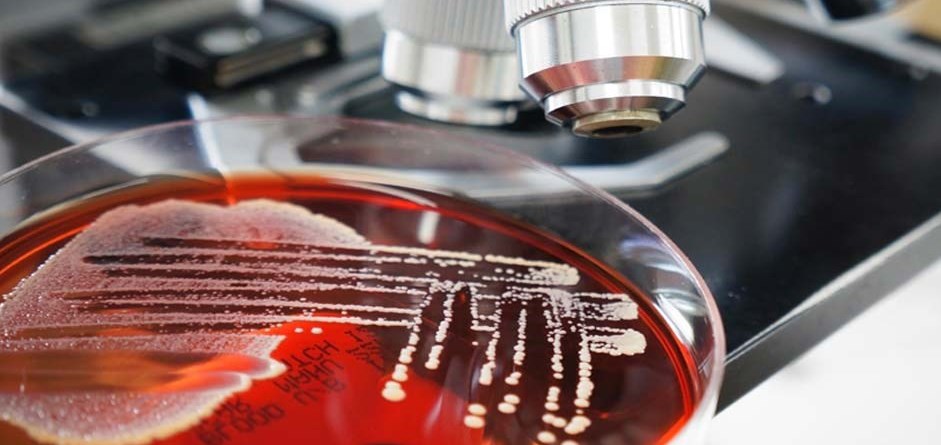
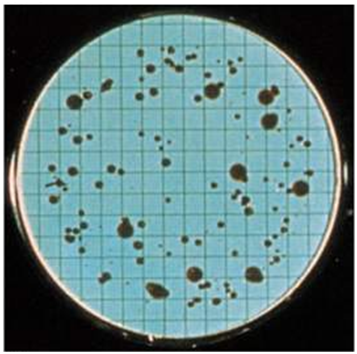
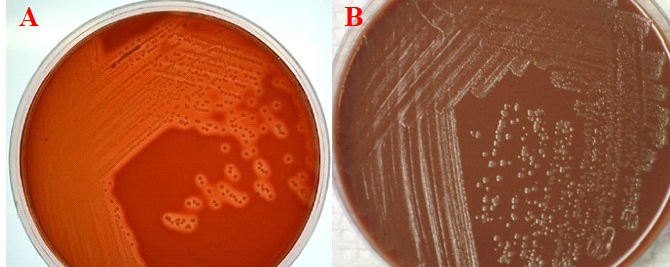
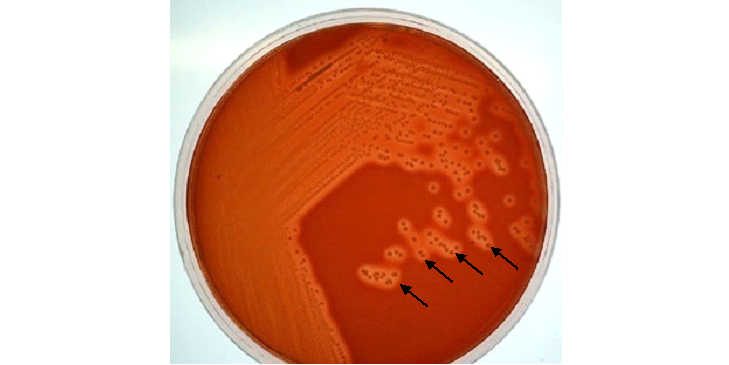
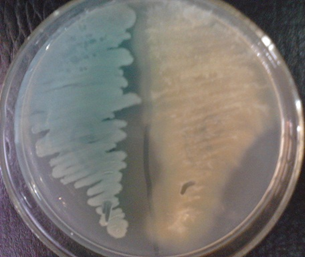
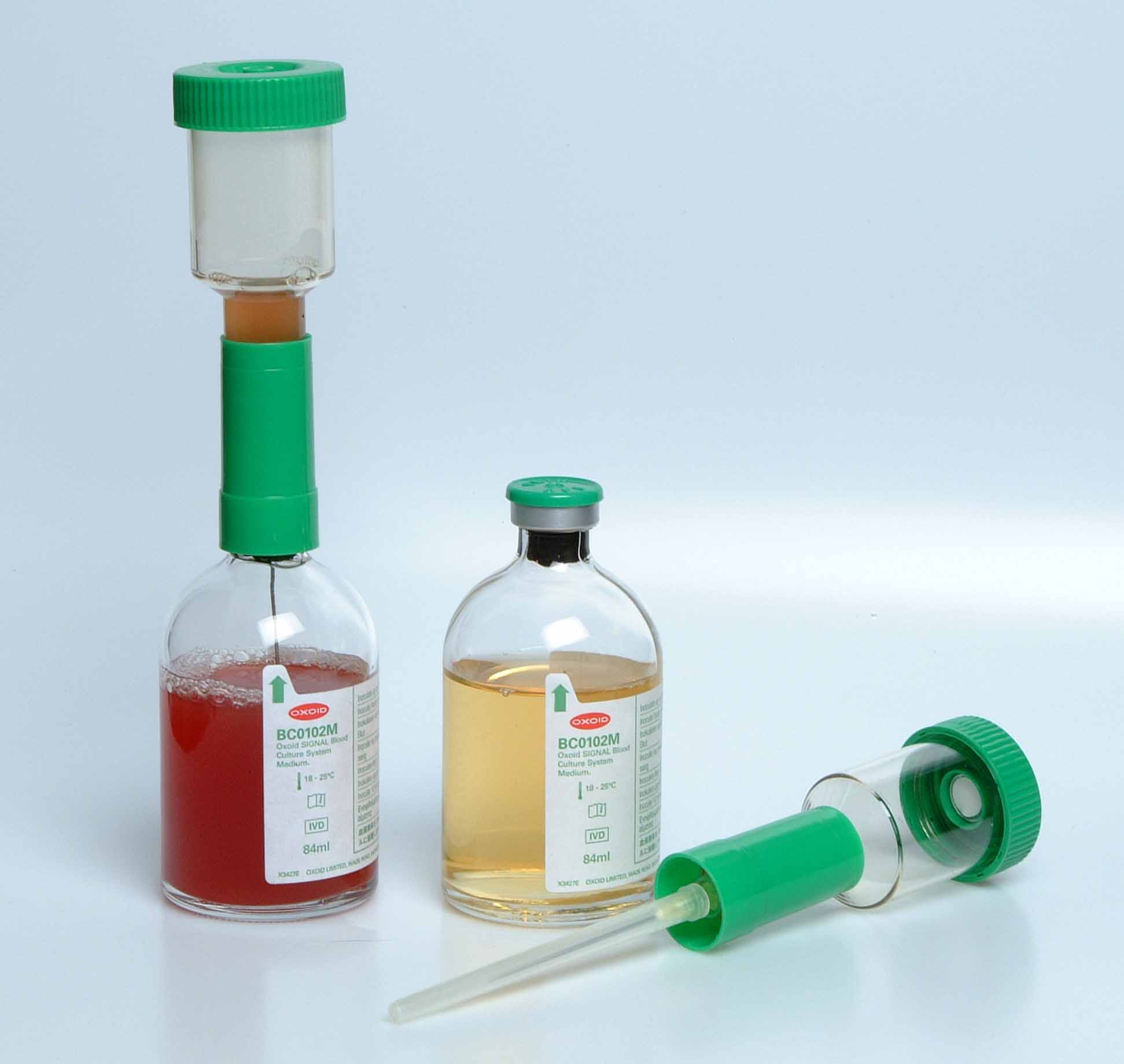
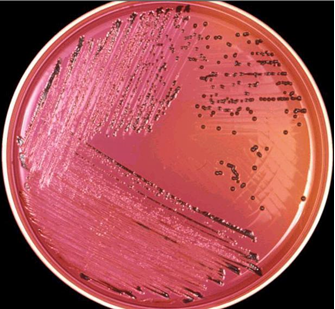
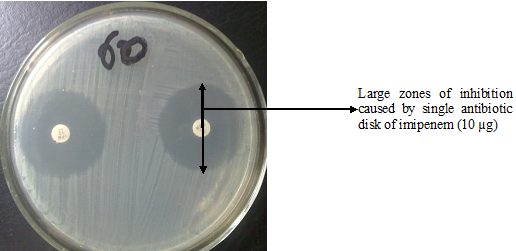
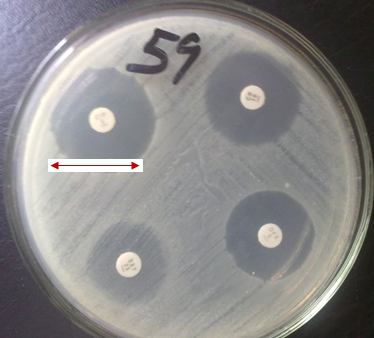
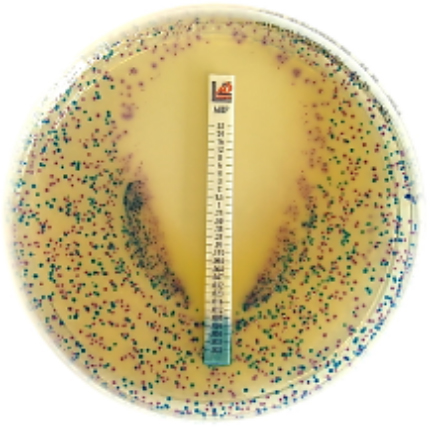
Antibiotics remain one of the most important discoveries in medical science, serving as a cornerstone […]
Category: Microbe Lab
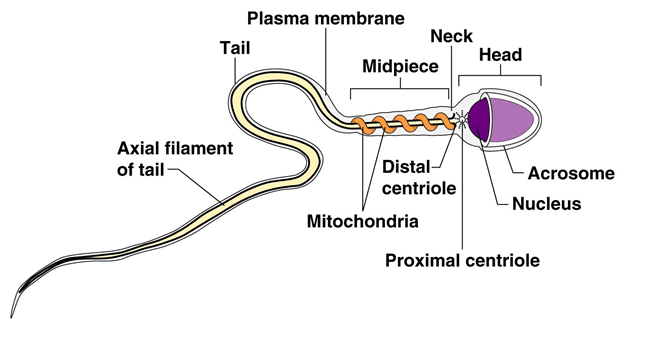
SEMINAL FLUID (SEMEN) MICROSCOPY, CULTURE & SPERM CELL COUNT
SEMEN MICROSCOPY AIM: To determine any abnormality in a seminal fluid (semen) as an aid […]
Risk group classification of microorganisms
The great majority of microorganisms are beneficial to man, plants, animals and the environment. These […]
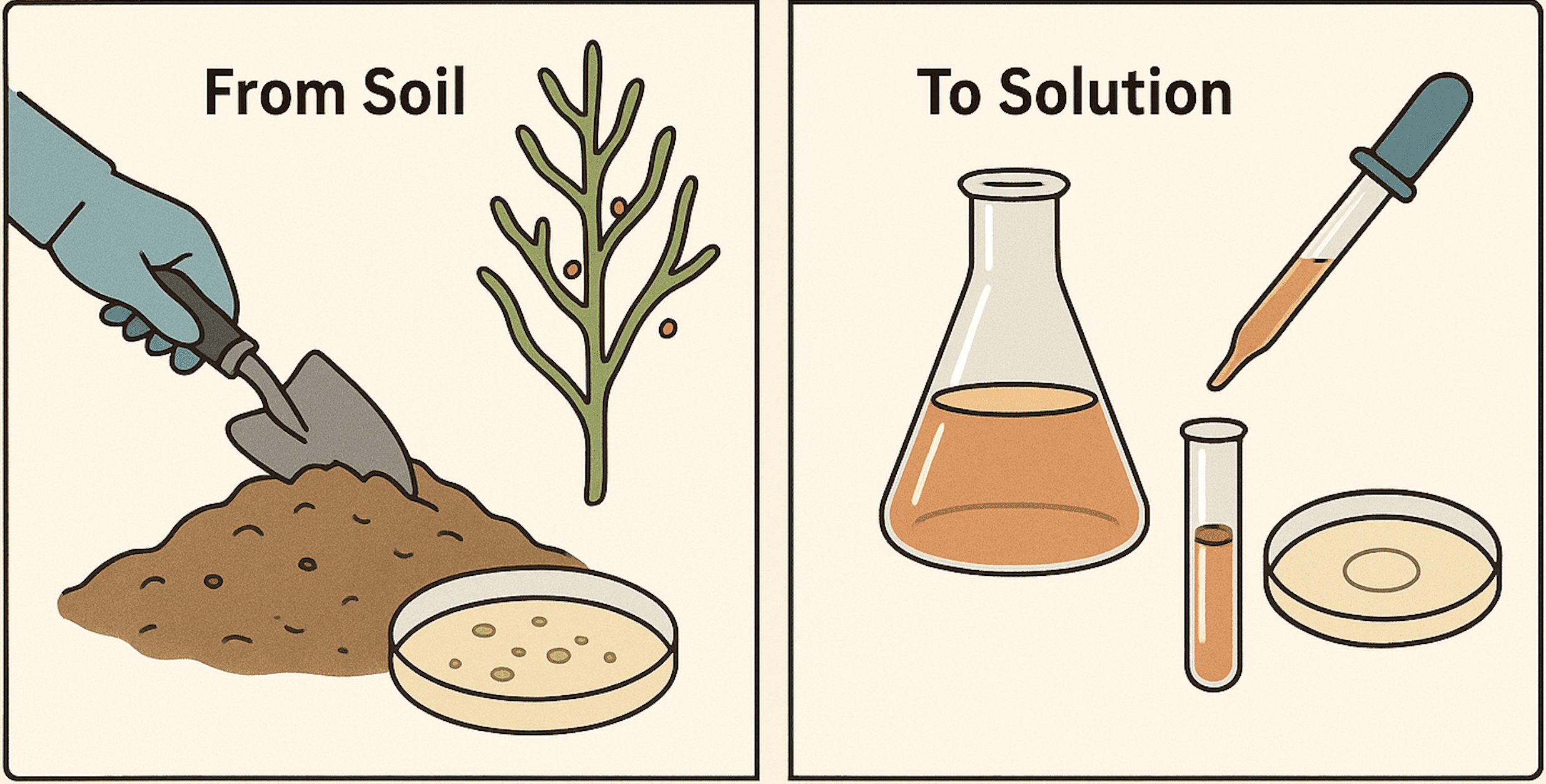
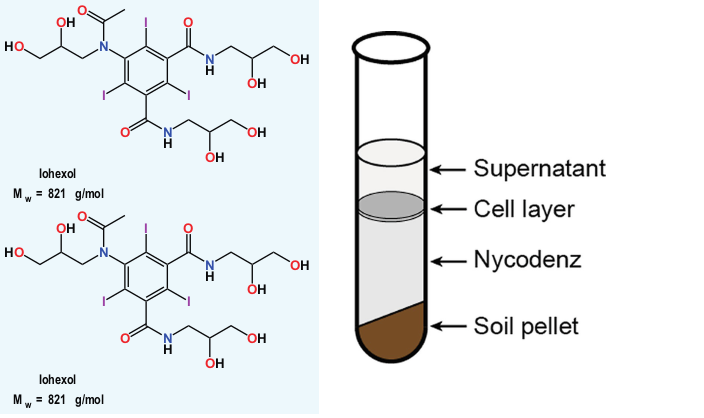
Nycodenz: application and properties
What is Nycodenz Nycodenz is a non-ionic, triiodinated radiopaque substance used primarily in molecular biology […]
