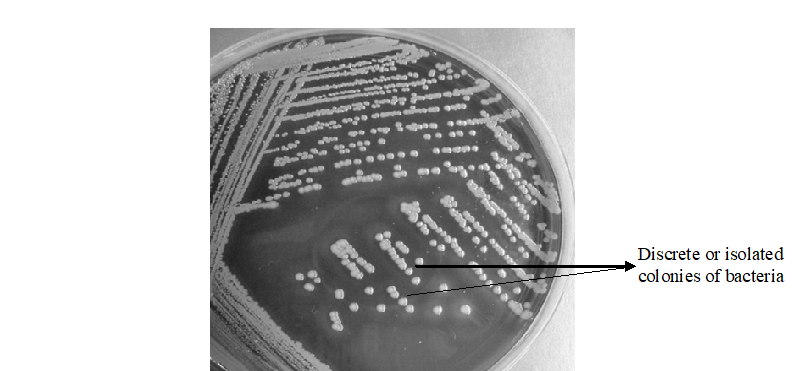
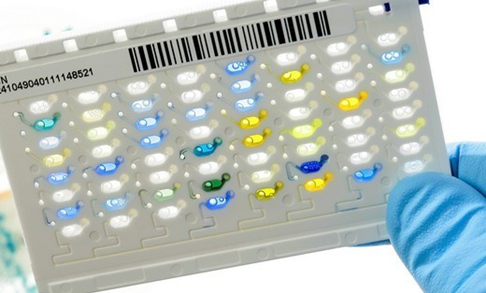
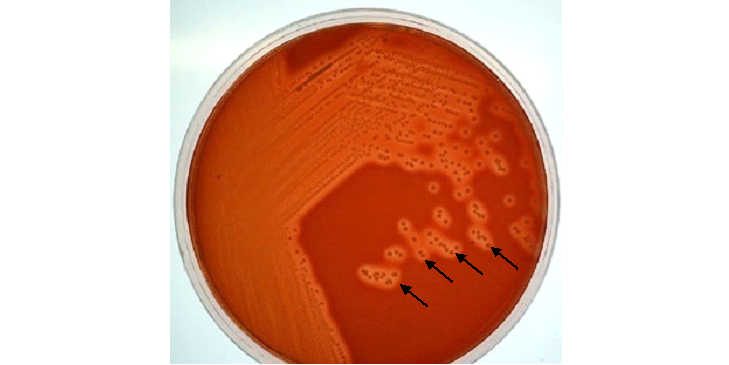
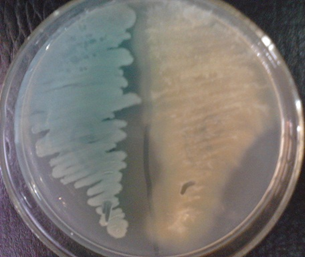
Antibiotics remain one of the most important discoveries in medical science, serving as a cornerstone […]
Category: Techniques in Microbiology Lab
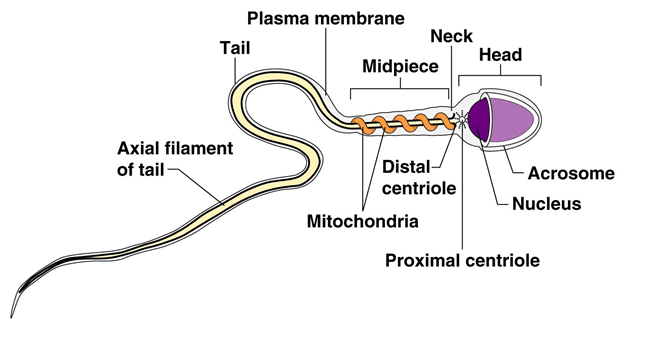
SEMINAL FLUID (SEMEN) MICROSCOPY, CULTURE & SPERM CELL COUNT
SEMEN MICROSCOPY AIM: To determine any abnormality in a seminal fluid (semen) as an aid […]
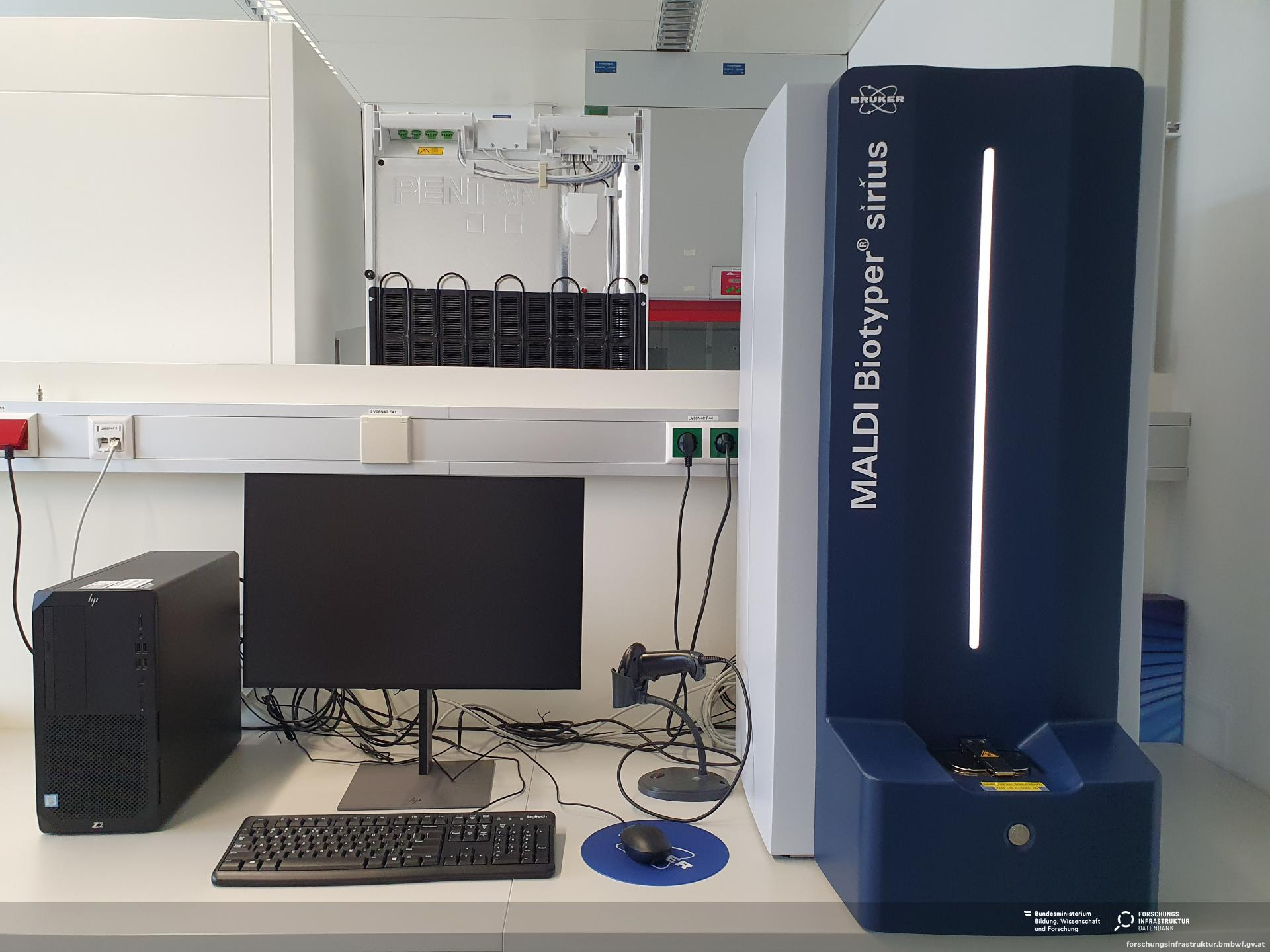
