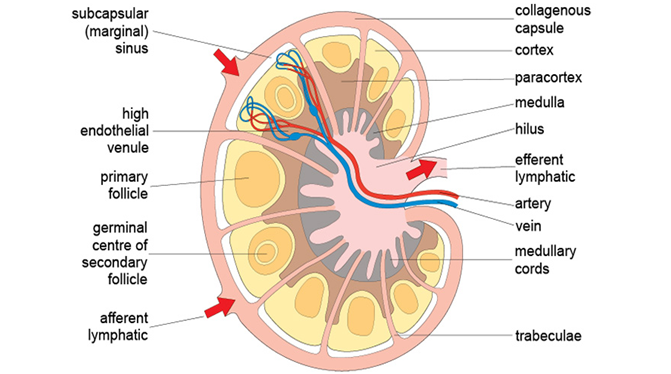
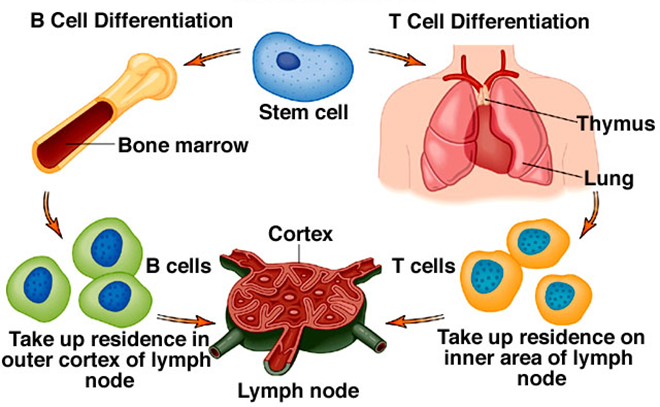
Innate immunity is the body’s natural inborn resistance to infection and it is quick in responding to invasive microbes. It is a component of the immune system that is an inherited protective mechanism, and which protect the body of an animals from many kinds of pathogens. Innate immunity is a nonspecific immune response to antigens, […]