Melting curve analysis in Real-time PCR
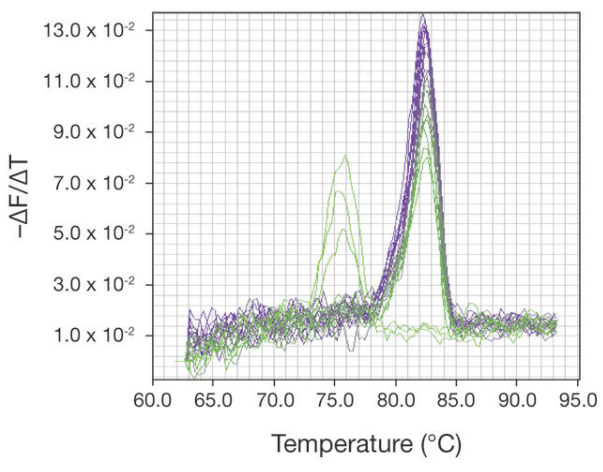
Melting curve analysis and detection systems Melting curve analysis can only be performed with realtime PCR detection technologies in which the fluorophore remains associated with the amplicon. Amplifications that have used SYBR® Green I or SYBR® GreenER™ dye can be subjected to melting curve analysis. Dual-labeled probe detection systems such as TaqMan® probes are not […]
Melting curve analysis in Real-time PCR Read More »
Biotechnology, Molecular Microbiology, Techniques in Microbiology Lab