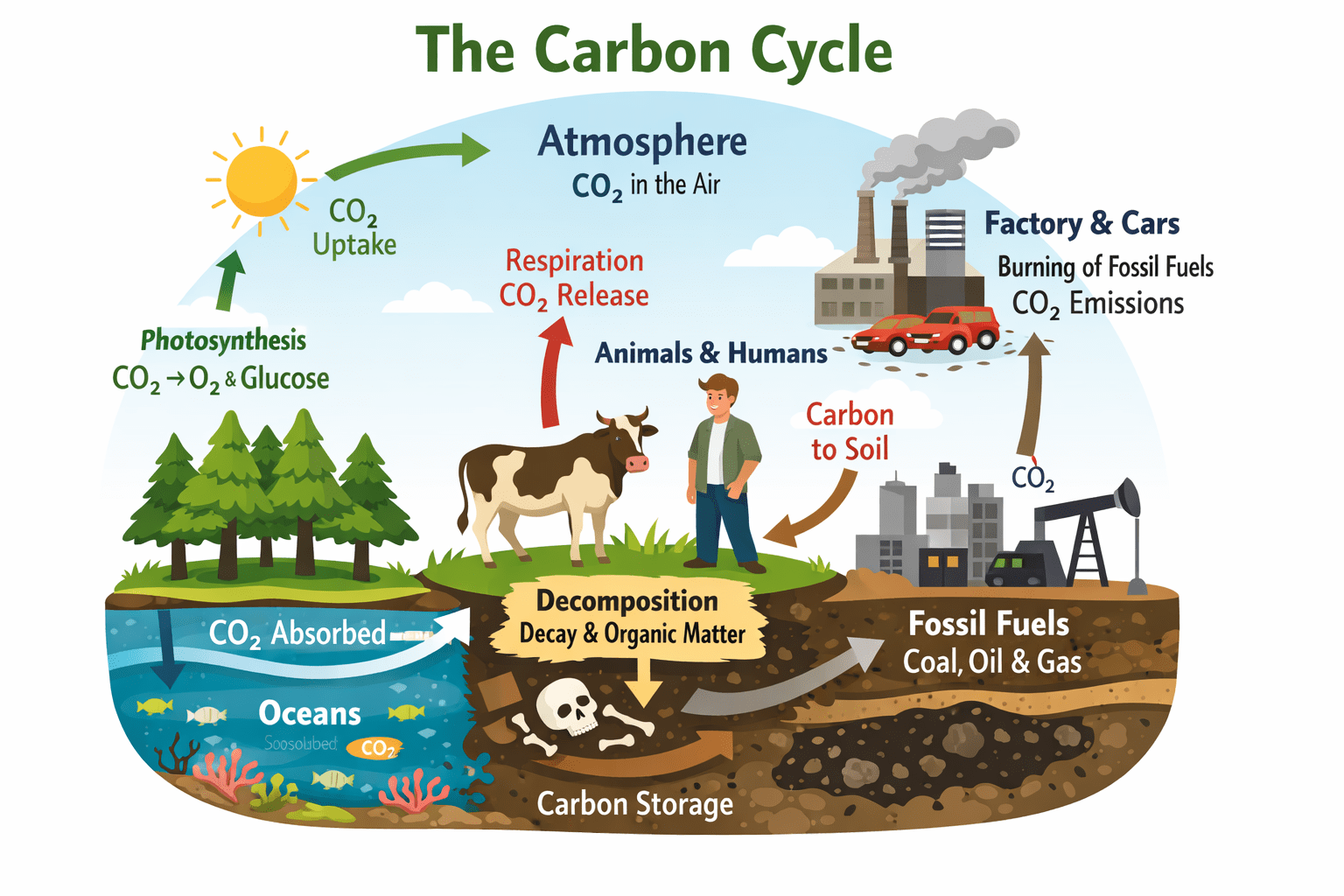
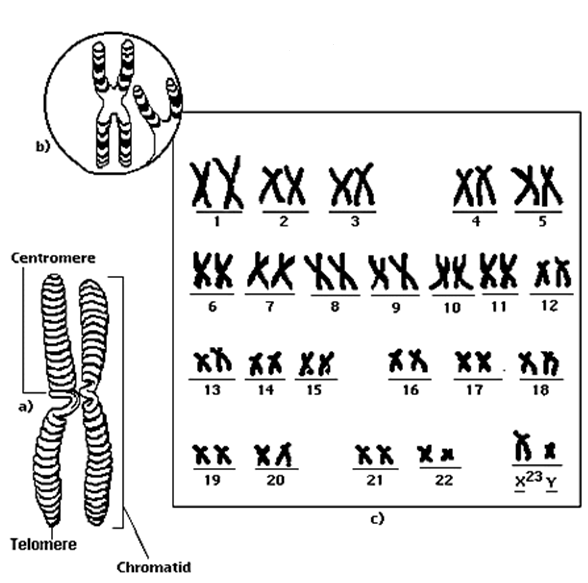
Carbon is the fundamental element that anchors all organic compounds in the ecosystem. It serves […]
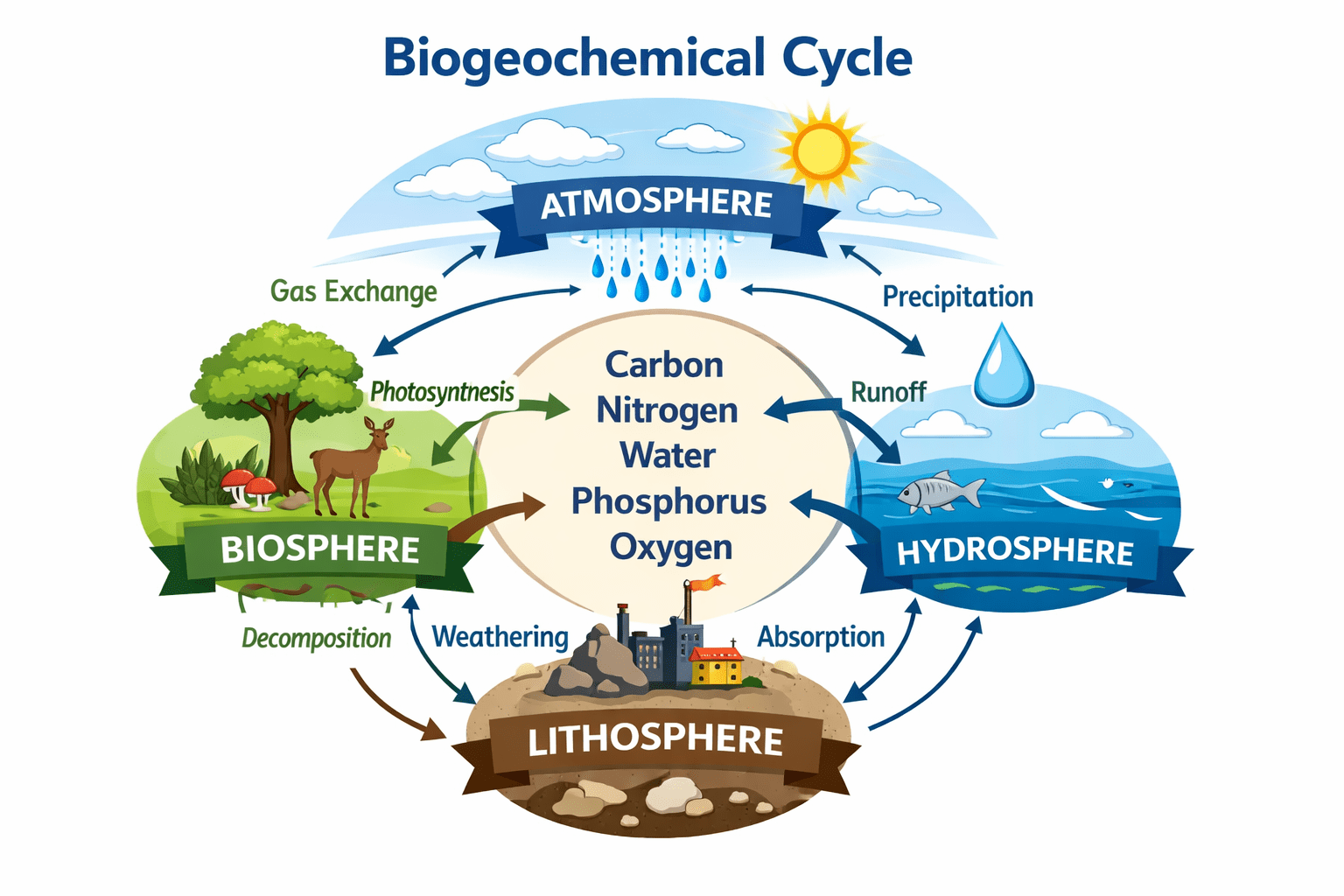
Biogeochemical Cycles and Their Importance to Life on Earth
The term biogeochemical is derived from the combination of three distinct but interrelated words: bio, geo, and chemical. The prefix bio refers […]
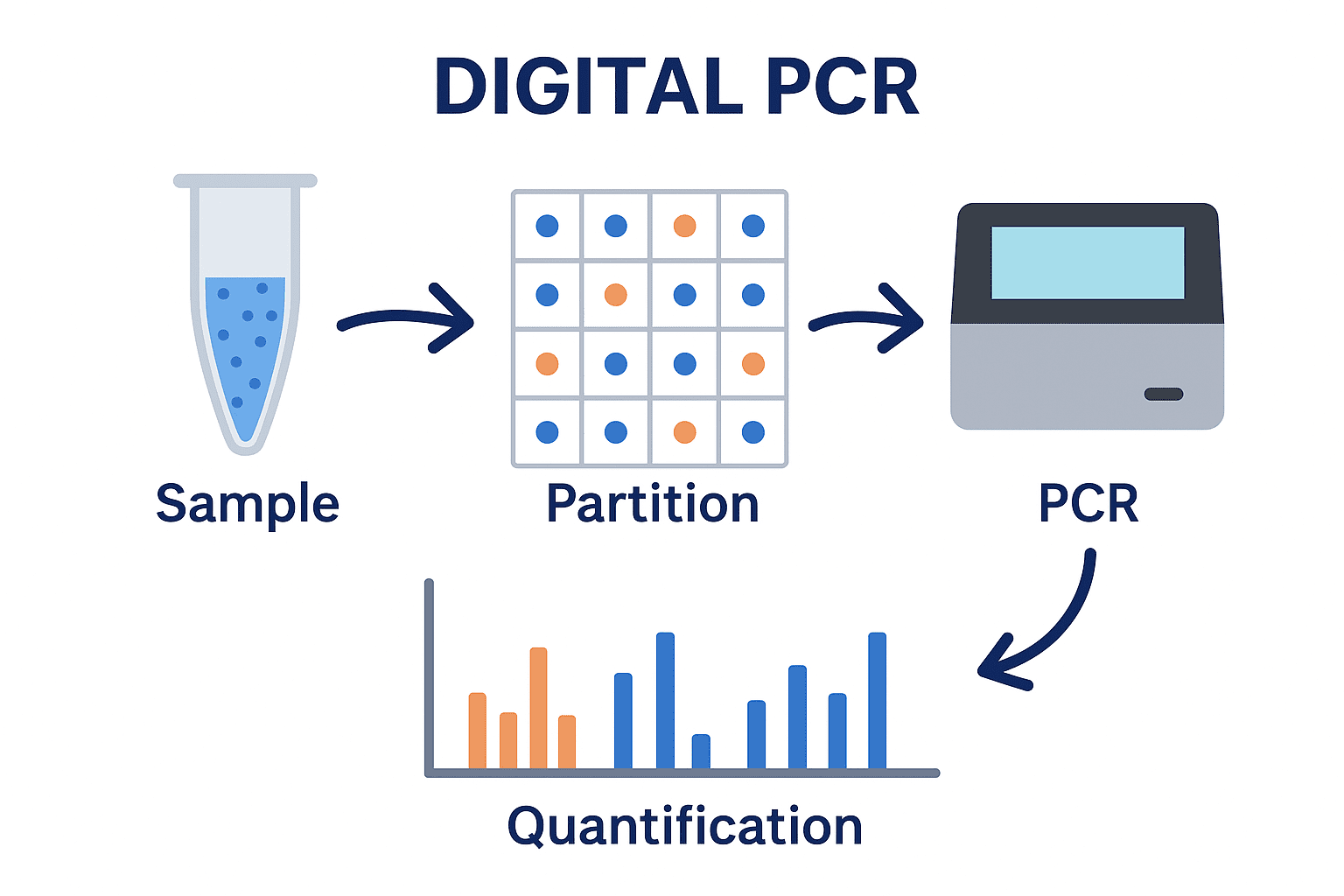
Digital PCR (dPCR): The Next Frontier in Absolute Nucleic Acid Quantification