Practical Tips for Resolving Conflict as a Scientist, Research Leader, Scholar
Conflict Resolution: Practical Tips for STEM Leaders These tips presented here was adapted from the […]
HOW TO DESIGN PRIMERS FOR YOUR PCR EXPERIMENT
Primers are short stretches of DNA that target unique sequences of a DNA molecule and […]
DIFFERENTIAL COUNT FOR CSF
AIM: To provide information on the different white blood cells (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes) […]
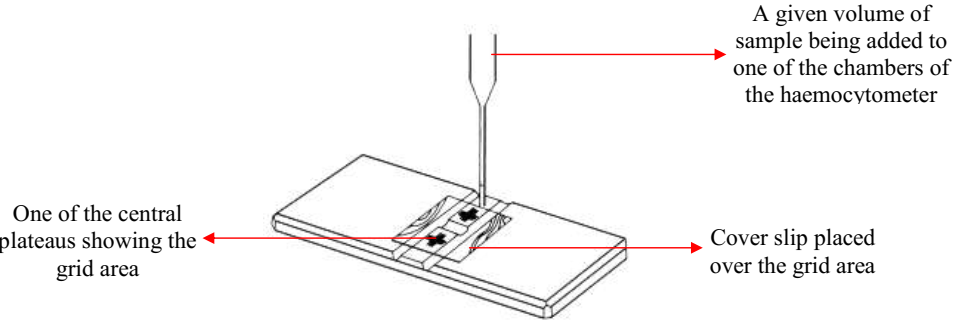
HAEMOCYTOMETER CELL COUNT FOR CSF SAMPLE
Cells of mammalian or prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells can be counted in the lab from […]
Important techniques in microbiology laboratory
DIRECT PLATE COUNTING Direct plate counting is a microbiological technique used to evaluate the actual […]
UNDERSTANDING MBL MICROBIOLOGY
Metallo-beta-lactamases (MBLs) are beta-lactamase enzymes produced by pathogenic bacteria, and which hydrolyzes the carbapenems (e.g. […]
ESBL Positive – Understanding Extended spectrum beta-lactamases tests
