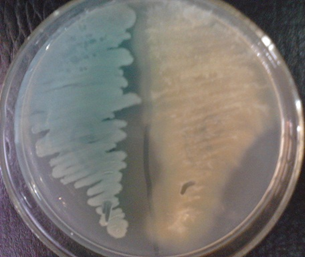
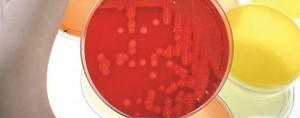
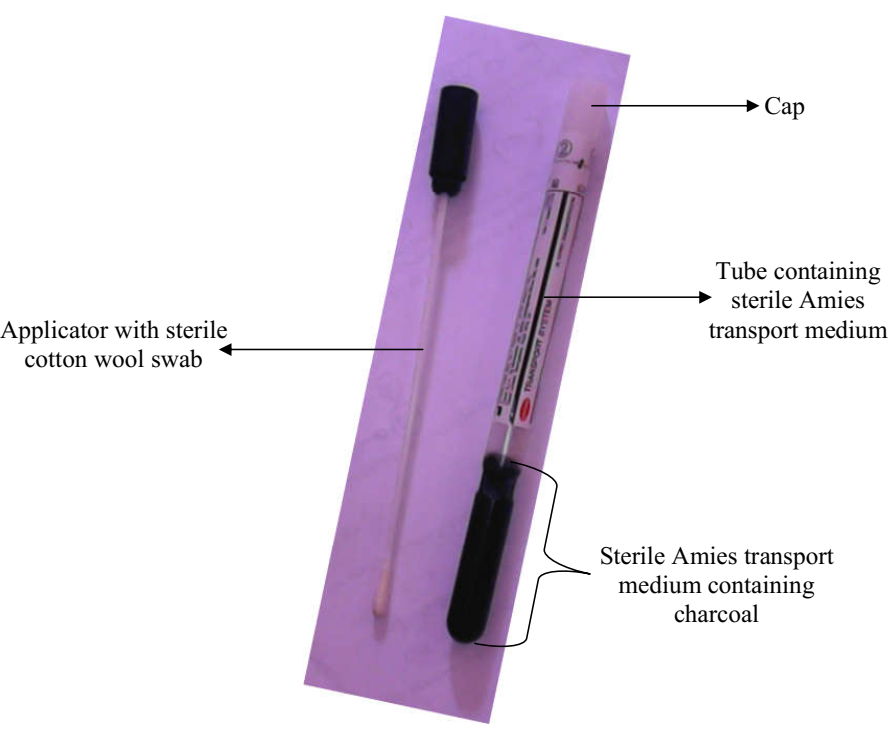
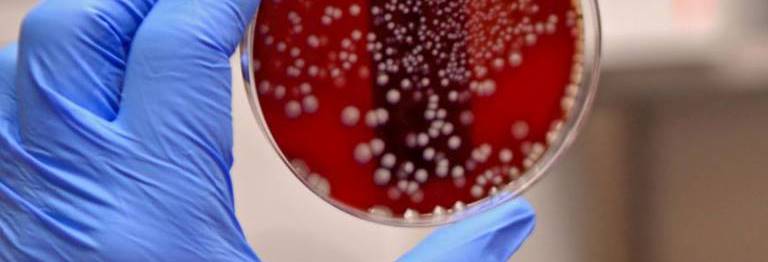
Sputum culture is often recommended in the diagnoses of lower respiratory tract infection (e.g. bacterial […]
Month: February 2023
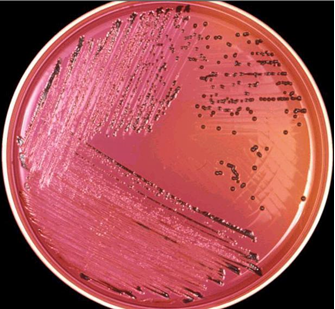
URINE CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Urine culture is performed in order to specifically identify organisms that may be causing a […]
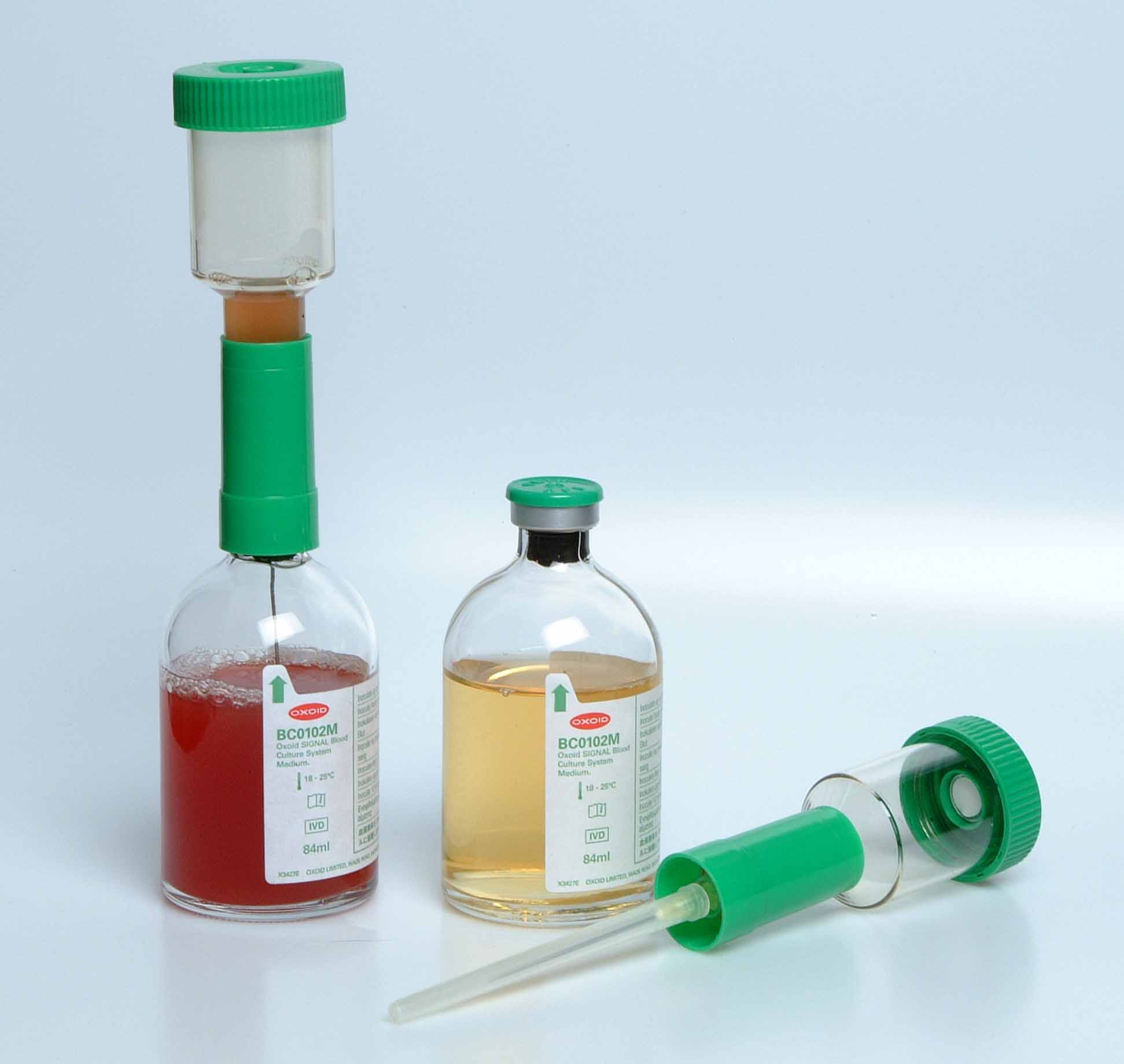
BLOOD CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Blood culture is the most important diagnostic method for detecting and diagnosing bacteraemia (presence of […]
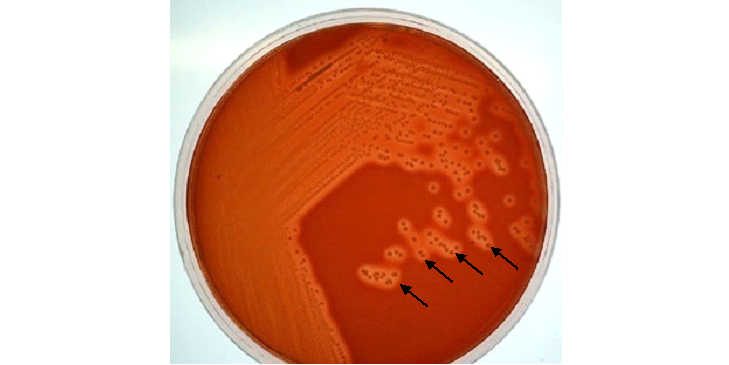
STOOL CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Stool culture is demanded in the bacteriology laboratory as method for detecting and diagnosing enteric […]
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS/DISEASES
The laboratory diagnosis of fungal infection is mainly based on microscopy and cultural techniques. Several […]
MYCOTOXINS
Mycotoxins are exotoxins produced by fungi. The area of microbiology that studies fungi and the […]
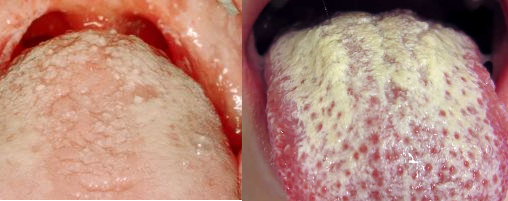
ORAL THRUSH (ORAL CANDIDIASIS)