Digital PCR (dPCR) is a method of quantifying nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) targets without […]
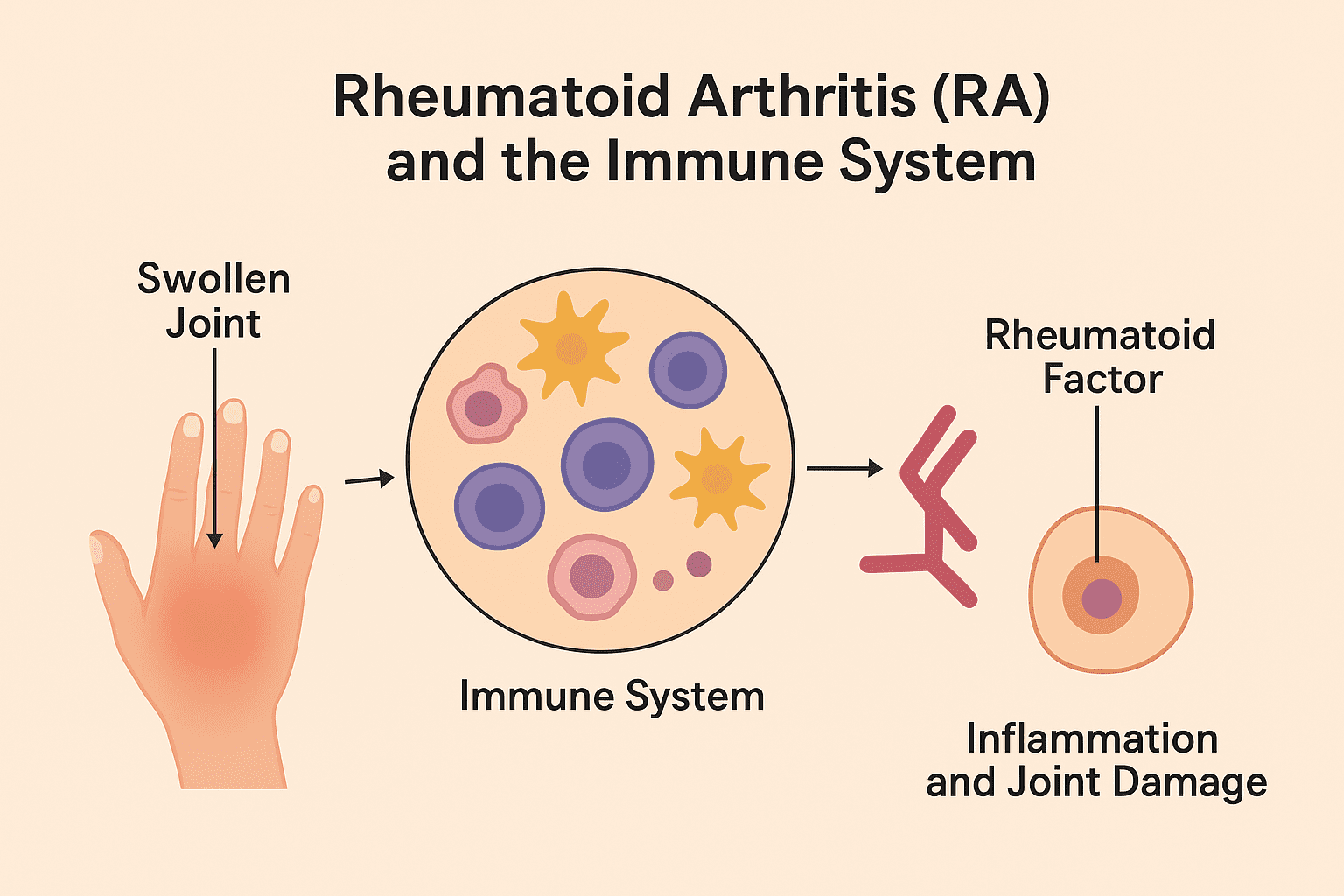
From Genes to Joints: Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis as an Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells and tissues, […]
Schistosomiasis and One Health: Tackling a Snail-Borne Threat to Humans, Animals, and Ecosystems
Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, is a debilitating water-borne disease caused by parasitic blood flukes […]