AUTOMATED SYSTEMS FOR BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION AND ANTIBIOGRAM: VITEK 2 AUTOMATED COMPACT SYSTEM & MALDI-TOF
AUTOMATED SYSTEMS FOR BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION AND ANTIBIOGRAM: VITEK 2 AUTOMATED COMPACT SYSTEM & MALDI-TOF There […]
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) workflow
The workflow of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) involves several critical […]
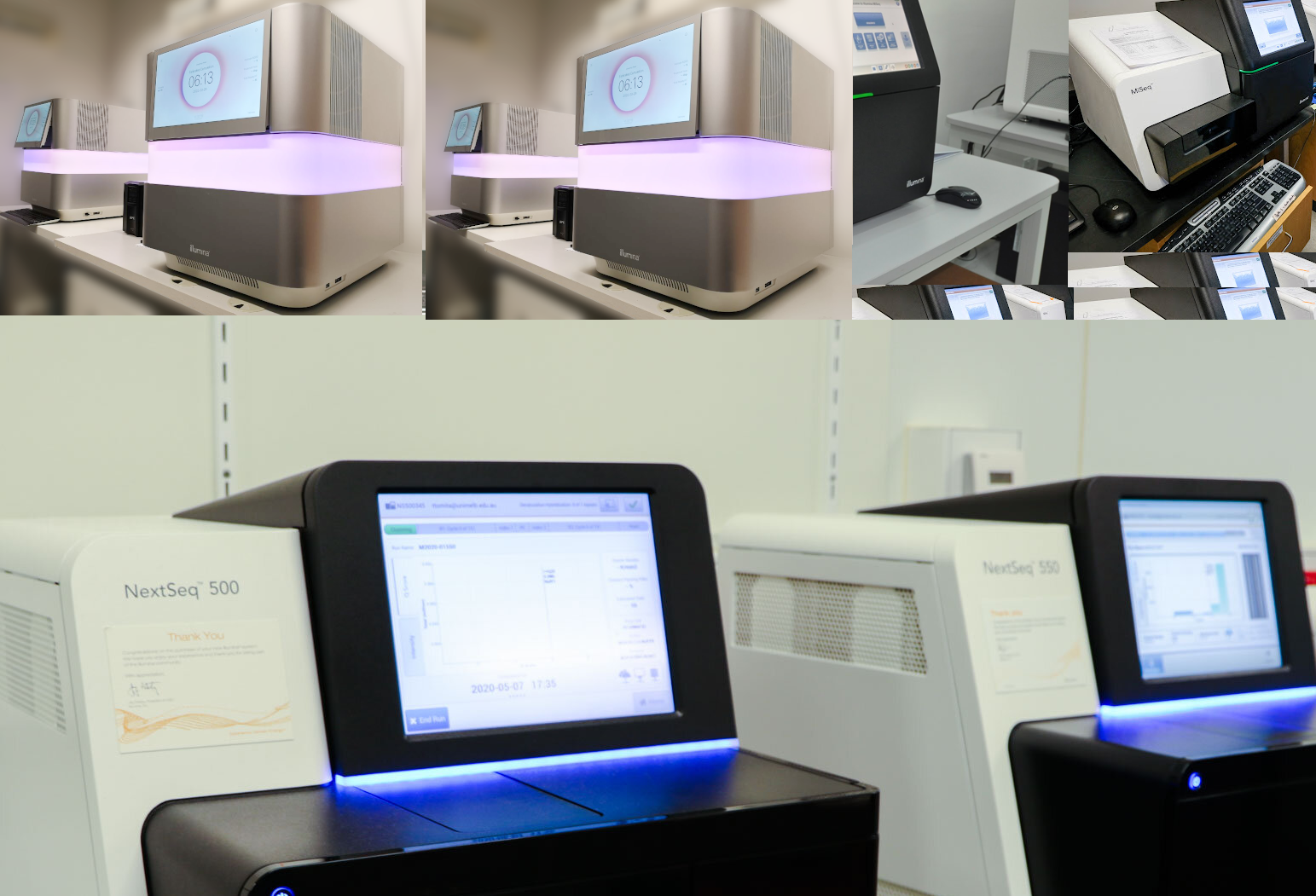
How does metagenomic sequencing differ from whole-genome sequencing (WGS)?
Metagenomic Sequencing Metagenomic sequencing and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) are distinct techniques, but they can generate […]
BLOTTING TECHNIQUE
Blotting is used in molecular biology to transfer nucleic acids and proteins from gel to a membrane for identification and analysis. Developed in the 1970s, it combines electrophoresis and immunological methods. There are three main types: Southern (DNA), Northern (RNA), and Western (proteins), each allowing detection and measurement of specific molecules.
