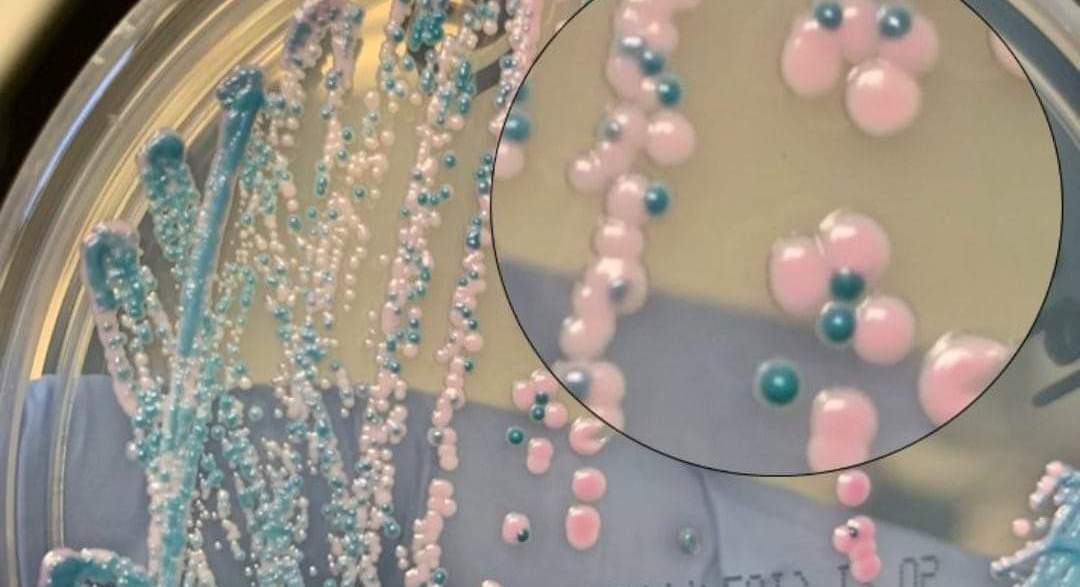
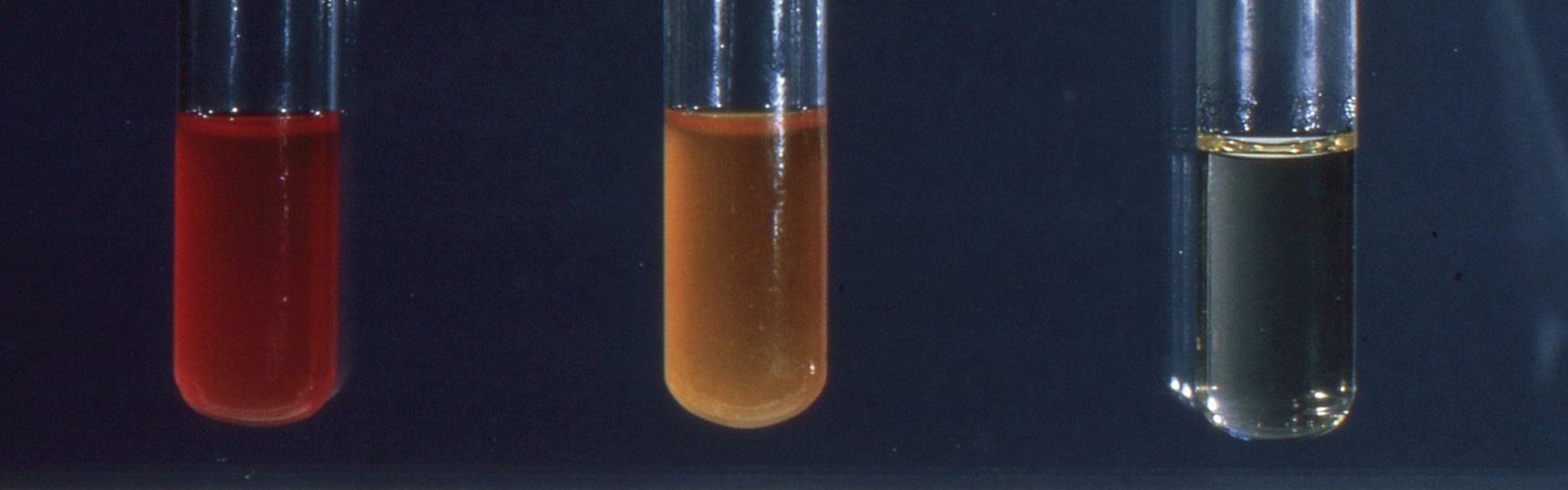
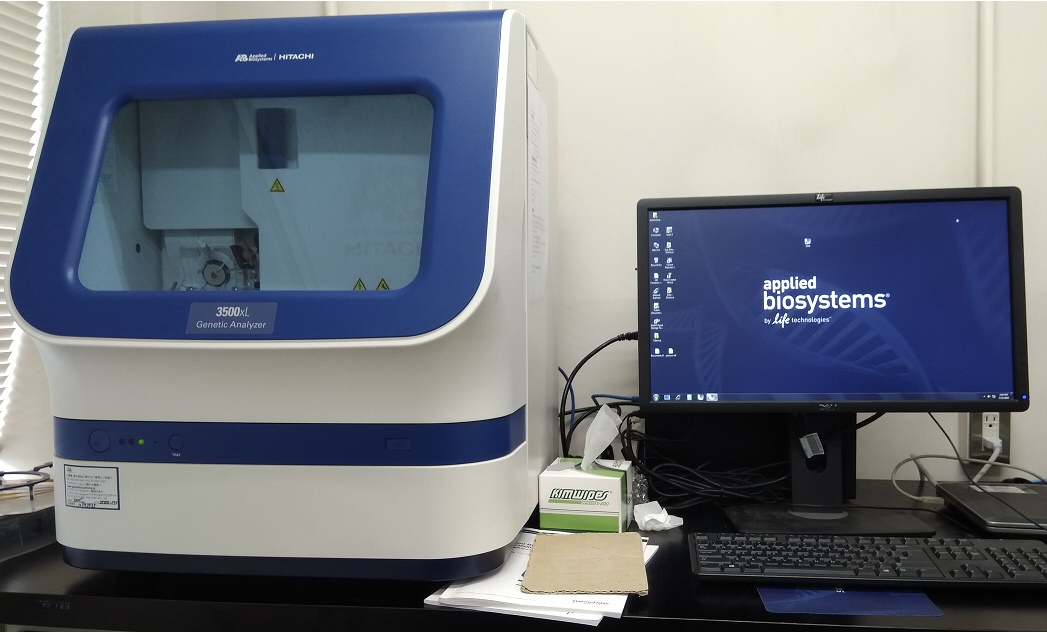
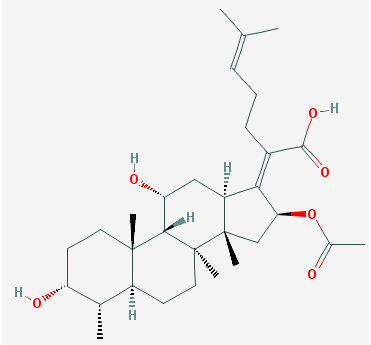
Fusidic acid is a bacteriostatic antimicrobial agent and/or antibiotic that is derived from the fungus, […]
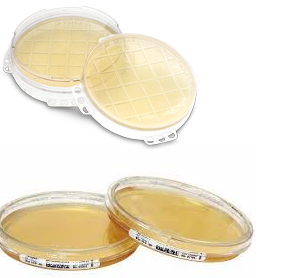
Cetrimide selective agar
Cetrimide selective agar is used for the selective cultivation and isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from clinical […]
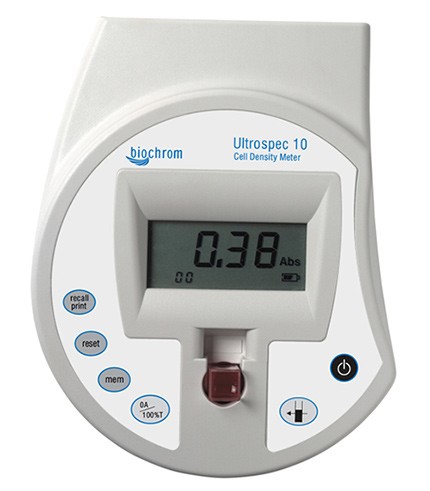
CELL DENSITY METER
Cell density meter is an instrument that is used for measuring of the density of […]
Calculation for preparing culture media
In this section, you will learn how to calculate for culture media preparation. Calculations for […]
Candida glabrata
Biology of Candida glabrata Candida glabrata is a fungus species of haploid yeast of the […]
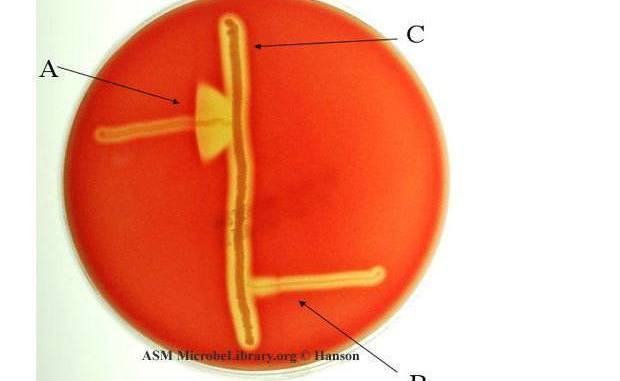
CAMP Test for Identification of Group B Streptococci
The CAMP test (named for the original authors: Christie, Atkins, and Munch-Petersen) was first used […]
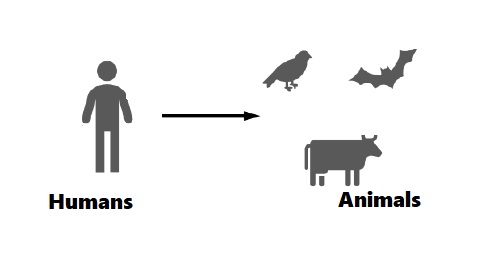
Anthroponotic Disease (Anthroponosis) & Sapronoses
An anthroponotic disease, or anthroponosis, is an infectious disease in which a disease causing agent […]