Oral thrush (oral candidiasis) is a localized fungal infection caused by C. albicans in the […]
Classification of parasites that parasitize humans
Generally, parasites can be classified into two major groups: Endoparasites are parasites that live inside […]
TRANSPEPTIDATION REACTION
Transpeptidation reaction is the chemical reaction that forms the peptide cross-links or bonds during the […]
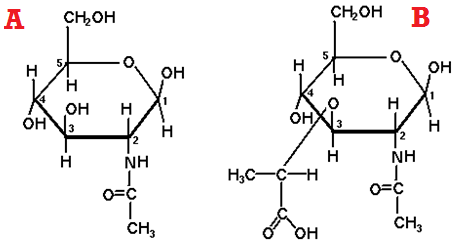
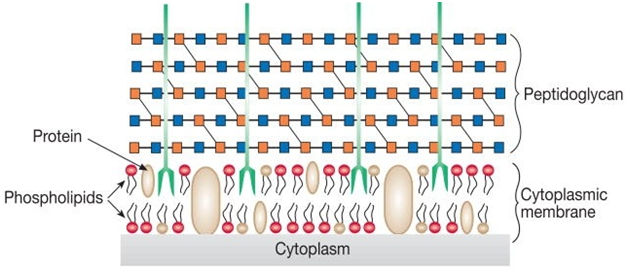
BACTERIAL CELL WALL
Cell wall is a layer that is present outside the plasma or cytoplasmic membrane of […]
EUKARYOTIC CELLS
Eukaryotic cells are organisms or cells that have a membrane-bound nucleus. They are distinct group […]
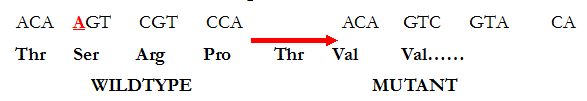
CLASSIFICATION OF MUTATION BY THEIR EFFECTS ON THE DNA MOLECULE
Based on their effects on the structural integrity of the DNA molecule, mutations can be […]
MUTATION: definition, types and causes
The term mutation is derived from the Latin word “mutare” – which means “to change”. […]
Molecular Manipulation of Microorganisms: significance and applications
Microorganisms including bacteria, fungi, algae and viruses are important tools used for a wide variety […]
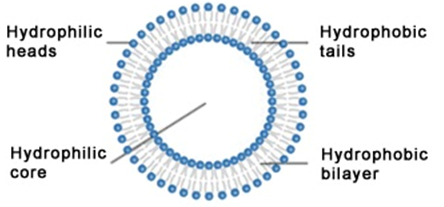
LIPOSOMES: relevance & applications
The phrase liposome is derived from two Greek words: Lipos which means “fat” and Soma […]