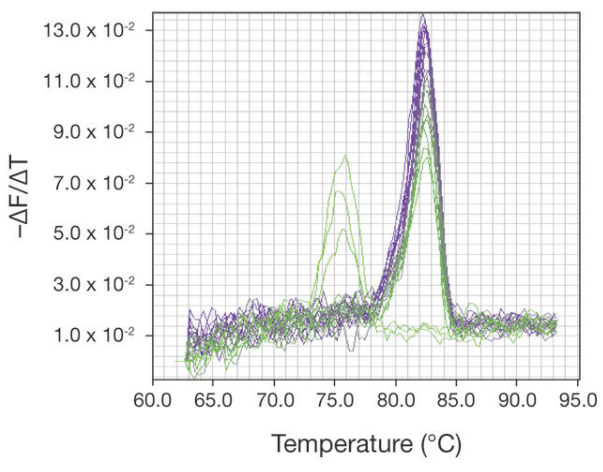
Melting curve analysis in Real-time PCR
Melting curve analysis and detection systems Melting curve analysis can only be performed with realtime […]
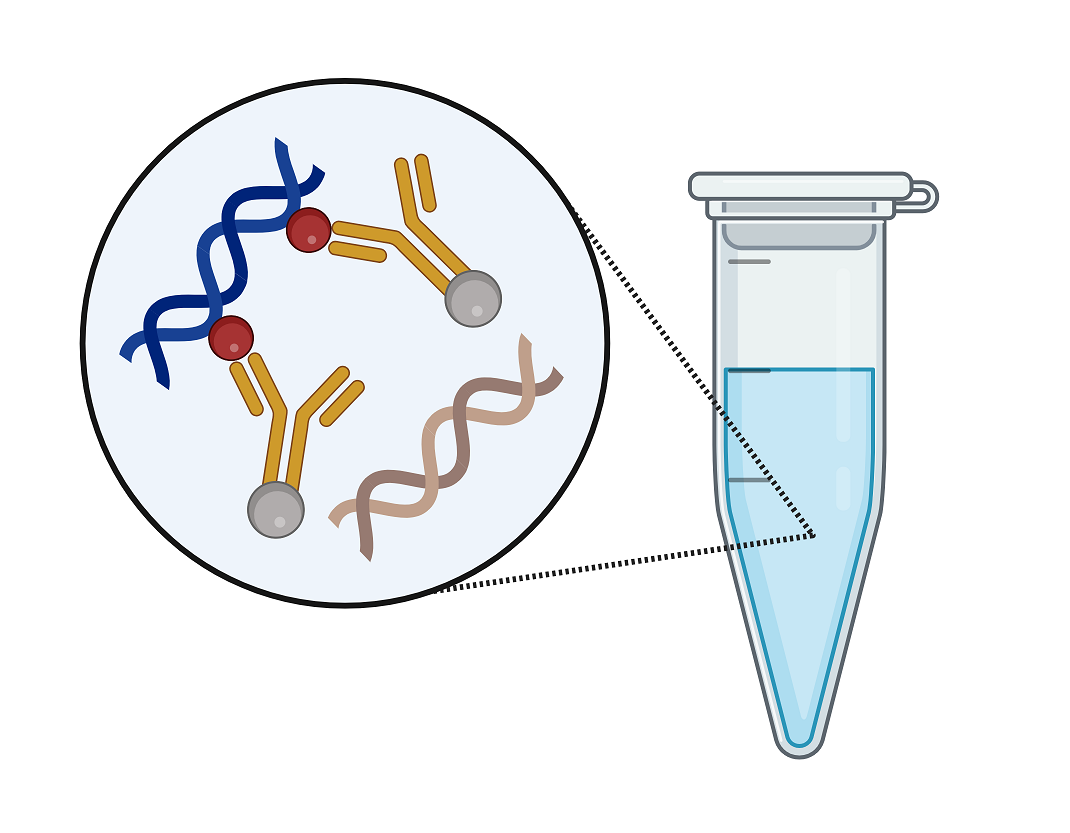
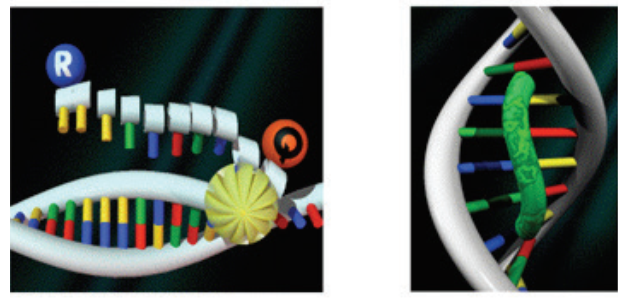
Real-time PCR probes
TaqMan® probe signal production Whether an MGB or non-MGB probe is chosen, both follow the […]
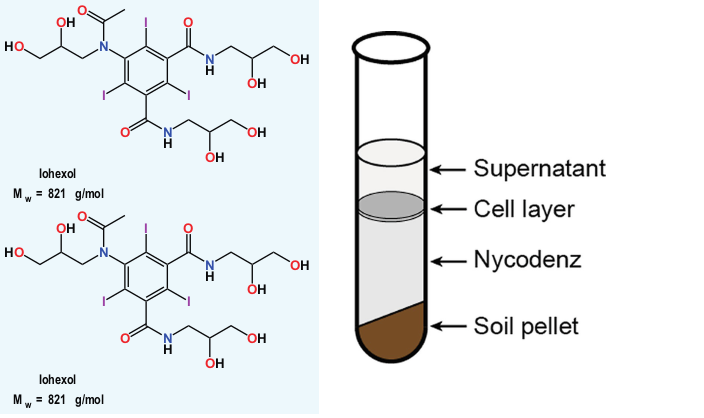
Nycodenz: application and properties
What is Nycodenz Nycodenz is a non-ionic, triiodinated radiopaque substance used primarily in molecular biology […]
Luria Broth (LB) and Luria Agar (LA) Media
Luria-Bertani (LB) broth is the most widely used medium for the growth of bacteria. It […]
Real-time PCR fluorescence detection systems
Real-time PCR fluorescence detection systems Real-time fluorescent PCR chemistries Many real-time fluorescent PCR chemistries exist, […]
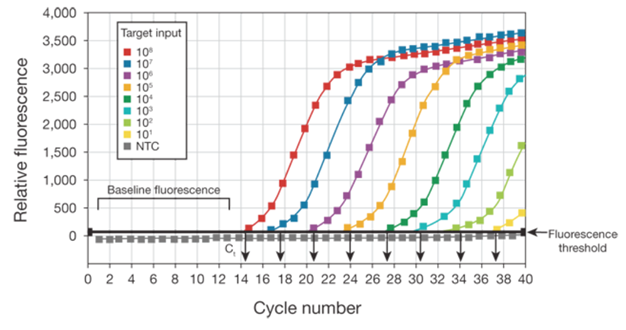
Real-time PCR analysis technology
BaselineThe baseline of the real-time PCR reaction refers to the signal level during the initial […]
Real-time PCR primer design
Good primer design is one of the most important parameters in real-time PCR. This is […]
REAL-TIME PCR COMPONENTS
DNA polymerasePCR performance is often related to the thermostable DNA polymerase, so enzyme selection is […]
STEPS INVOLVED IN PERFORMING REAL-TIME PCR