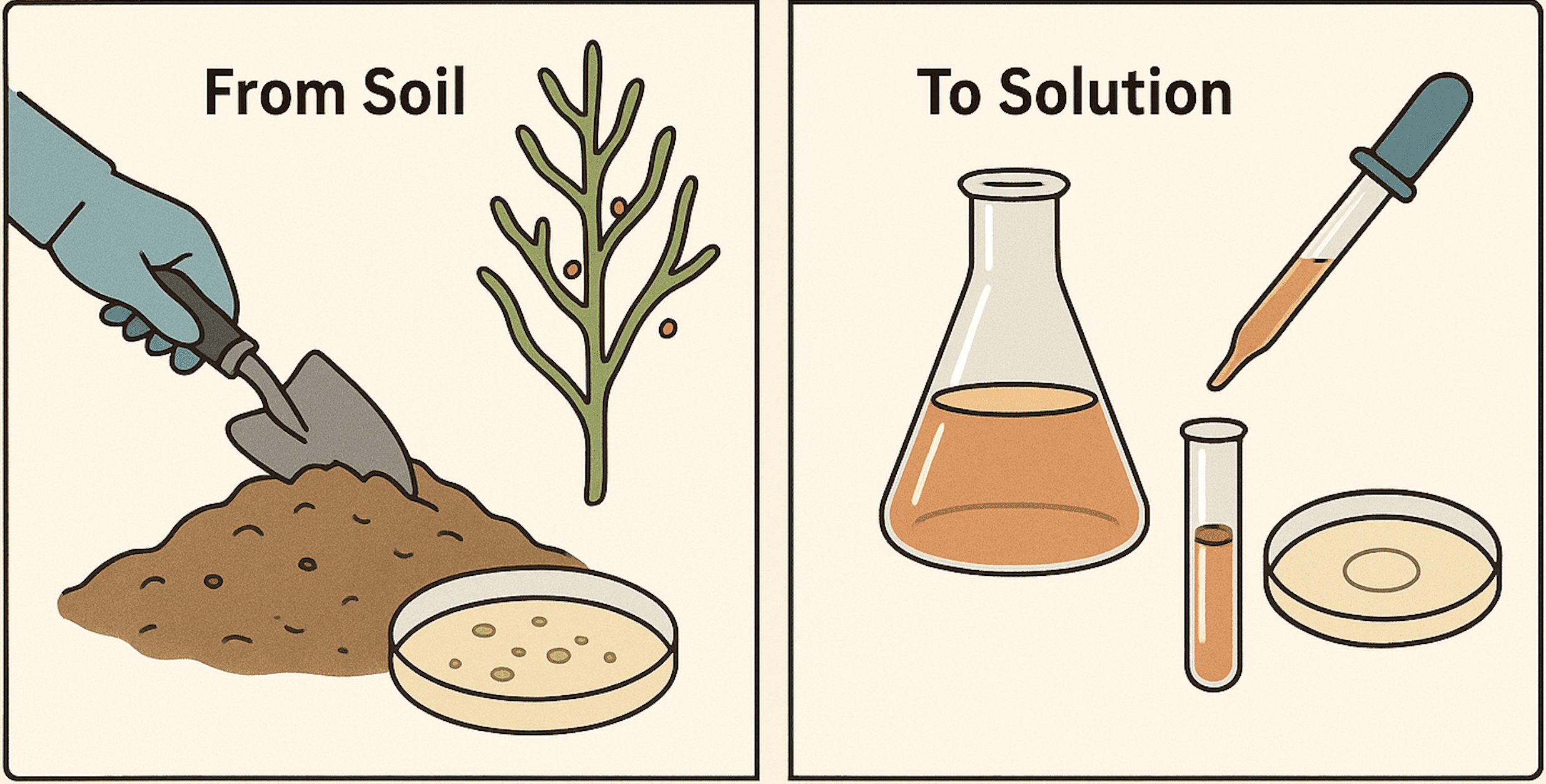
From Soil to Solution: How Streptomycin is Extracted and Evaluated
Antibiotics remain one of the most important discoveries in medical science, serving as a cornerstone […]
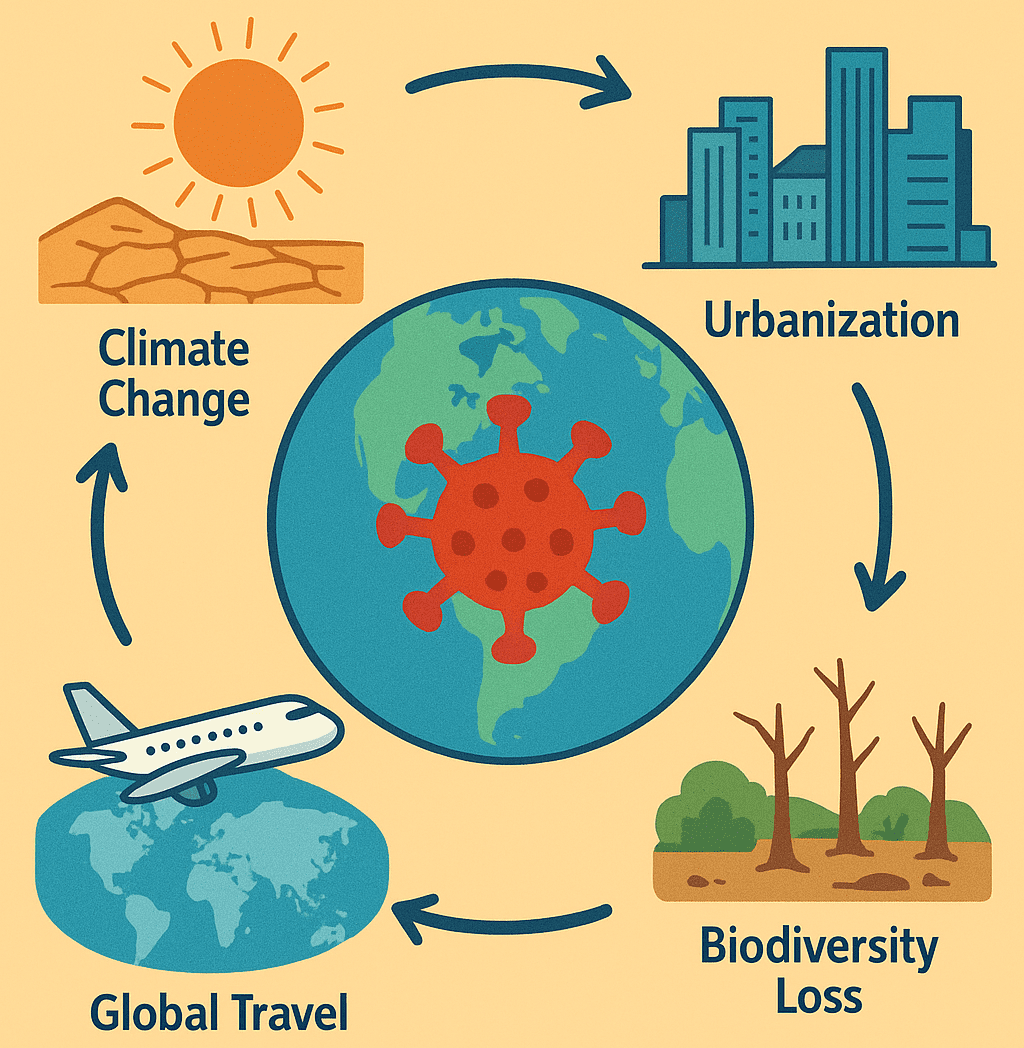
How Global Change Contributes to the Spread of Infectious Diseases
The dynamics of infectious disease transmission are shaped by a complex interplay of environmental, biological, […]
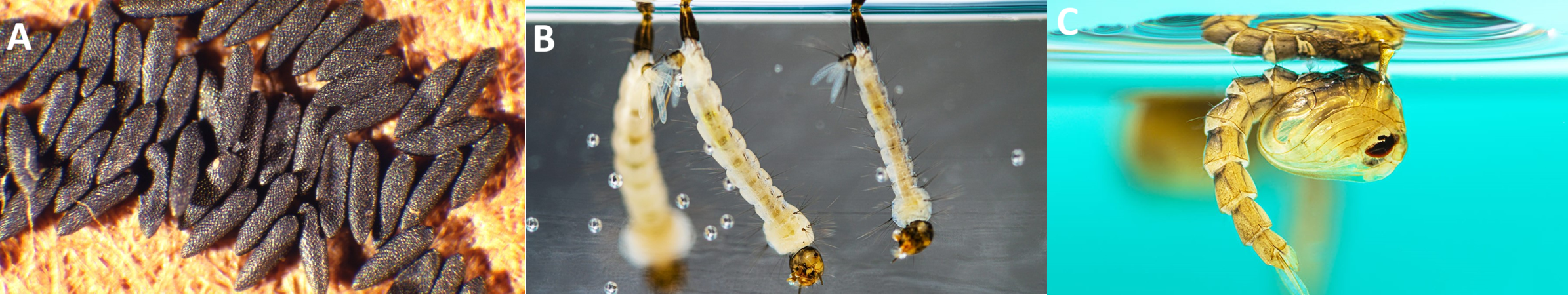
From Mosquito Bite to Global Threat: Is Chikungunya the Next Pandemic?