ROUTES OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION
Therapeutic drugs are administered in various ways, and these include parenteral and oral administration. Other […]
PHARMACOKINETICS & PHARMACODYNAMICS
Pharmacokinetics is simply the study of how the body reacts to therapeutic agents or drugs […]
DRUG INTERACTION
To be clinically effective for the treatment of infectious diseases, every drug must reach a […]
MONITORING OF WATER QUALITY
Water quality is defined as the suitability of water to sustain various uses or processes […]
ACTIVE AIR MONITORING
Active air monitoring also involve the use of settle plates or sedimentation culture plates (as […]
PASSIVE AIR MONITORING
Passive air monitoring is usually done using special type of Petri dish plates known as […]
Glass Plating Beads for spreading bacteria/fungi on culture plate
Glass Plating Beads are reusable beads which helps to spread suspensions of microorganisms (bacteria or […]
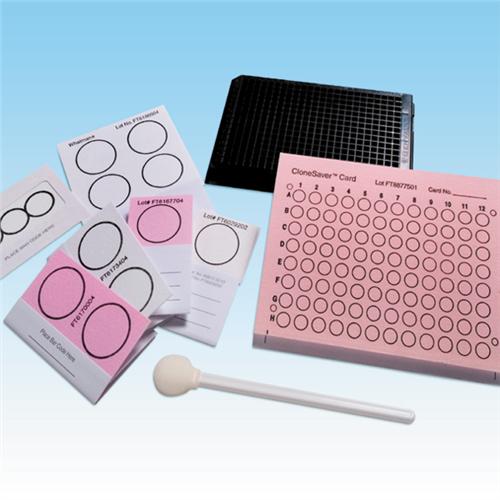
FTA CARDS
The acronym FTA stands for “Flinders Technology Association”. FTA CARDS are chemically treated Whatman filter […]
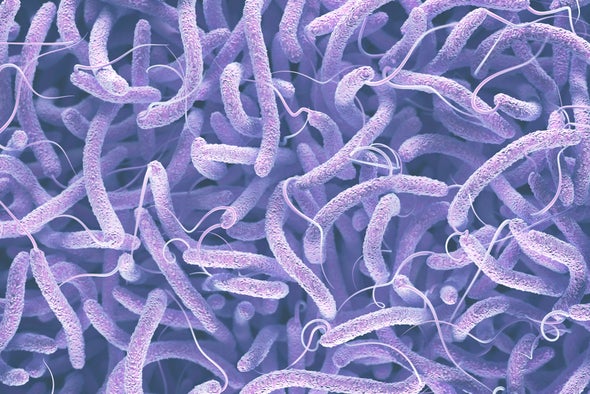
Cholera – a public health threat
Cholera is an infectious disease that causes severe watery diarrhea, which can lead to dehydration […]
Assessing RNA Purity, Concentration and Integrity