Real-time PCR is a variation of the standard PCR technique that is commonly used to […]
INTRODUCTION TO REAL TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (RT PCR)
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is one of the most powerful technologies in molecular biology. […]
HOW TO DESIGN PRIMERS FOR YOUR PCR EXPERIMENT
Primers are short stretches of DNA that target unique sequences of a DNA molecule and […]
DIFFERENTIAL COUNT FOR CSF
AIM: To provide information on the different white blood cells (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes) […]
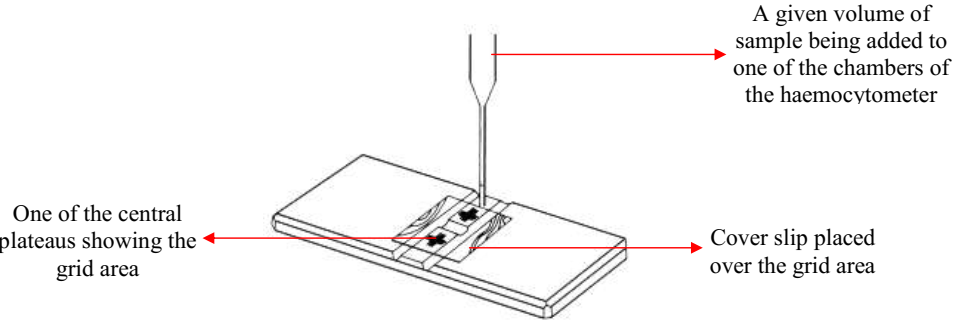
HAEMOCYTOMETER CELL COUNT FOR CSF SAMPLE
Cells of mammalian or prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells can be counted in the lab from […]
Important techniques in microbiology laboratory
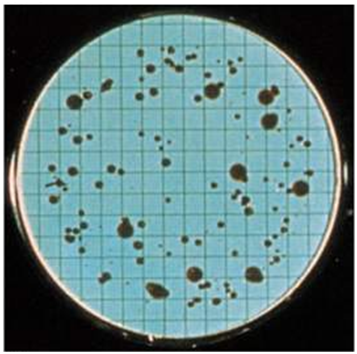
DIRECT PLATE COUNTING Direct plate counting is a microbiological technique used to evaluate the actual […]
The 3 Rs (Reduction, Refinement, Replacement): Guiding Principles in the Use of Animals For Biomedical/Scientific Research
The use of laboratory animals including mice, rats, rabbits and primates for scientific/biomedical research is […]
RATIONALE FOR THE CONTINUED USE OF ANIMALS FOR RESEARCH
Animals including (primates, dogs, cats, rabbits, mice) are still being used to conduct scientific/biomedical research […]
Issues Surrounding the Use of Animals in Scientific Research
