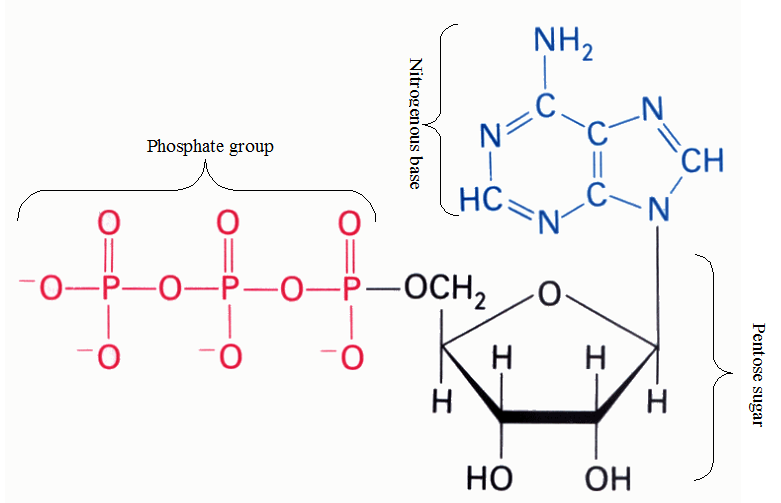
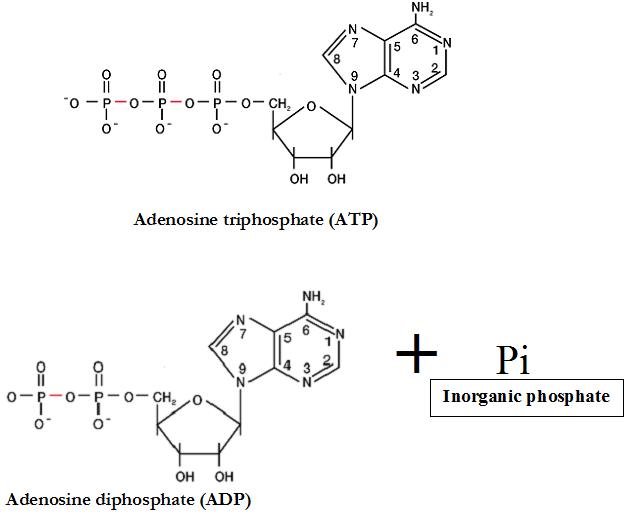
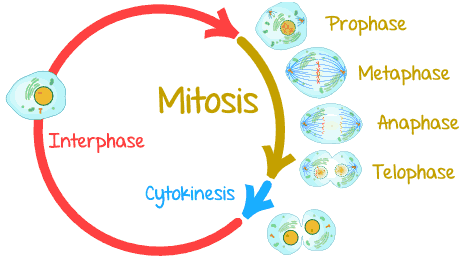
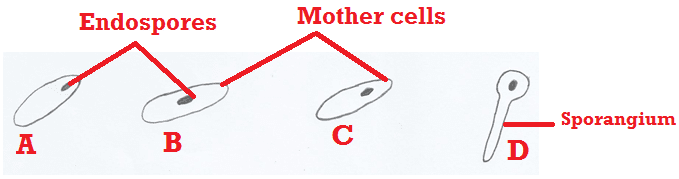
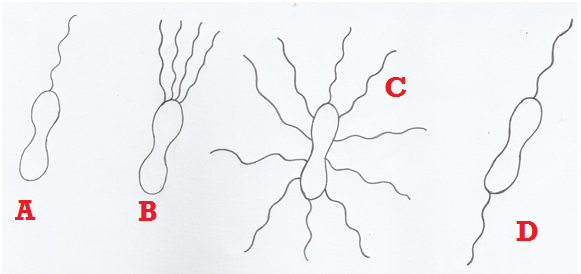
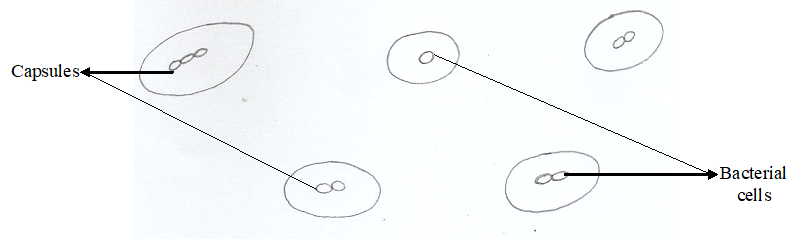
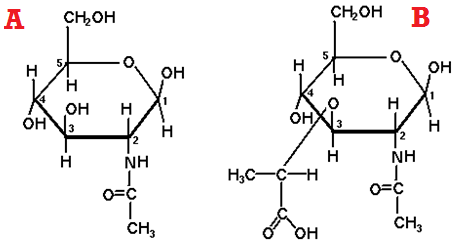
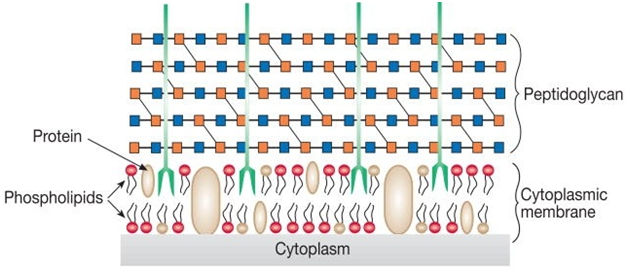
TYPES OF METABOLISM
Metabolic reactions help to maintain a state of balance or equilibrium in the cell. And the energy released during these processes is used by the cell for growth and other cellular activities. The growth of microorganisms requires the polymerization of building blocks (e.g. amino acids and nucleotides) into proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids. These […]
TYPES OF METABOLISM Read More »
Microbial Physiology & Metabolism