PORTAL OF ENTRY OF INFECTIOUS AGENTS INTO THE BODY
Pathogenic bacteria enter the human body in various ways and through various medium or routes. […]
HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP)
Hazard analysis critical control point (HACCP) is an internationally recognized food safety system that is […]
INDICATOR ORGANISMS
Indicator organisms are microorganisms that signify the possible contamination of food or food products as […]
SINGLE CELL PROTEINS
Thepopulation of the world is increasing at an alarming rate, and this calls for sustainable […]
FOOD POISONING
Food poisoning/food infection is defined as the microbial infection or disease that is caused by […]
FOOD BORNE DISEASES
Food borne diseases are diseases caused by the ingestion of food borne pathogens. They are […]
SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINATION OF FOOD
Microbial contamination of food is almost inevitable owing to the ubiquity of microorganisms – which […]
EXTRINSIC FACTORS OF FOOD SPOILAGE
Extrinsic factors of food spoilage are the non-substrate factors that affect the spoilage of foods […]
INTRINSIC FACTORS OF FOOD SPOILAGE
Intrinsic factors of food spoilage are those inherent factors that are associated with the food […]
FOOD SPOILAGE
What is food spoilage? Food spoilage is simply defined as the change in the overall […]
Collection and processing of various clinical samples in the microbiology lab
COLLECTION OF SPUTUM Sputum specimens are collected from patient’s suspected to have respiratory disorders example […]
Specimen Collection in Microbiology Lab
The sample collection unit is one of the most important units in the clinical microbiology […]
GOOD LABORATORY PRACTICE (GLP)
Good laboratory practice (GLP) is simply defined as a laboratory quality measure or protocol that […]
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS BASED ON HAZARDS AND LABORATORY
Pathogenic microorganisms inclusive of viruses, bacteria, and fungi portends health challenges to the general public […]
IMPORTANCE OF MICROORGANISMS
Microorganisms are studied for diverse reasons. These microscopic forms of life play tremendous significant roles […]
IMMUNOGLOBULIN D (IgD)
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is an antibody with the basic four polypeptide structure of an immunoglobulin […]
IMMUNOGLOBULIN G (IgG)
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a monomeric antibody and the most predominant immunoglobulin in secondary (memory) […]
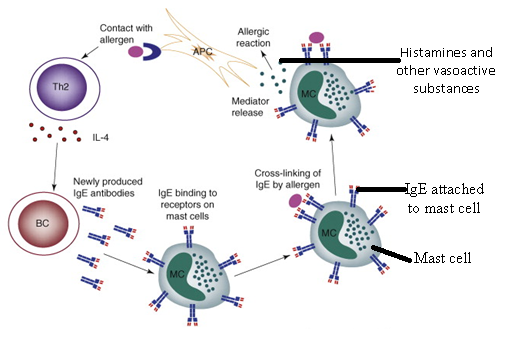
IMMUNOGLOBULIN E (IgE)