What does it mean to be ESBL positive? Learn how to detect these antibiotic-resistant bacteria […]
The 3 Rs (Reduction, Refinement, Replacement): Guiding Principles in the Use of Animals For Biomedical/Scientific Research
The use of laboratory animals including mice, rats, rabbits and primates for scientific/biomedical research is […]
RATIONALE FOR THE CONTINUED USE OF ANIMALS FOR RESEARCH
Animals including (primates, dogs, cats, rabbits, mice) are still being used to conduct scientific/biomedical research […]
Issues Surrounding the Use of Animals in Scientific Research
Animals such as mice, rats, rabbits, monkeys and primates are used in biomedical research to […]
GRAM SMEAR OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF) SAMPLE
AIM: To detect the presence of pus cells and bacteria in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimen. […]
MICROSCOPY OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF)
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples are obtained with extra precautions using a technique called lumbar puncture. […]
MEMBRANE FILTRATION TECHNIQUE
Filtration is simply defined as the separation of particles from fluid or liquids by the […]
Selenite F broth
In the microbiology laboratory, pure cultures of microorganisms (e.g., bacteria) are critical to the success […]
CULTURE OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF)
AIM: To isolate organism from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimen as an aid in the diagnosis […]
MICROSCOPY OF SPUTUM SPECIMEN
AIM: To detect the presence of pus cells and predominant bacteria in sputum specimens as […]
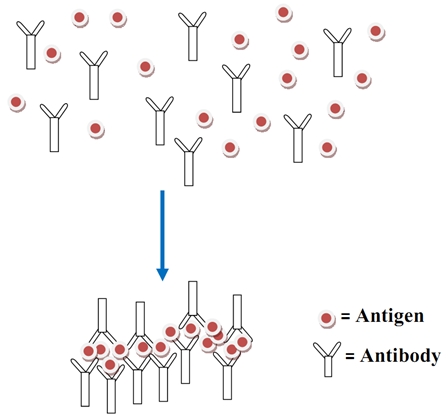
ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY REACTION
Antigen-antibody reaction is an immunological reaction in which a particular antibody molecule reacts with a […]
ELISA
ELISA is the acronym for “enzyme linked immunosorbent assay”. It is an immunoassay or serological […]
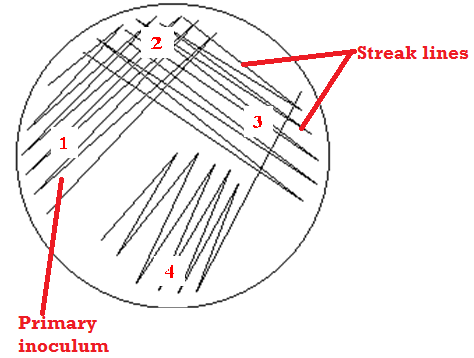
STREAKING TECHNIQUE
Streaking is a microbiological technique that is used to obtain pure cultures of microorganisms (particularly […]
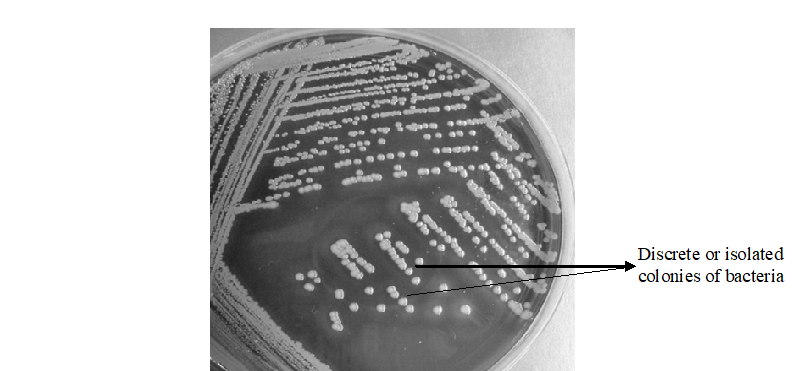
ISOLATION TECHNIQUE
Isolation technique is a microbiology procedure which is used to obtain pure cultures of microorganisms […]
