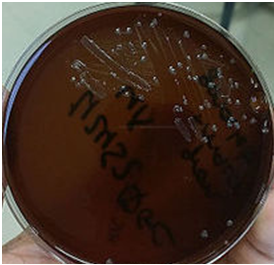
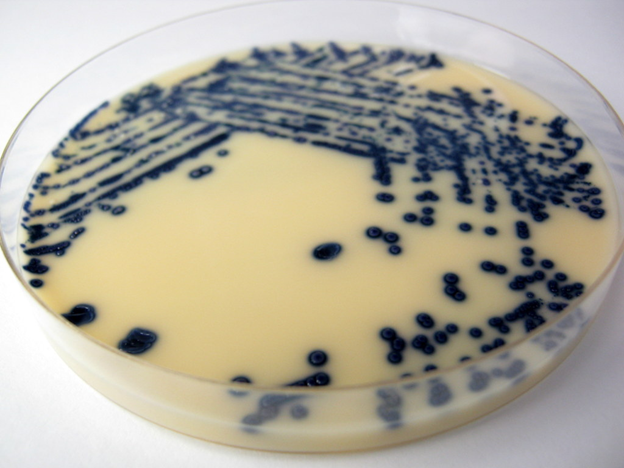
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a Gram-negative, oxidase-positive, non-motile, non-sporulating, non-capsulate, diplococcus found asymptomatically in humans. N. […]
Bacillus anthracis
Bacillus anthracis is a mesophilic, Gram-positive, aerobic, catalase-positive, rod-like and spore-forming bacterium that causes anthrax […]
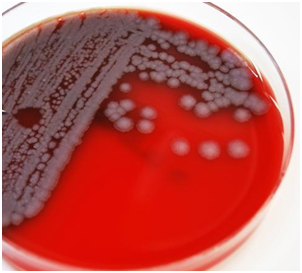
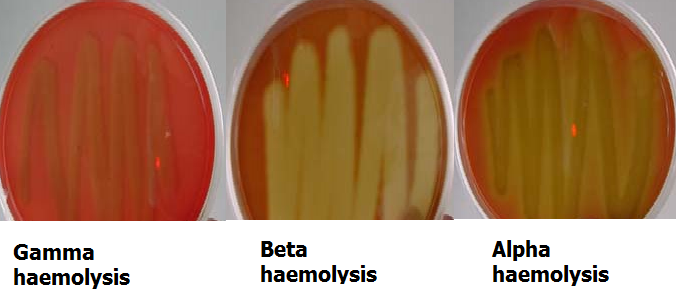
MICROBIAL HAEMOLYSIS IN BLOOD AGAR
Haemolysis is the breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs). Certain bacterial species including Streptococcus and […]
HISTORY OF ANTIBIOTICS – a synopsis on how it all started
Over the past 70 years, antibiotics have saved countless number of lives across the globe […]
PATHOGENICITY ISLANDS
Pathogenicity islands (PAIs) are the regions of bacterial chromosome (usually of foreign origin) that contain […]
BACTERIAL ENZYMES THAT EXCITE PATHOGENICITY
Pathogenic bacteria produce numerous enzymes that help to increase their pathogenicity and/or virulence during an […]
ENDOTOXIN PRODUCING BACTERIA
Endotoxins are microbial toxins which are produced only on cell lysis i.e. on cell death. […]
EXOTOXIN PRODUCING BACTERIA
Exotoxins are extracellular toxins produced by living bacterial cells. They are protein molecules excreted by […]
BACTERIAL TOXINS
Toxins are specific microbial products or secretions which at very low concentrations can act specifically […]
Characteristics of Pathogenic Microorganisms (Bacteria)
Bacterial pathogens that cause infections in humans have innate characteristic mechanisms with which they use […]
INOCULUM SIZE OF MICROBES
Inoculum size is defined as the number of invading pathogenic microorganisms that is sufficient enough […]
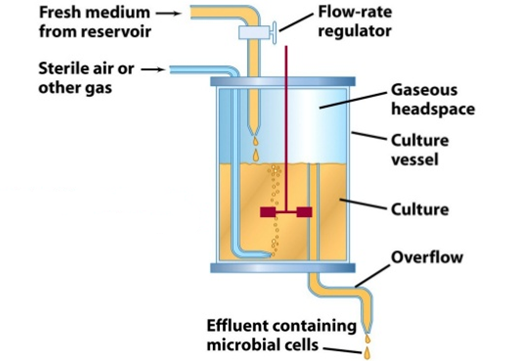
CONTINUOUS AND SEMI-CONTINUOUS FERMENTATION
Introduction to Fermentation Processes Fermentation is a metabolic process by which microorganisms convert organic compounds—primarily […]