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is an antibody that is known to bind to host tissue cells […]
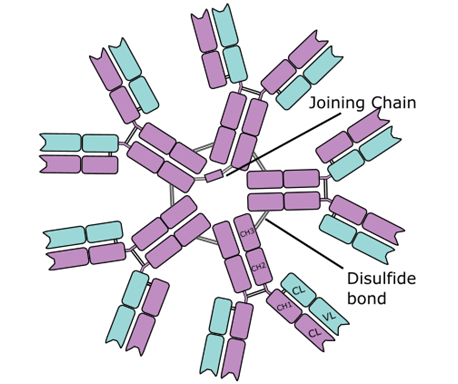
IMMUNOGLOBULIN M (IgM)
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is an antibody that mainly exist as a pentamer i.e. it consists […]
COLOSTRUM
Colostrum is the first secretion of the mammary gland (breast) produced before proper lactation commences […]
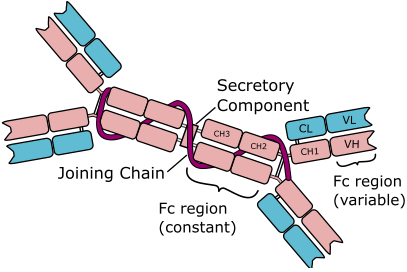
IMMUNOGLOBULIN A (IgA)
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is an antibody found in serum (as a monomer of about 150,000 […]
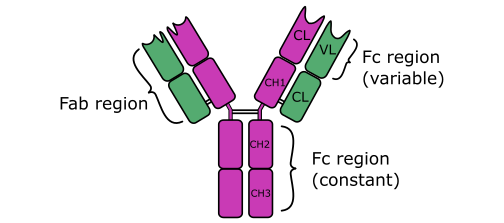
TYPES OF ANTIBODIES
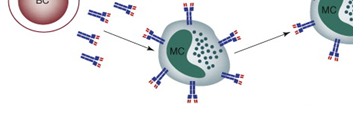
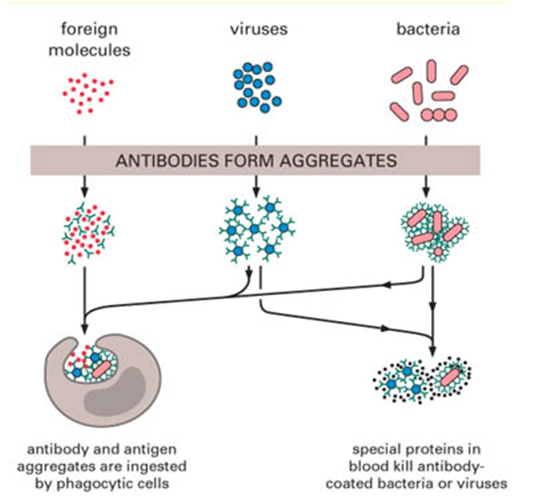
Immunoglobulins do not actually kill or eliminate pathogenic microorganisms or antigens from the body. The […]
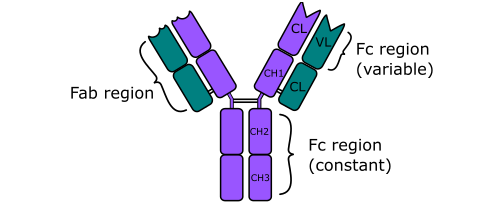
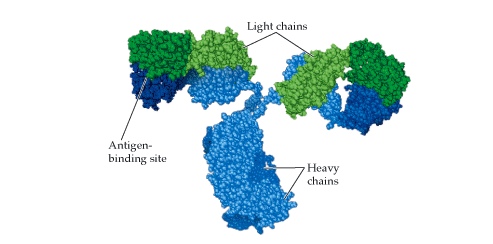
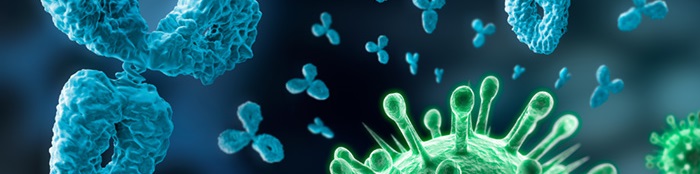
ANTIBODIES (Immunoglobulins)
Antibodies are soluble protein molecules produced by the B cells of the immune system in […]
CHARACTERISTICS OF ANTIGENS
However antigenic a foreign molecule/substance may be, to be immunogenic and qualify to be called […]
CARE OF THE MICROSCOPE
Due to the critical role of microscope in microbiological and other biomedical researchers, it is […]