Animals such as mice, rats, rabbits, monkeys and primates are used in biomedical research to […]
INCUBATION & STERILIZATION TECHNIQUE
Microorganisms are incubated in the incubator at different temperatures and time interval depending on the […]
CULTURING TECHNIQUE
Culturing technique is used for the propagation of microorganisms in the microbiology laboratory; and it […]
GRAM SMEAR OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF) SAMPLE
AIM: To detect the presence of pus cells and bacteria in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimen. […]
MICROSCOPY OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF)
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples are obtained with extra precautions using a technique called lumbar puncture. […]
MEMBRANE FILTRATION TECHNIQUE
Filtration is simply defined as the separation of particles from fluid or liquids by the […]
CULTURE OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF)
AIM: To isolate organism from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimen as an aid in the diagnosis […]
MICROSCOPY OF SPUTUM SPECIMEN
AIM: To detect the presence of pus cells and predominant bacteria in sputum specimens as […]
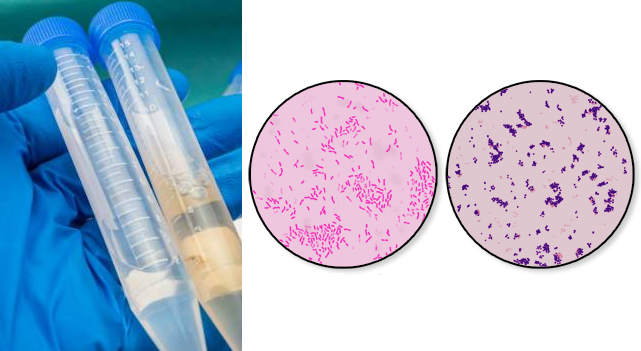
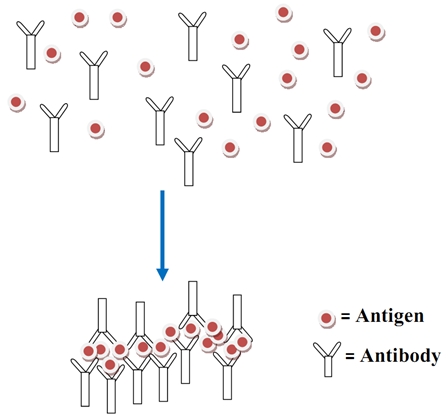
ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY REACTION