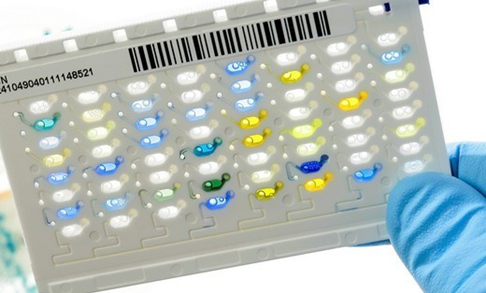
FEATURES OF THE VITEK 2 AUTOMATED COMPACT SYSTEM FOR BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION AND ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY TEST (AST)
Helping the physician select the best treatment at a much faster pace based on the […]
SPUTUM CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Sputum culture is often recommended in the diagnoses of lower respiratory tract infection (e.g. bacterial […]
URINE CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Urine culture is performed in order to specifically identify organisms that may be causing a […]
BLOOD CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Blood culture is the most important diagnostic method for detecting and diagnosing bacteraemia (presence of […]
STOOL CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Stool culture is demanded in the bacteriology laboratory as method for detecting and diagnosing enteric […]
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS/DISEASES
The laboratory diagnosis of fungal infection is mainly based on microscopy and cultural techniques. Several […]
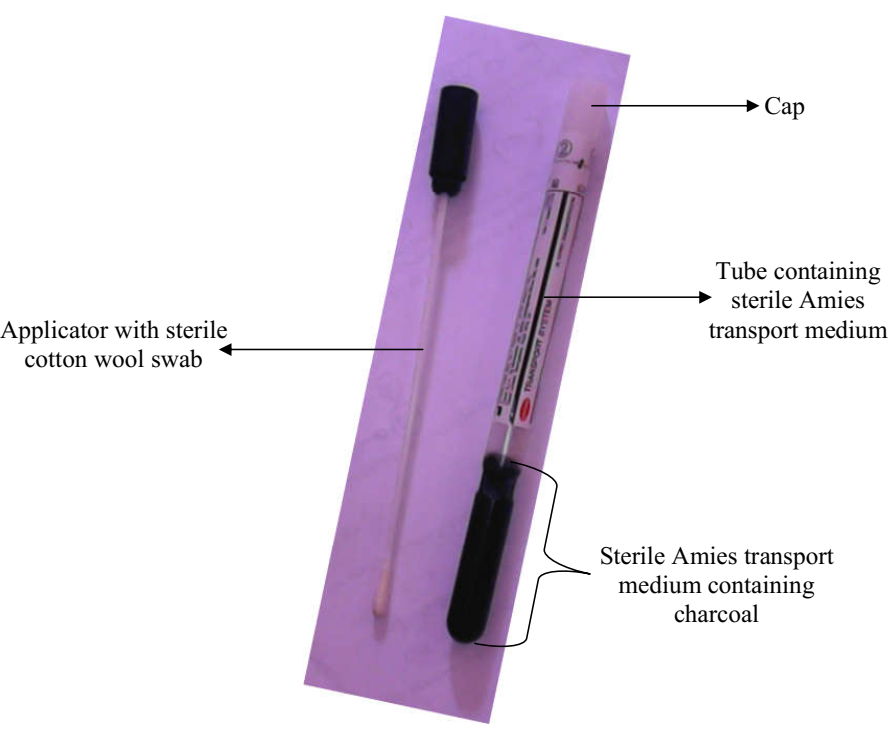
Collection and processing of various clinical samples in the microbiology lab
COLLECTION OF SPUTUM Sputum specimens are collected from patient’s suspected to have respiratory disorders example […]
Specimen Collection in Microbiology Lab
The sample collection unit is one of the most important units in the clinical microbiology […]
GOOD LABORATORY PRACTICE (GLP)
Good laboratory practice (GLP) is simply defined as a laboratory quality measure or protocol that […]
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS BASED ON HAZARDS AND LABORATORY
Pathogenic microorganisms inclusive of viruses, bacteria, and fungi portends health challenges to the general public […]
TYPES OF MICROSCOPES
There abound several numbers of microscopes that can be used by a microscopist to view […]
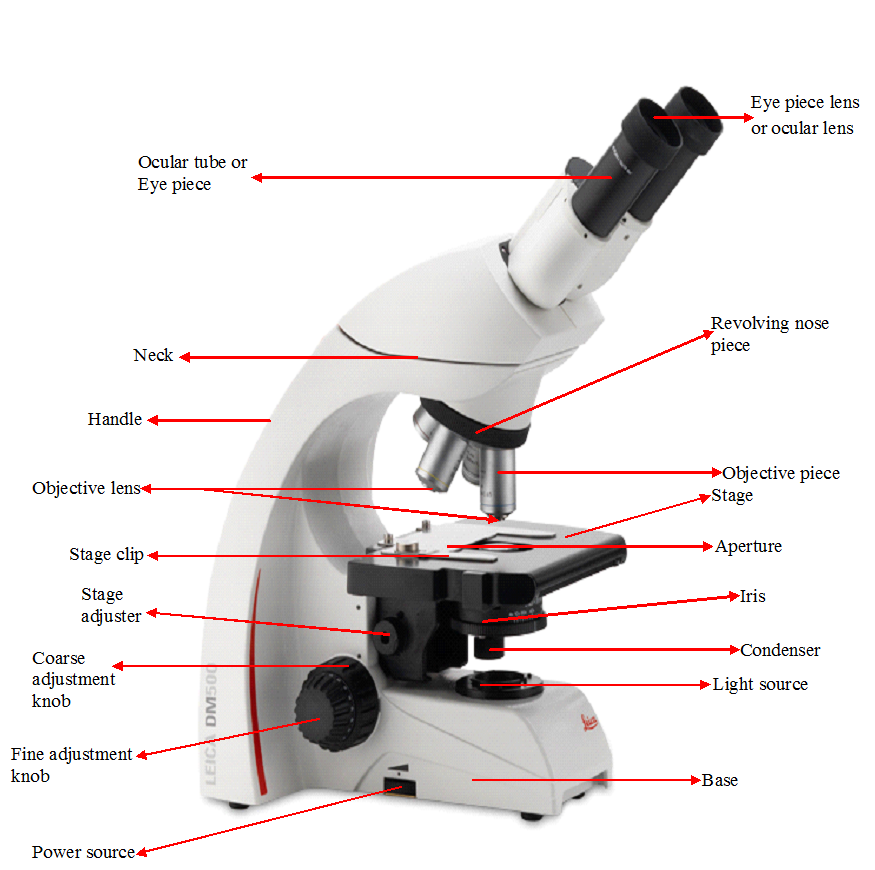
FUNCTIONS OF THE PARTS OF A MICROSCOPE
The microscope has various parts that perform specific function; and it is important that scientists […]