TYPES OF MICROSCOPES
There abound several numbers of microscopes that can be used by a microscopist to view […]
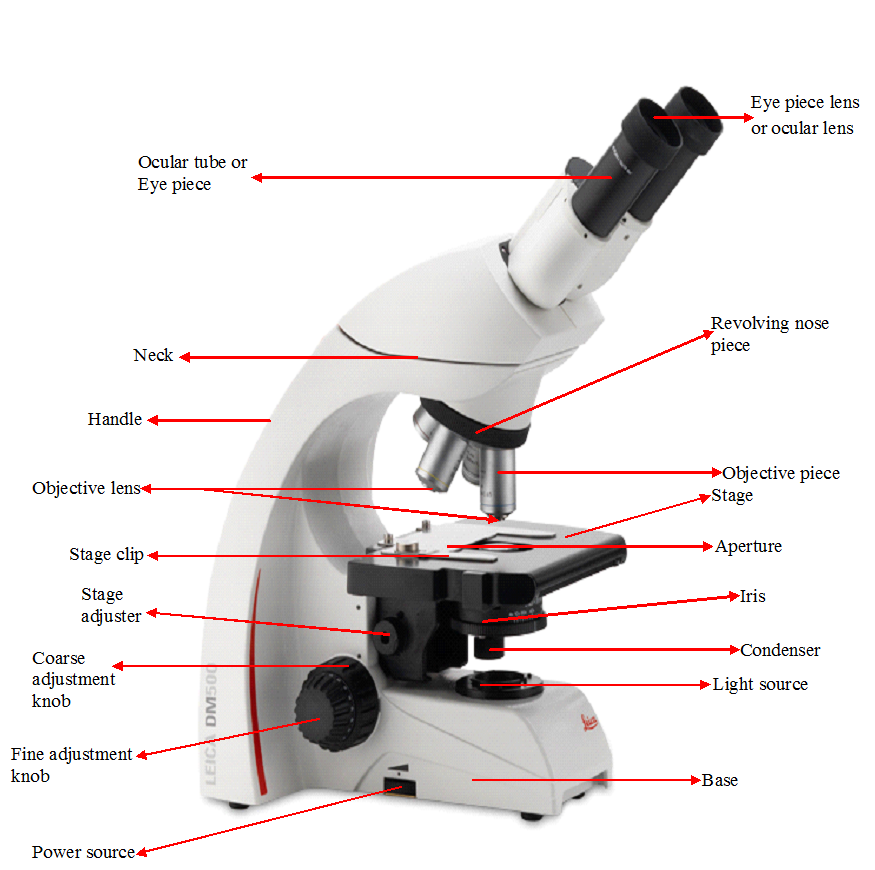
FUNCTIONS OF THE PARTS OF A MICROSCOPE
The microscope has various parts that perform specific function; and it is important that scientists […]
DNA VIRUSES
DNA viruses have only the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules as their nucleic acid; and the […]
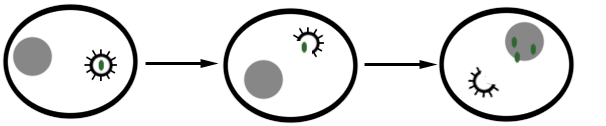
REPLICATION IN VIRUSES – viral replication
Replication is defined as the process in which a cell divides to make copies of […]
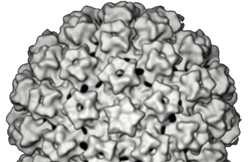
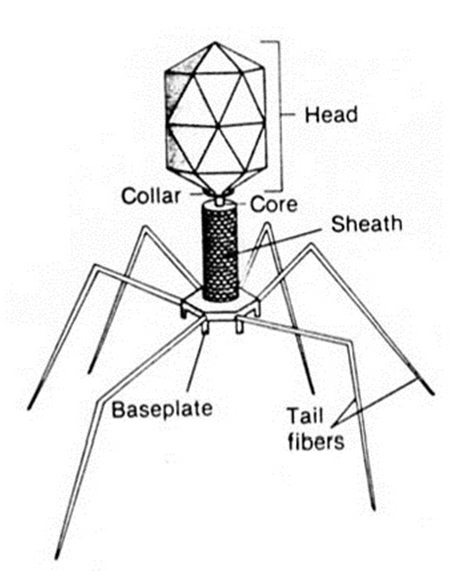
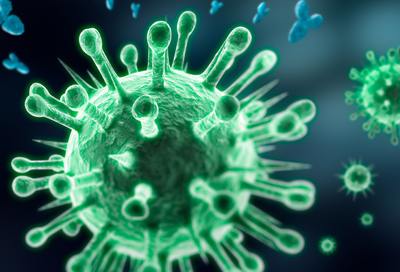
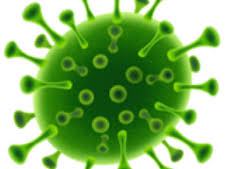
MORPHOLOGY OF VIRUSES
As shown in Figure 1 above, a virion is composed mainly of three parts viz: […]
VIRAL COMPOSITIONS
Viruses are infectious agents that have a simple acellular structure that is mainly made up […]
METHODS USED FOR THE INACTIVATION OF VIRUSES
Several reasons exist for the inactivation of viruses I either to use them for a […]
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF VIRUSES
Viruses have several physicochemical properties including pH, molecular size or mass, stability to heat and […]