The integrity, purity and concentration of the RNA so isolated should be confirmed before proceeding […]
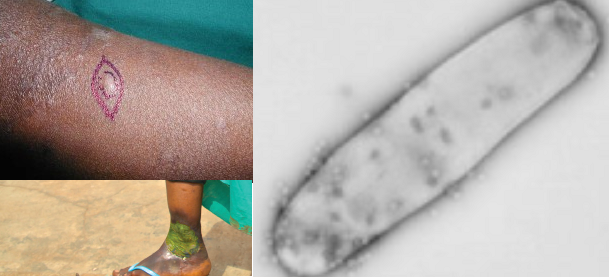
Buruli ulcer (Mycobacterium ulcerans infection)
Key facts about Buruli ulcer Buruli ulcer, caused by Mycobacterium ulcerans, is a chronic debilitating disease that […]
Microbiological Risk Assessment
Microbiological risk assessment (MRA) is a structured process that is used for determining the public health […]
MONITORING OF AIR QUALITY
Air quality is defined as the degree to which the ambient air in a particular […]
RULES OF GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE (GMP)
GMP encompasses the rules governing the manufacture of a safe and efficacious pharmaceutical product, drug […]
CRITICAL ASPECTS OF GMP (sources of microbial contamination)
Some of the main sources of contamination in the course of production in a food […]
PRINCIPLES OF GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE (GMP)
GMP guidelines are not prescriptive instructions on how to manufacture any product including food, drugs, […]
GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE (GMP)
Good manufacturing practice (GMP) is simply defined as those general rules that govern the manufacture […]
QUALITY ASSURANCE