Chikungunya (CHIKV) is a mosquito-borne viral disease marked by sudden onset fever and severe joint […]
Metaproteomics & Transcriptomics
What is Metaproteomics? Metaproteomics refers to the large-scale characterization of the complete set of proteins […]
AmpC ENZYMES
AmpC β-lactamases are a class of enzymes produced by certain bacteria that confer resistance to […]
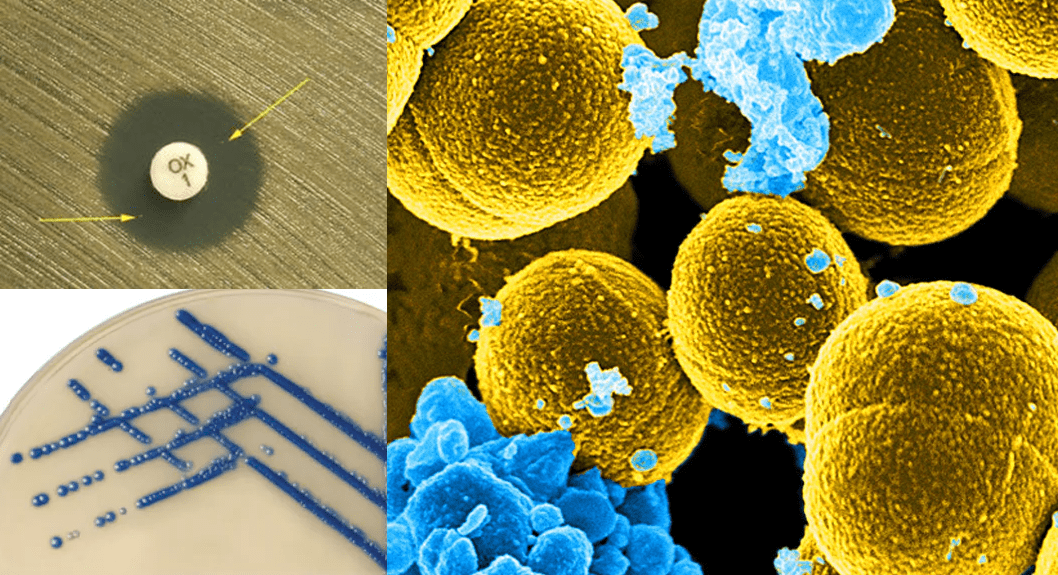
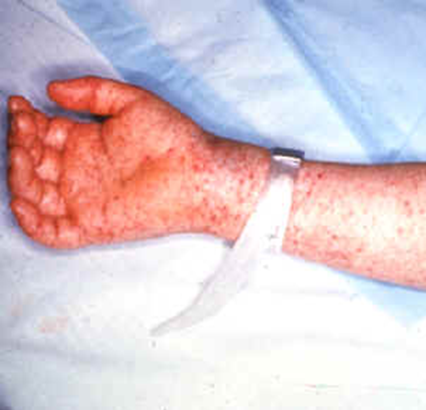
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): A Global Health Threat
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a type of bacterium that has become resistant to many […]
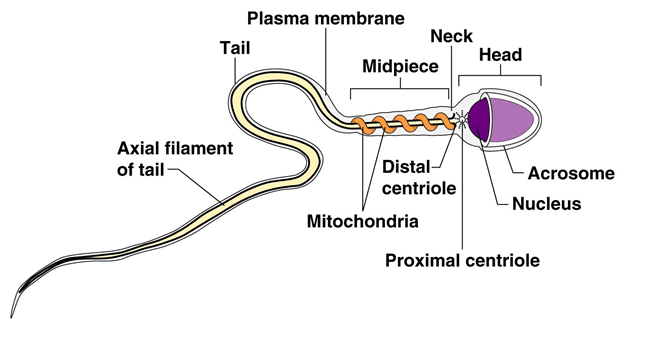
SEMINAL FLUID (SEMEN) MICROSCOPY, CULTURE & SPERM CELL COUNT
SEMEN MICROSCOPY AIM: To determine any abnormality in a seminal fluid (semen) as an aid […]
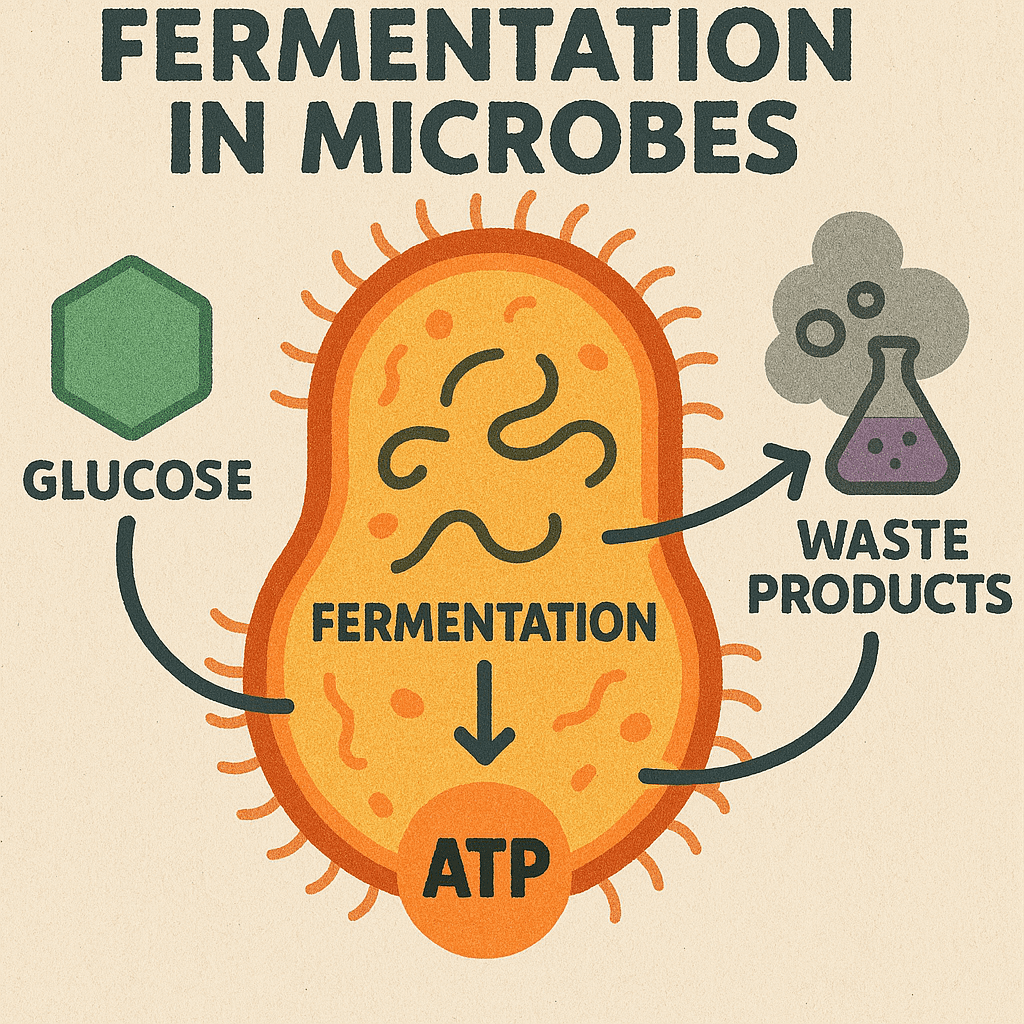
Microbial Fermentation: Processes, Pathways, and Applications
Fermentation is a metabolic process that enables cells to extract energy from organic molecules in […]
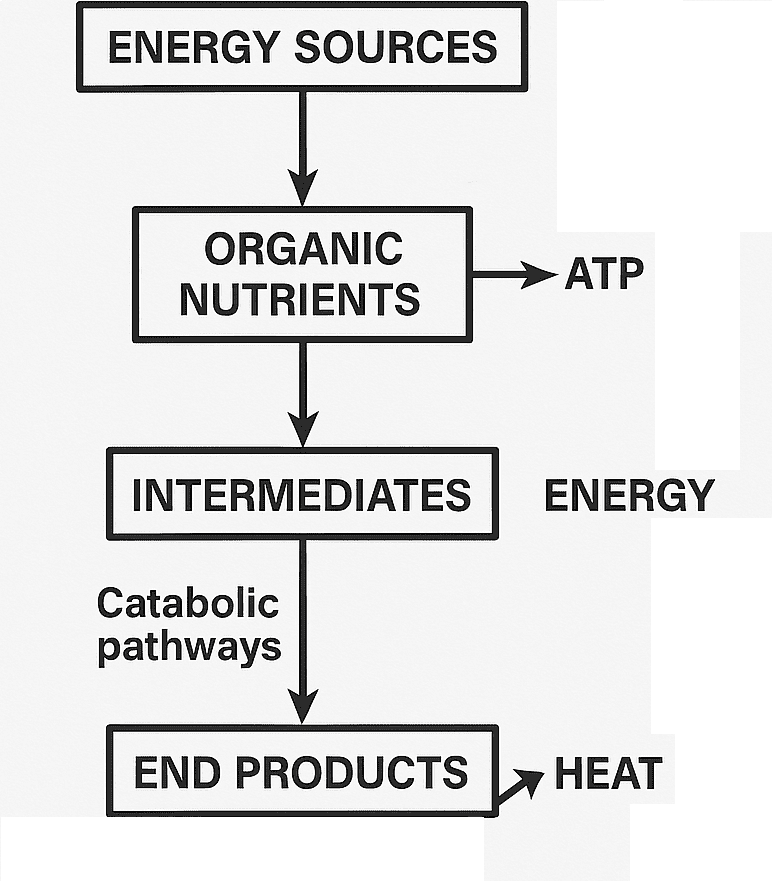
CATABOLIC PROCESSES IN MICROBIAL CELL (CATABOLISM)
RESPIRATION IN MICROBIAL CELL Respiration in microbial cells is generally an energy-yielding type of metabolism […]
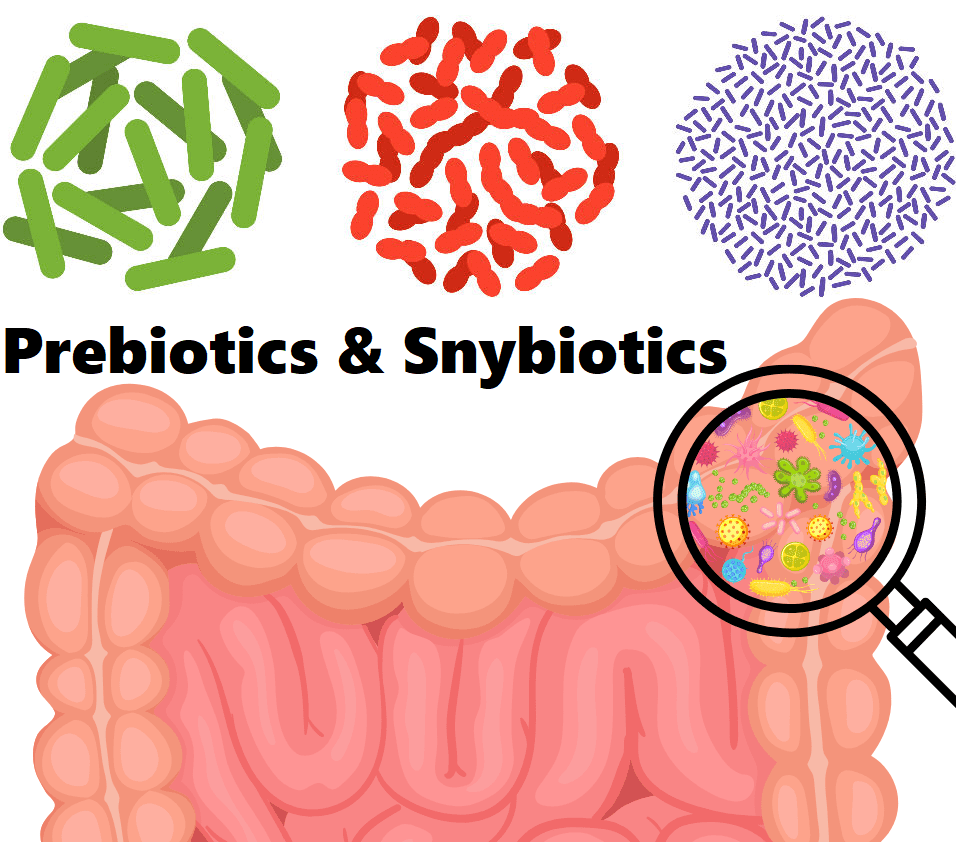
Harnessing the Power of Prebiotics and Synbiotics: A New Frontier in Gut Health and Beyond
IntroductionIn recent decades, scientific interest in gut health has intensified significantly, driven by a growing […]