Fed-Batch Fermentation: A Comprehensive Overview
Fed-batch fermentation is a critical and widely used process in modern biotechnology and industrial microbiology. […]
Batch Fermentation: Principles, Process, Applications, and Evaluation
Introduction Fermentation is a biological process through which microorganisms convert substrates (typically carbohydrates) into valuable […]
Benefits of Fermentation: A Comprehensive Exploration
Fermentation is one of the oldest and most fundamental biotechnological processes known to mankind, with […]
THERMOCYCLER (PCR Machine)
Thermocycler or thermal cycler is a piece of equipment is used for the copying or […]
SYSTEMIC MYCOSES
Systemic mycoses are fungal infections that affect deep tissues and organs of the body; and […]
SUBCUTANEOUS MYCOSES
Subcutaneous mycoses are fungal infections that affect the subcutaneous tissues below the skin, and the […]
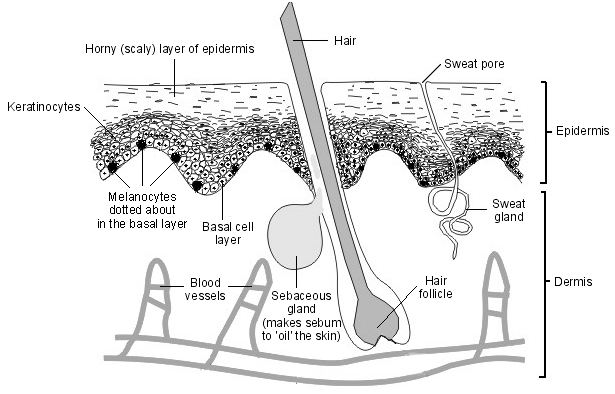
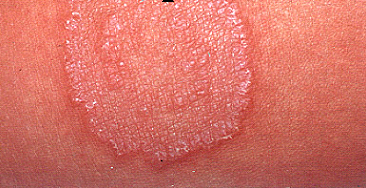
CUTANEOUS MYCOSES
Cutaneous mycoses are fungal infections of the skin, nails and hairs; and they are mainly […]
SUPERFICIAL MYCOSES
Superficial mycoses are fungal infections which are only limited to the keratinized outer layer of […]
MYCOSES – fungal infections
Mycoses are infections caused by pathogenic fungi. And they include superficial mycoses, cutaneous mycoses, subcutaneous […]
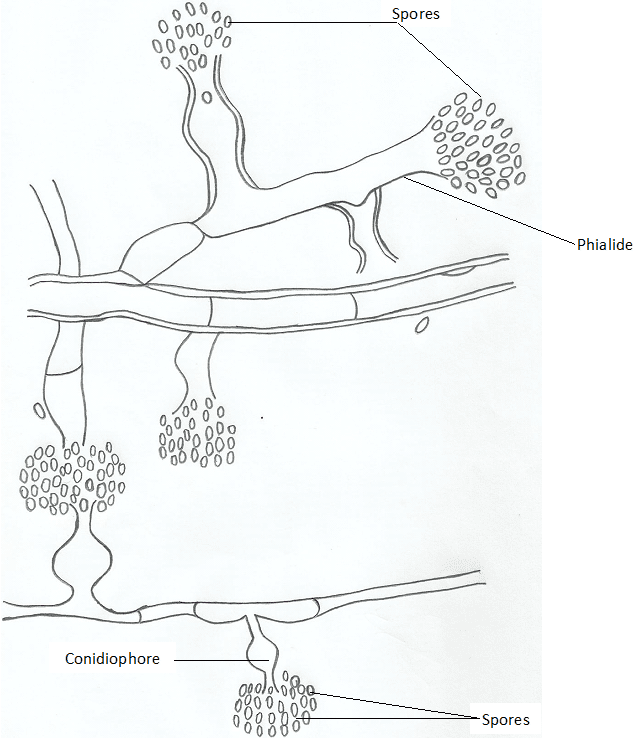
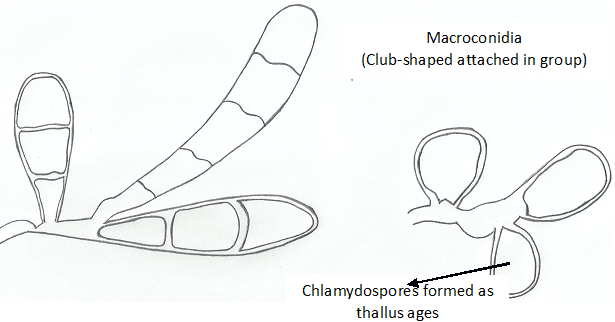
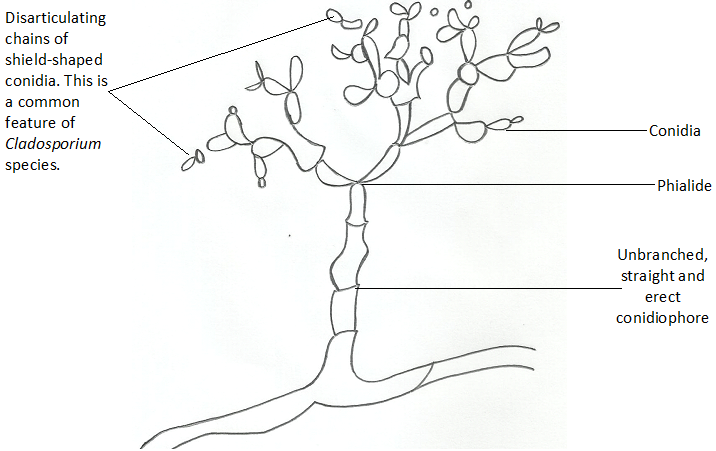
STRUCTURES OF FUNGI
The spores (conidia) are produced in dry chains from the tips of the phialides, with […]
FORMS & PREVENTION OF HALITOSIS
There are various forms of halitosis (bad breath) that an individual can experience at different […]
HALITOSIS – BAD BREATH AND YOU
Bad breath is clinically known as halitosis. Halitosis is an oral health condition that affects […]
PERIODONTITIS
Periodontitis is defined as the microbial infection of the periodontal membrane leading to pyorrhea, and […]
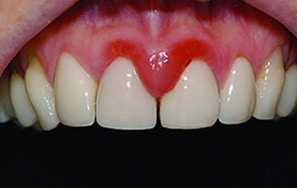