Quality assurance (QA) is a planned and systematic process used for evaluating and monitoring the […]
QUALITY CONTROL
Quality control (QC) is defined as a monitoring system that is used for detecting and […]
HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE OF CELL CULTURE
The history of cell culture cannot be complete without the mention of Henrietta Lacks, whose […]
DESCRIPTIVE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY
Descriptive epidemiological studies look at the frequency and distribution of a disease/infection within a population. […]
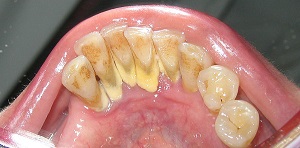
DENTAL PLAQUE
Dental plaque is defined as the tenacious microbial deposit that forms on the hard tissue […]
HYDROGEN SULPHIDE TEST
Hydrogen sulphide test: Hydrogen sulphide test is used to identify bacteria that produce the gas, […]
METHYL RED TEST
Methyl red test is used to identify pathogenic bacteria that produce acid from glucose phosphate. […]
AMYLASE (STARCH HYDROLYSIS) TEST
Amylase (Starch hydrolysis) test is used to identify bacteria that hydrolyze starch (including amylopectin and […]
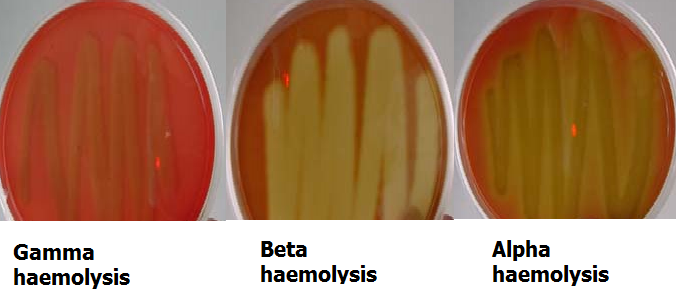
BLOOD AGAR HAEMOLYSIS TEST
Blood agar haemolysis is used to determine the haemolytic ability of some pathogenic microorganisms including […]
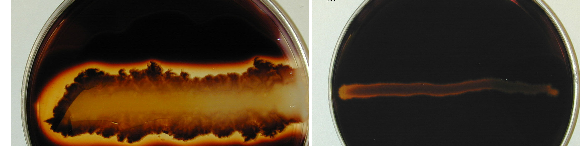