Antigen-antibody reaction is an immunological reaction in which a particular antibody molecule reacts with a […]
ELISA
ELISA is the acronym for “enzyme linked immunosorbent assay”. It is an immunoassay or serological […]
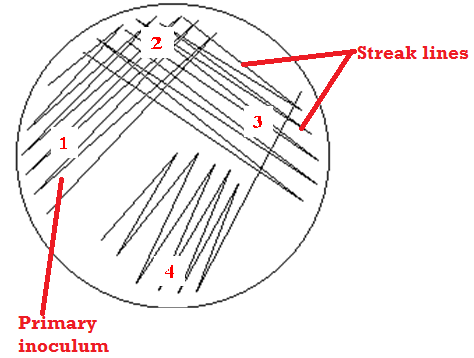
STREAKING TECHNIQUE
Streaking is a microbiological technique that is used to obtain pure cultures of microorganisms (particularly […]
ISOLATION TECHNIQUE
Isolation technique is a microbiology procedure which is used to obtain pure cultures of microorganisms […]
GENOTYPIC DETECTION OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANT MICROBES
The genotypic detection and characterization of antibiotic resistant genes in pathogenic bacteria is more specific […]
FEATURES OF THE VITEK 2 AUTOMATED COMPACT SYSTEM FOR BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION AND ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY TEST (AST)
Helping the physician select the best treatment at a much faster pace based on the […]
PCR TECHNIQUE
PCR is the acronym for “polymerase chain reaction”. Polymerase chain reaction is the molecular biology […]
ENZYMES USED IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TECHNIQUES
Restriction endonucleases are DNA cutting enzymes specifically found and isolated from bacteria; and which nick […]
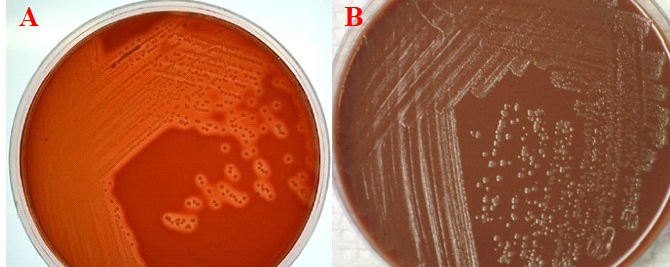