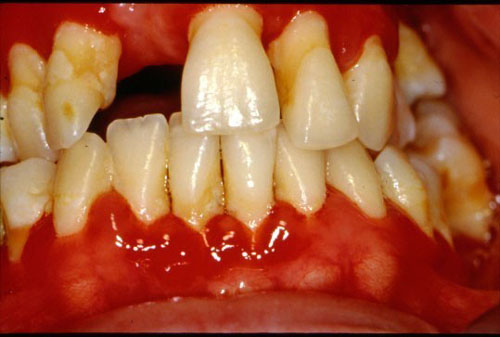
GINGIVITIS
Gingivitis is simply defined as the inflammation of the gum (gingivae) caused by microbial activity. […]
TECHNIQUES OF REVIVING MICROBIAL CULTURES
The procedures described below are guidelines of the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). They are […]
IMPORTANCE OF IMMUNIZATION
Immunization is the process whereby a person is made immune or resistant to an infectious […]
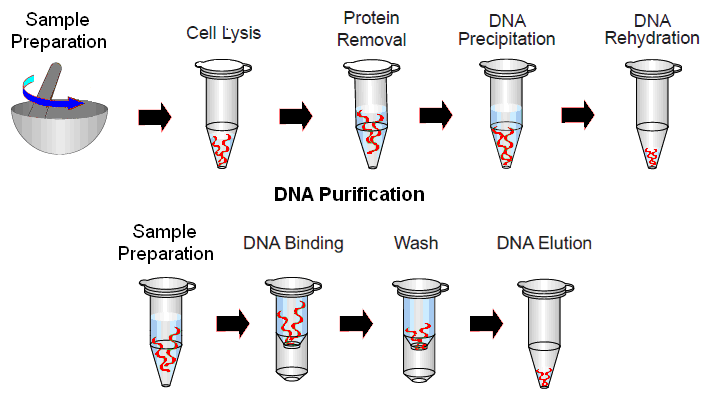
GENOMIC DNA ISOLATION
The Isolation of Genomic DNA from the bacterium, Escherichia coli is explained in this section […]
Epidemic Disease Occurrence
Level of disease The amount of a particular disease that is usually present in a […]
Desoxycholate Citrate Agar (DCA)
Desoxycholate Citrate Agar (DCA) is a selective medium for the isolation of Salmonella and Shigella […]
ANTIGEN RETRIEVAL PROTOCOL FOR PARAFFIN-EMBEDDED TISSUE
In the previous section on DEPARAFFINIZATION PRIOR TO IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY STAINING, we looked at deparaffinization and […]
ANTIBODY SELECTION AND STAINING FOR IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
We have looked at deparaffinization and rehydration of paraffin-embedded tissue, as well as antigen-retrieval protocol […]
ADENOVIRUS INFECTION
Adenoviruses are found in the viral family known as Adenoviridae. They are non-enveloped viruses with […]
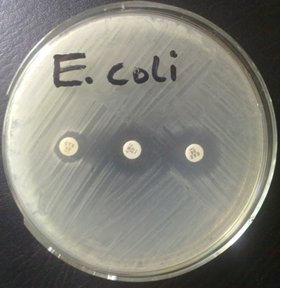
NITROCEFIN TEST FOR BETA-LACTAMASE PRODUCTION
The production of beta-lactamase enzymes by Gram negative bacteria including E. coli, P. aeruginosa and […]
TRYPAN BLUE & HAEMOCYTOMETER
Trypan blue is defined as a dye or stain that enables us to distinguish between […]
WAYS TO SEPARATE DNA FROM OTHER CELLULAR MATERIALS: BINDING AND WASHING
When phenol or a mixture of phenol:chloroform is mixed with a cell Lysate, two phases […]
Vancomycin resistance in Enterococci
Enterococcus (plural: Enterococci) is a group of bacteria that is normally found in the intestines […]