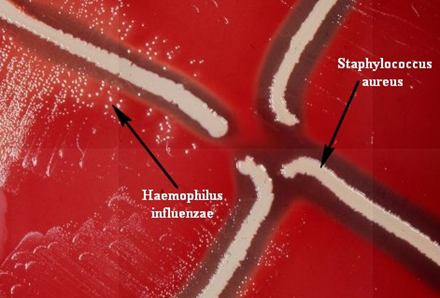
SATELLITISM TEST
Satellitism test is a culture-based test which is used to identify Haemophilus influenzae in the […]
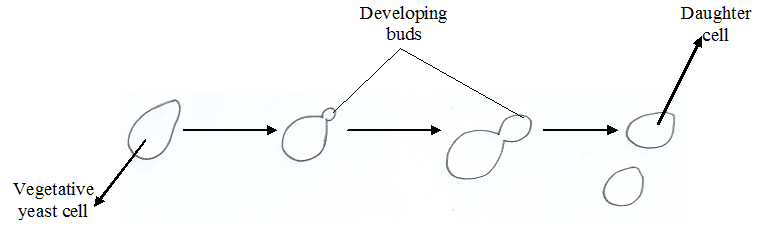
FUNGAL REPRODUCTION
Fungal reproduction is unique and distinct from those of other microbial cells such as bacteria. […]
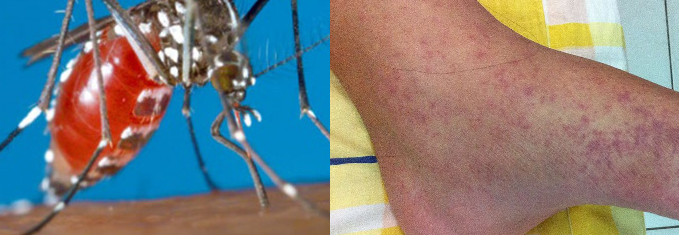
ZIKA VIRUS INFECTION
Key facts about zika virus infection Zika virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that was first […]
CHIKUNGUNYA INFECTION
Chikungunya is a mosquito-borne viral disease first described during an outbreak in southern Tanzania in […]
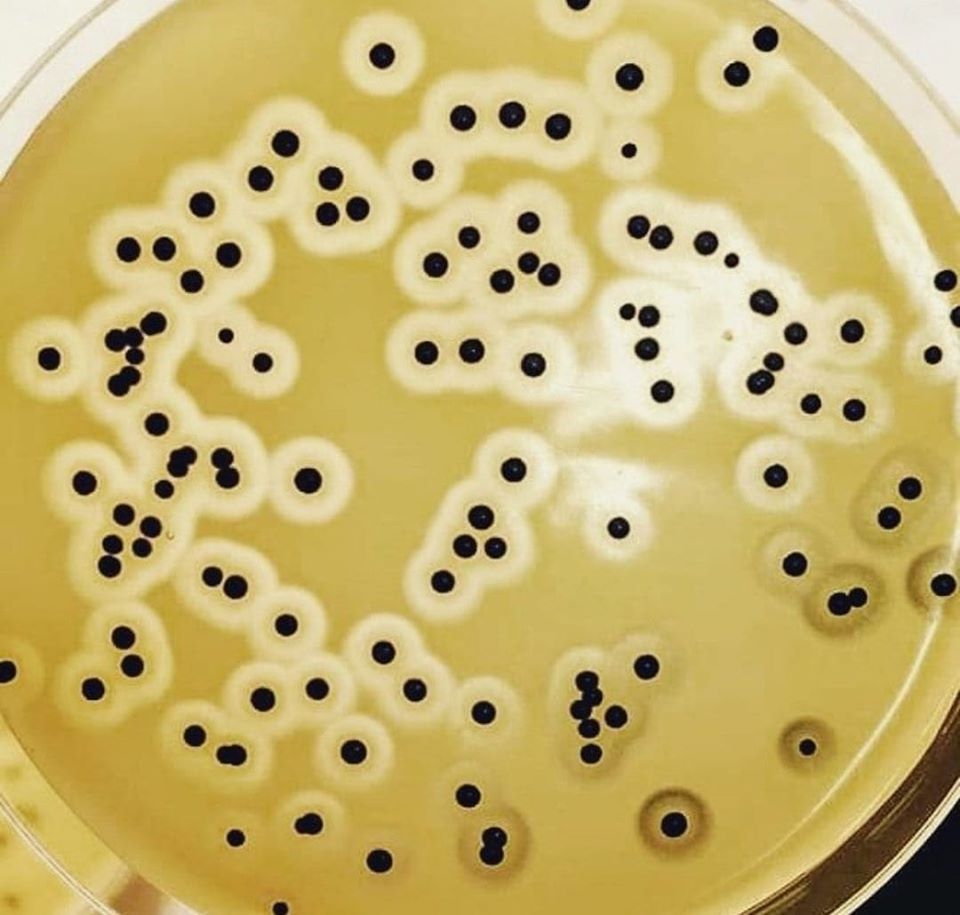
BAIRD–PARKER AGAR
Baird–parker agar is a selective medium for the enumeration of Staphylococcus aureus in foods and […]
COMMON MISTAKES INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS MAKE IN SCHOLARSHIP APPLICATIONS
6 COMMON MISTAKES INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS MAKE WHILE APPLYING FOR SCHOLARSHIPS OR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE ADMISSION […]
Links for dilution calculation
Links for dilution calculation in biological sciences and other fields of sciences: These links will […]
P value
The phrase “P value” also means ‘calculated probability’. P value is defined as the probability […]
200+ LATEST MICROBIOLOGY SEMINAR TOPICS
Discover 200+ Cutting-Edge Microbiology Seminar Topics for Students & Researchers (2025 Updated) Attention Microbiology Students […]
MICROBIOLOGY PROJECT TOPICS
Below are some PROJECT TOPICS for your undergraduate and postgraduate (M.Sc. & Ph.D.) research studies. […]
PROKARYOTIC CELLS
Prokaryotic cells are microbial cells that have chromosomes that are not separated from the cytoplasm […]
TOOLS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY
Biotechnology uses the tools of molecular biology (i.e. genetic engineering) to produce novel products through […]
AXENIC (Gnotobiotic) ANIMALS
Axenic animals are laboratory controlled animals that are germ-free i.e. animals that are not contaminated […]
APPERTIZATION
Appertization is simply defined as the heat-treatment of food at certain temperature levels that inhibit […]
SAFETY IN THE LABORATORY
Safety in the clinical microbiology laboratory should not be taken for granted. It is paramount […]
SLIME MOULDS
Slime moulds are eukaryotic organisms that have fungus-like features as well as some animal- or […]
Significance and Applications of Microorganisms
Microorganisms, often referred to as microbes, are tiny life forms that are invisible to the […]