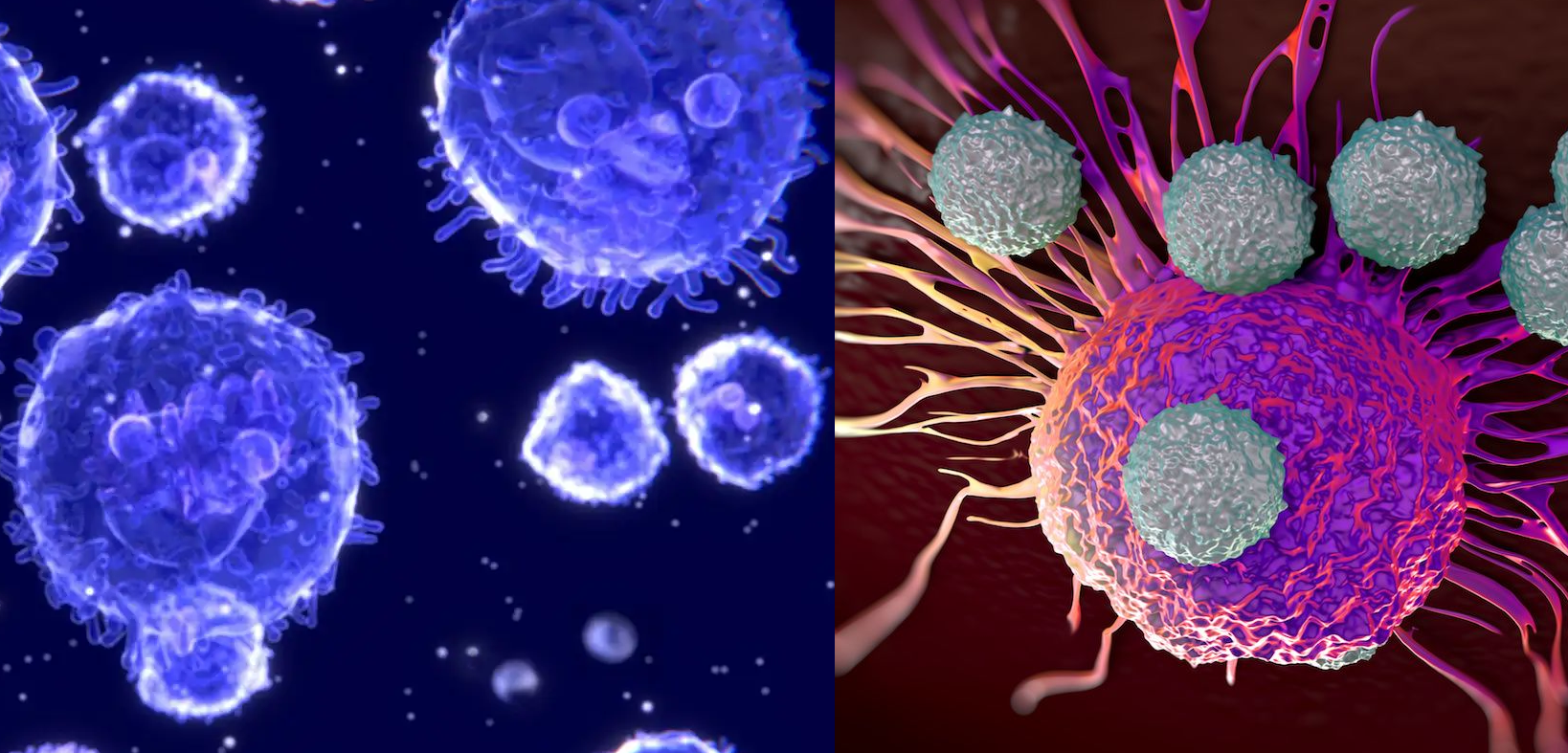
CELLS OF INNATE IMMUNITY
Innate immunity is found in nearly all forms of life, and exposure to foreign substances […]
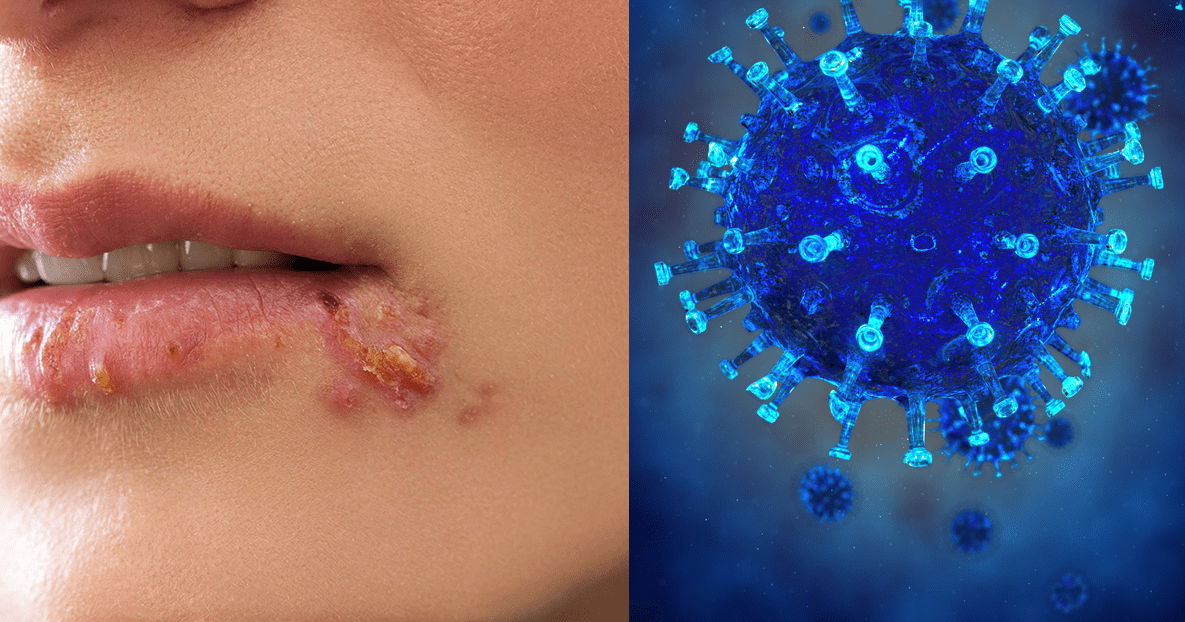
HERPESVIRIDAE FAMILY
Gammaherpesvirinae family has two genera viz: Lymphocryptovirus (that contain Epstein-Barr virus) and Rhadinovirus (that contain […]
Types of culture media
GENERAL PURPOSE MEDIA General purpose media or basic medium is a routine culture media which […]
LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES
Listeria monocytogenes is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive, non-spore forming, aerobic or anaerobic intracellular rod bacterium in […]
Factors in the Design and Construction of Industrial Fermenters: An Interdisciplinary Approach to Cost-Efficient Bioprocessing
The success of any industrial fermentation process heavily depends on the efficiency, reliability, and appropriateness […]
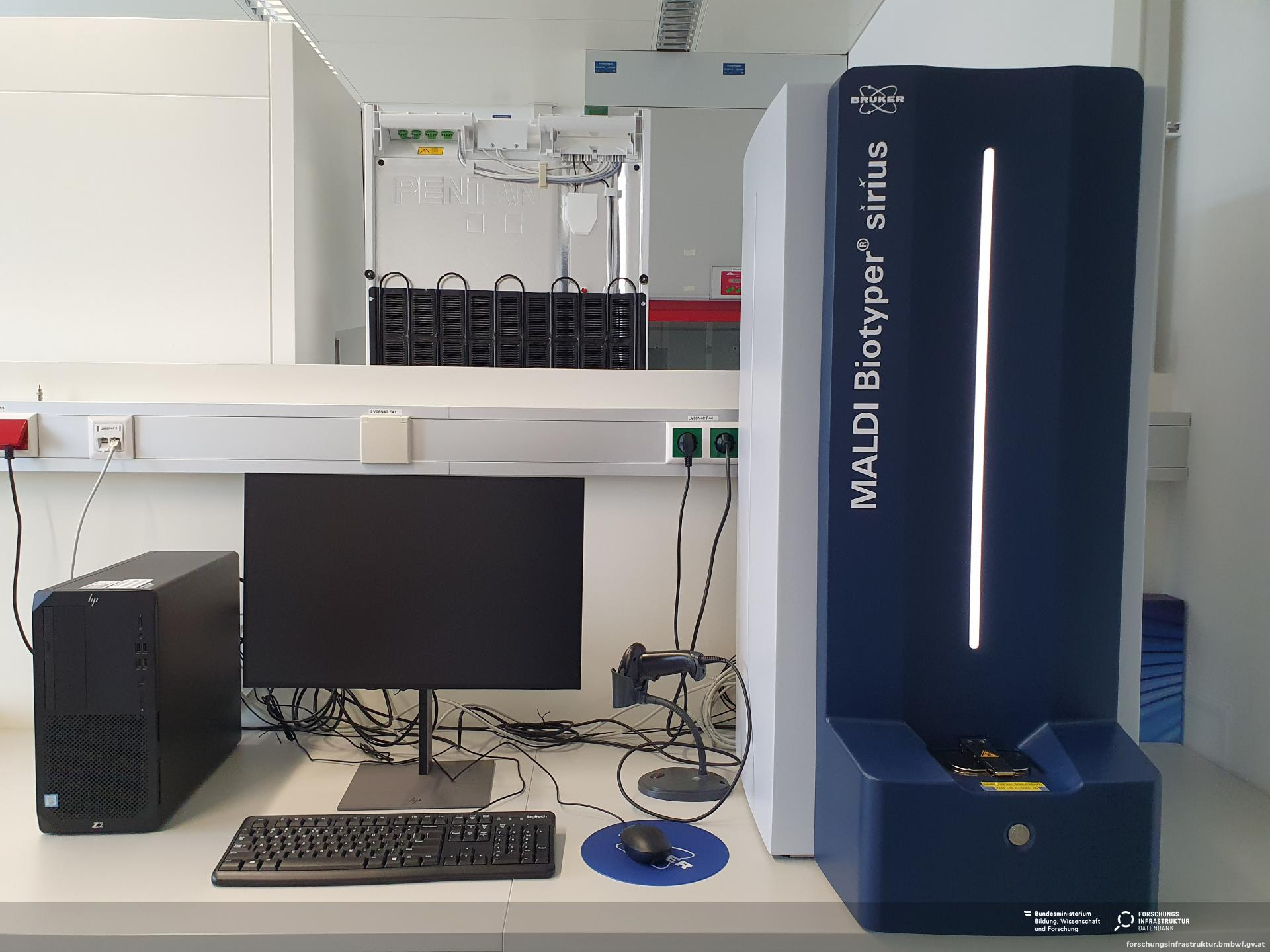
AUTOMATED SYSTEMS FOR BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION AND ANTIBIOGRAM: VITEK 2 AUTOMATED COMPACT SYSTEM & MALDI-TOF
AUTOMATED SYSTEMS FOR BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION AND ANTIBIOGRAM: VITEK 2 AUTOMATED COMPACT SYSTEM & MALDI-TOF There […]
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) workflow
The workflow of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) involves several critical […]
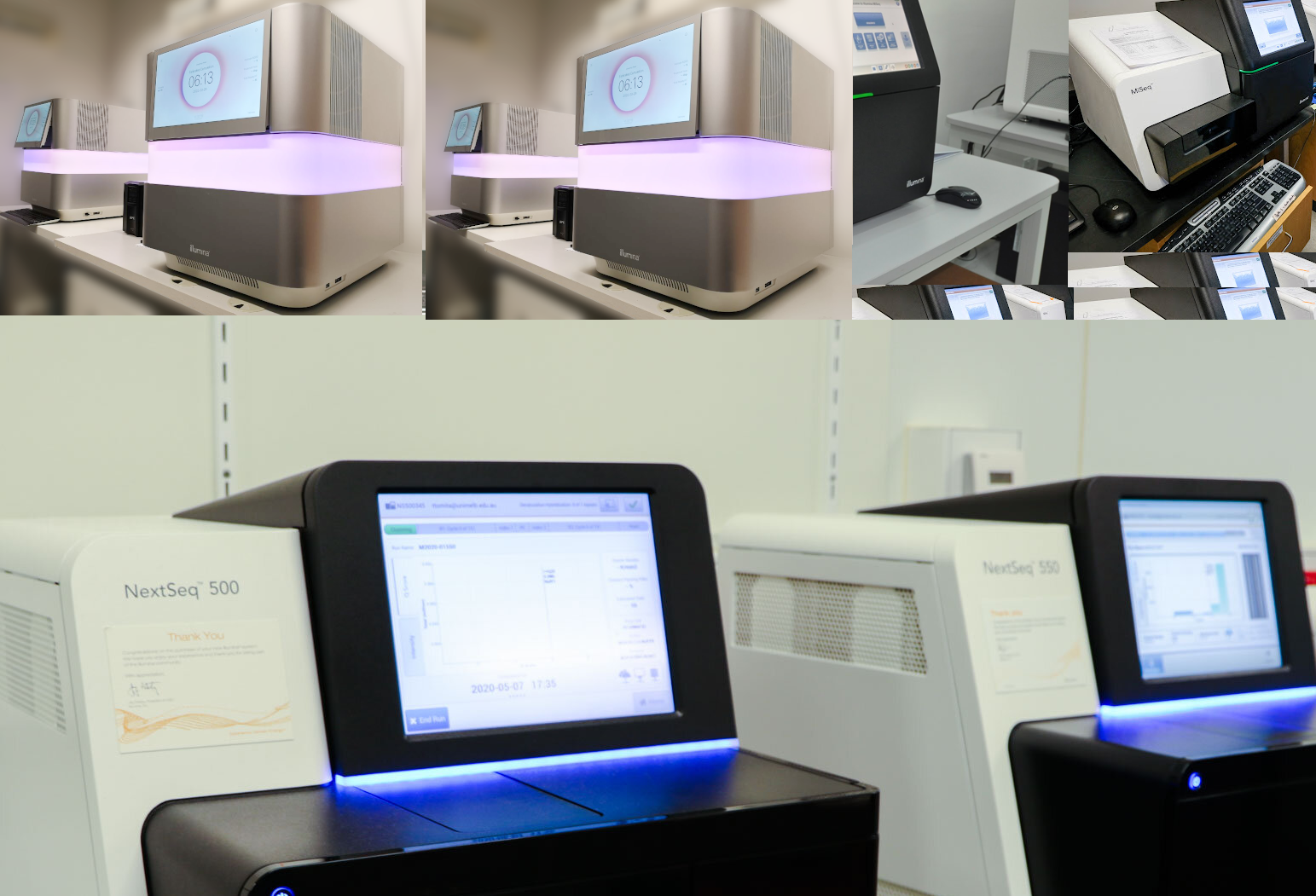
How does metagenomic sequencing differ from whole-genome sequencing (WGS)?