TYPES OF SOLID SUPPORT FOR BINDING DNA
The types of solid support for binding DNA are as follows: 1. Silica Matrix Silica […]
What are ESBLs?
ESBLs (extended spectrum beta-lactamases) are enzymes that mediate resistance to extended-spectrum (third generation) cephalosporins (e.g., […]
What is a stem cell?
A stem cell is a cell with the unique ability to develop into specialised cell types […]
WHO Global Principles for the Containment of Antimicrobial Resistance in Animals Intended for Food
Purpose: To minimize the negative public health impact of the use of antimicrobial agents in […]
DIAGNOSTIC VIRUS ASSAYS
Diagnostic methods accurately identify viral infections in patients. This is a prerequisite to control and […]
ECHINOCOCCOSIS(HYDATIDOSIS, OR HYDATID DISEASE)
BIOLOGY AND CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF ECHINOCOCOCCUS Human echinococcosis (hydatidosis, or hydatid disease) is caused by […]
Differences between Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) & Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Laboratory Testing Regulations
People are often confused by differences between Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) regulations and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) […]
CEFTAZIDIME-IMIPENEM ANTAGONISM TEST (CIAT)
Ceftazidime-imipenem antagonism test (CIAT) is one of the phenotypic confirmation tests that can be used […]
Botulism – a public health menace
Key facts Foodborne botulism is a serious, potentially fatal disease. However, it is relatively rare. […]
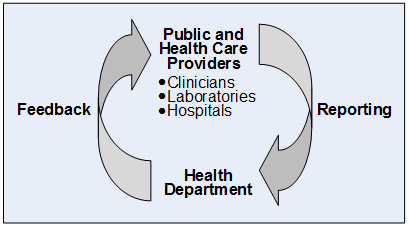
Core Epidemiologic Functions
In the mid-1980s, five major tasks of epidemiology in public health practice were identified. These […]
YELLOW FEVER
The yellow fever virus is found in tropical and subtropical areas of Africa and South […]
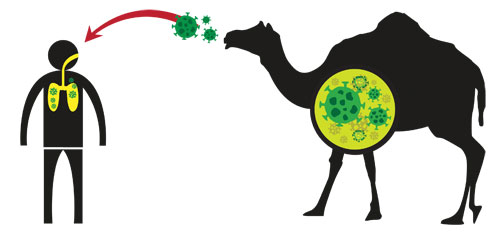
MIDDLE EAST RESPIRATORY SYNDROME (MERS)
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) is an illness caused by a virus (more specifically, a […]