Petri dishes are shallow glass or plastic plates that are cylindrical in shape, and which are used to cultivate microorganisms in the microbiology laboratory. Glass Petri dishes are heat-stable and can be sterilized in the autoclave and re-used over a long period of time. But plastic Petri dishes (disposable) cannot be re-used or autoclaved because they are heat-labile, and are only used once.
Petri dishes are important microbiological apparatuses, and they provide a platform for the phenotypic or physical examination of microorganisms (particularly bacteria and fungi) based on their colonial characteristics on solid growth media. After the inoculation of microbial cultures or experimental samples, culture media plates (i.e. Petri dishes) are incubated upside down (with the part containing the agar on top) in order to ensure the sterility of the medium.
Droplets of water from the other side of the plate (not containing agar) onto the agar medium could introduce contaminating organisms to the growth vessel, and thus contaminate the whole cultivation process. Petri dishes (Figure 1) are mainly used for bacteriological and mycological investigations in the microbiology laboratory; and they are quite different from those used for other investigations such as cell culture techniques.
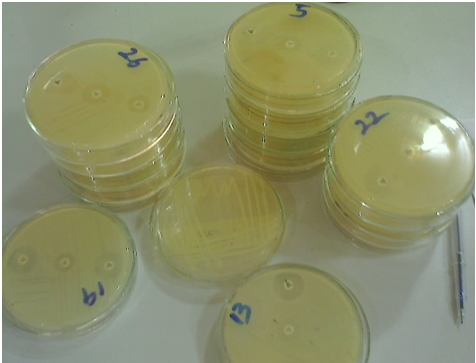
MAINTENANCE/CARE OF PETRI DISHES
- Petri dishes should not be opened prior to usage.
- Glass Petri dishes should be properly washed and sterilized prior to their usage for microbial cultivation in the laboratory.
- Disposable Petri dishes should be autoclaved after use before disposal.
REFERENCES
Cheesbrough, M (2006). District Laboratory Practice in Tropical countries Part I Cambridge
Chung K.T, Stevens Jr., S.E and Ferris D.H (1995). A chronology of events and pioneers of microbiology. SIM News, 45(1):3–13.
Dictionary of Microbiology and Molecular Biology, 3rd Edition. Paul Singleton and Diana Sainsbury. 2006, John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Canada.
Goldman E and Green L.H (2008). Practical Handbook of Microbiology, Second Edition. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, USA.
Madigan M.T., Martinko J.M., Dunlap P.V and Clark D.P (2009). Brock Biology of microorganisms. 12th edition. Pearson Benjamin Cummings Publishers. USA.
Nester E.W, Anderson D.G, Roberts C.E and Nester M.T (2009). Microbiology: A Human Perspective. Sixth edition. McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc, New York, USA.
Prescott L.M., Harley J.P and Klein D.A (2005). Microbiology. 6th ed. McGraw Hill Publishers, USA.
Willey J.M, Sherwood L.M and Woolverton C.J (2008). Harley and Klein’s Microbiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Higher Education, USA.
Discover more from #1 Microbiology Resource Hub
Subscribe to get the latest posts to your email.