Metagenomic Sequencing Metagenomic sequencing and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) are distinct techniques, but they can generate […]
CURRENT CALLS & Scholarships for Training, Postdoc, Higher Education & Jobs
Women Grant Writing Programme (June–September 2025) The AREF-MRC Towards Leadership Programme 2025/2026 Research Development Fellowship 2025/26 […]
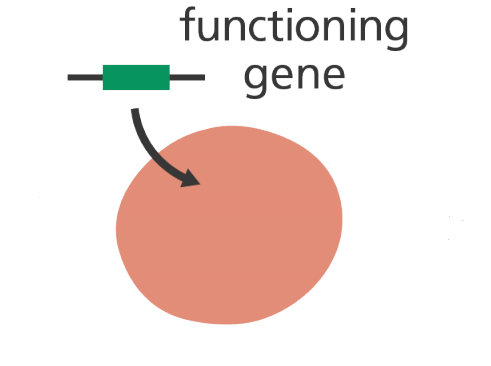
RISKS, PROBLEMS AND ETHICAL ISSUES OF GENE THERAPY
Gene therapy is used to deliver functional genes or therapeutic DNA into target cells and […]
APPLICATIONS OF GENE THERAPY IN TREATING MOLECULAR DISEASES
Molecular diseases (genetic disorders) are non-infectious inheritable diseases which are usually caused by mutations that […]
POTENTIAL USES OF GENE THERAPY
Gene therapy techniques are an emerging field of experimental medicine and therapy for treating or […]
HOW GENE THERAPY WORKS
Genes are made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules – which are the main genetic material […]
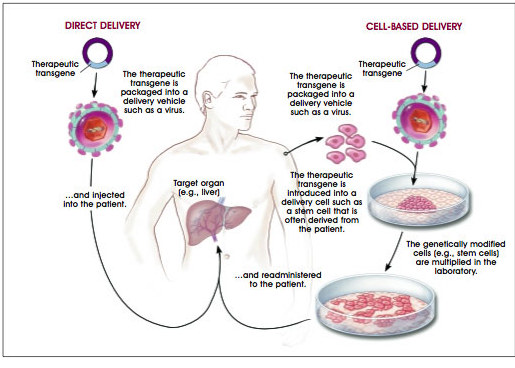
EX VIVO DELIVERY FOR GENE THERAPY
Ex vivo delivery can also be called cell-based delivery protocol of gene therapy. It is […]
IN VIVO DELIVERY FOR GENE THERAPY
In vivo delivery for gene therapy can also be called a direct delivery protocol for […]
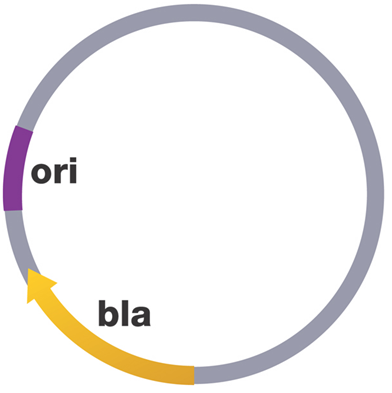
PLASMIDS
Plasmids are extrachromosomal DNA molecules found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic microorganisms that have the […]