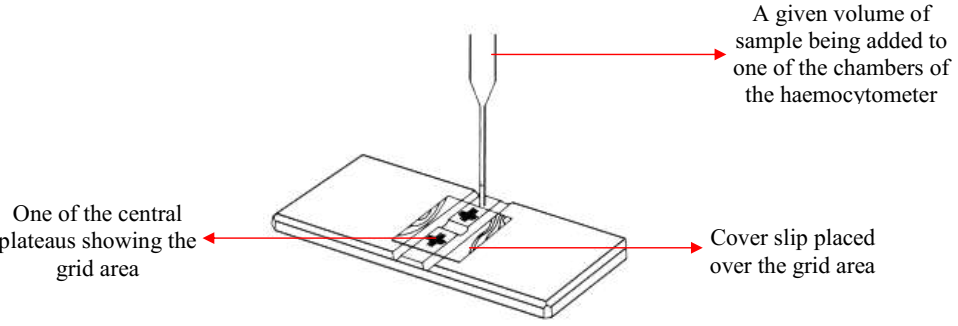
TRYPAN BLUE & HAEMOCYTOMETER
Trypan blue is defined as a dye or stain that enables us to distinguish between […]
P value
The phrase “P value” also means ‘calculated probability’. P value is defined as the probability […]
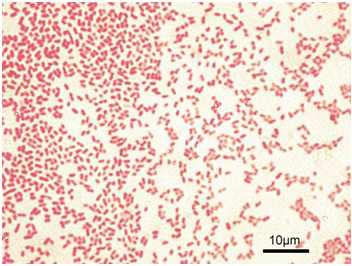
GRAM STAINING TECHNIQUE
Gram staining is a general purpose bacteriological identification technique used in the bacteriology section of […]
MICROBIAL COUNT: Total Count & Viable Count
Viable cell count: Viable cell count gives an estimate of the total number of living […]
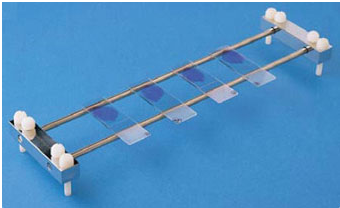
SLIDE RACK & STAINING RACK
Slide rack is a piece of vessel used for packing and storing clean glass slides […]
PETRI DISHES
Petri dishes are shallow glass or plastic plates that are cylindrical in shape, and which […]
PREPARATION OF BACTERIAL SMEAR & HEAT FIXING
Bacterial smear is defined as a dehydrated or dried preparation of a bacterial suspension (cells) […]
PRECAUTIONARY MEASURES TO OBSERVE WHILE WORKING IN THE MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY
REFERENCES Atlas R.M (2010). Handbook of Microbiological Media. Fourth edition. American Society of Microbiology Press, […]
STAINING TECHNIQUE
Staining is any microbiological process which increases the contrast of organisms when certain dyes or […]
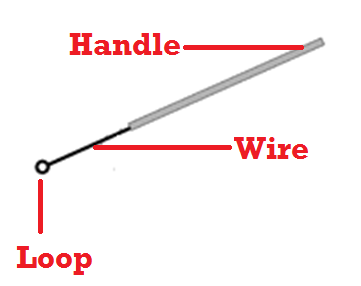
INOCULATING LOOP
Inoculating loop or wire loop is a general purpose piece of instrument that allows microbiologist […]
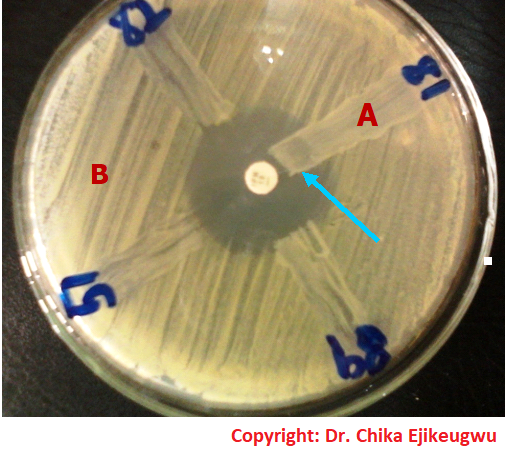
OUTPUT OF ANTIMICROBIAL DRUG SUSCEPTIBILITY TESTING
The output of an antimicrobial drug susceptibility test is often expressed as raw data which […]
Overview of antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) / Antibiogram
When a pathogenic microorganism is isolated from the specimen of a patient, the clinical microbiology […]
Chromogenic culture media for detecting antimicrobial resistance mechanisms
Chromatic Super CAZ/AVI Chromogenic medium for detecting Ceftazidime-avibactam resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Chromatic Super CAZ/AVI is […]
Safety in Microbiology Lab
Safety first is a general slogan that is obtainable in virtually every spheres of life. […]