GENE THERAPY TARGETING AND DELIVERY
The efficient delivery of therapeutic proteins or DNA into specific cells or tissues of an […]
PREREQUISITES OR STEPS FOR GENE THERAPY
Gene therapy is an experimental discipline or research that uses functional gene (i.e. therapeutic DNA) […]
HISTORY OF GENE THERAPY
The history of gene therapy techniques dates back to the early 1970s and 1980s when […]
GENE THERAPY
Gene therapy is defined as the specific genetic manipulation and modification of an organism’s genome […]
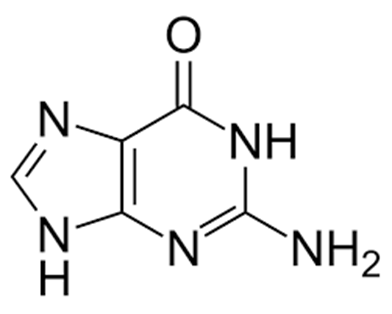
NITROGENOUS BASES – Purine and Pyrimidines
Genes in the DNA code for proteins; and it is the gene that directs the […]
Genes
Genes are sections of the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that codes for the synthesis of a […]
Writing a manuscript and mastering abstracts: A GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
How you structure your article can affect how much it gets read—and cited. Each section […]
BLOTTING TECHNIQUE
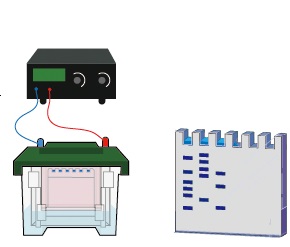
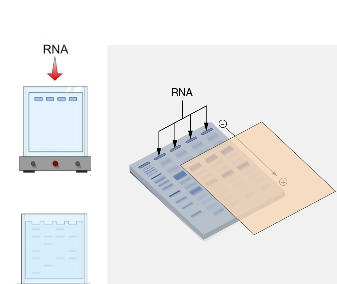
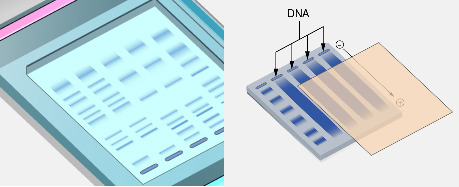
Blotting is used in molecular biology to transfer nucleic acids and proteins from gel to a membrane for identification and analysis. Developed in the 1970s, it combines electrophoresis and immunological methods. There are three main types: Southern (DNA), Northern (RNA), and Western (proteins), each allowing detection and measurement of specific molecules.
WESTERN BLOTTING TECHNIQUE
Western blotting technique or protein immunoblot is used to identify specific proteins separated according to […]
NORTHERN BLOTTING TECHNIQUE
Northern blotting technique is used to detect specific sequences of ribonucleic acid (RNA). The protocol […]
SOUTHERN BLOTTING TECHNIQUE
Southern blotting, developed by Sir Edward M. Southern in 1975, is a molecular technique used to detect specific DNA sequences. It involves transferring DNA from a gel to a nitrocellulose membrane, followed by hybridization with radiolabeled probes. This method is pivotal in DNA analysis, forensic science, and paternity testing.
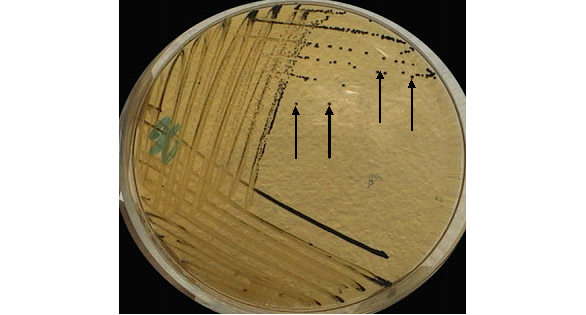
STREPTOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE
Streptococcus pneumoniae, prevalent in the human upper respiratory tract, causes various infections including pneumonia, often in vulnerable individuals. Its virulence is linked to its polysaccharide capsule, interfering with phagocytosis. Early detection and treatment with appropriate antibiotics and preventive vaccination are vital, especially for high-risk groups like the elderly and immunocompromised individuals.
SHIGELLA DYSENTERIAE
Shigella dysenteriae is a Gram-negative, non-motile bacterium causing bacillary dysentery. It’s transmitted primarily through the fecal-oral route, requiring a low dose to initiate infection. Symptoms include bloody diarrhea and abdominal cramps. Diagnosis involves stool cultures, and treatment may include antibiotics for severe cases. Prevention focuses on hygiene and clean water.
TREPONEMA PALLIDUM
Treponema pallidum, a Gram-negative spirochaete, causes syphilis, a contagious STD spread through direct contact, including mother-to-child transmission. The disease progresses through primary, secondary, and tertiary stages without treatment, potentially causing severe complications. Laboratory diagnosis relies on serological tests, as the bacterium cannot be cultured in vitro. Prevention includes safe sexual practices and treating infected individuals.
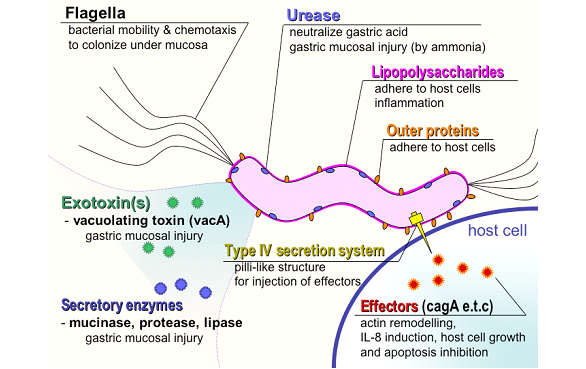
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium causing peptic and gastric ulcers, linked to stomach cancer. It survives stomach acidity by producing urease, creating an alkaline environment. Spread via fecal-oral route, it induces inflammation in the gastric mucosa. Diagnosis involves invasive and non-invasive tests, treatment includes antibiotics and protein-pump inhibitors. Prevention focuses on hygiene.
SALMONELLA (S. TYPHI)
Salmonella Typhi, a Gram-negative rod, causes typhoid fever in humans, transmitted through contaminated food and water. Non-typhoid strains, like S. Typhimurium, cause gastrointestinal infections. Infections primarily spread via the fecal-oral route, and effective prevention includes good hygiene, proper food handling, and clean water. Treatment involves antibiotics and hydration.
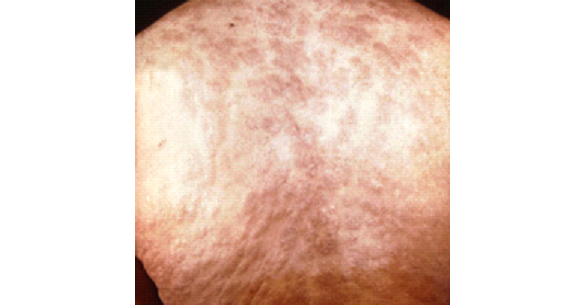
RICKETTSIA PROWAZEKII
Rickettsia prowazekii is an obligate intracellular parasite causing epidemic typhus, primarily transmitted via lice bites. Symptoms include vasculitis, thrombosis, and systemic infections. Diagnosis involves serological tests and cell culture. Treatment includes chloramphenicol and tetracyclines; prevention focuses on vector control and hygiene. RMSF and Q fever are related rickettsial diseases.
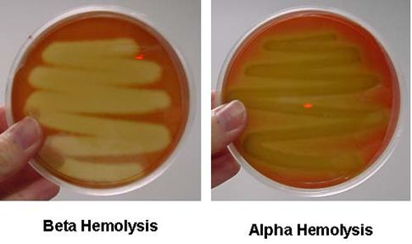
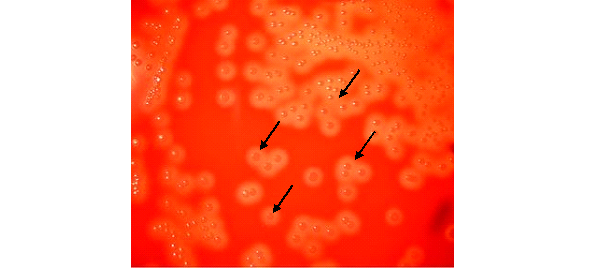
STREPTOCOCCUS PYOGENES
Streptococcus pyogenes, a Group A Streptococcus, is a Gram-positive bacterium causing pharyngitis and various streptococcal diseases like scarlet fever, cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis. It produces numerous virulence factors including streptolysins and exotoxins. Diagnosis involves cultural, microscopic, and serological tests. Treatment includes antibiotics like penicillin, and no vaccines exist currently.
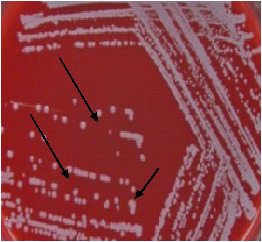
STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
Staphylococcus aureus, a Gram-positive bacterium, is often found in the nose and skin of humans. It causes various infections including pneumonia, gastroenteritis, and toxic shock syndrome, aided by its production of toxins and enzymes. Resistant strains like MRSA are prevalent. Prevention relies on hygiene practices, as vaccines are unavailable.