SPUTUM CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Sputum culture is often recommended in the diagnoses of lower respiratory tract infection (e.g. bacterial […]
URINE CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Urine culture is performed in order to specifically identify organisms that may be causing a […]
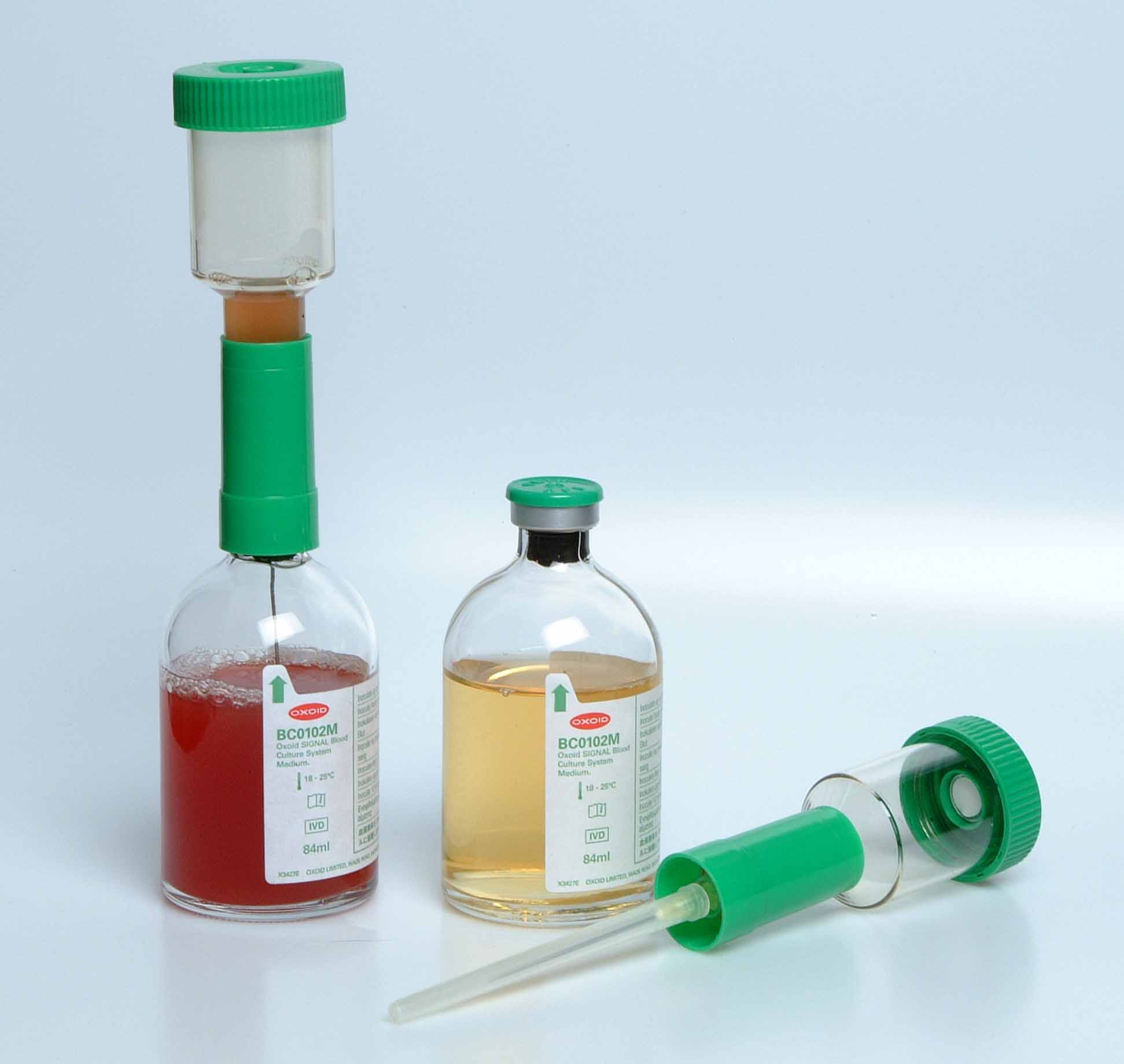
BLOOD CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Blood culture is the most important diagnostic method for detecting and diagnosing bacteraemia (presence of […]
STOOL CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Stool culture is demanded in the bacteriology laboratory as method for detecting and diagnosing enteric […]
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS/DISEASES
The laboratory diagnosis of fungal infection is mainly based on microscopy and cultural techniques. Several […]
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS BASED ON HAZARDS AND LABORATORY
Pathogenic microorganisms inclusive of viruses, bacteria, and fungi portends health challenges to the general public […]
TYPES OF MICROSCOPES
There abound several numbers of microscopes that can be used by a microscopist to view […]
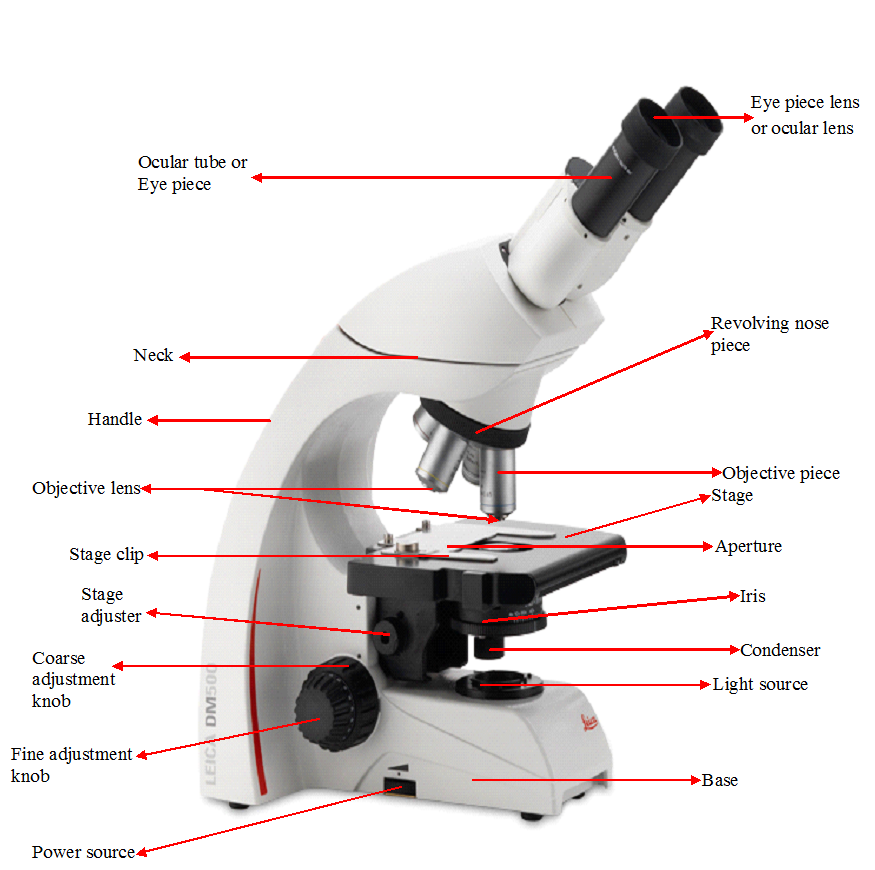
FUNCTIONS OF THE PARTS OF A MICROSCOPE
The microscope has various parts that perform specific function; and it is important that scientists […]
THERMOCYCLER (PCR Machine)
Thermocycler or thermal cycler is a piece of equipment is used for the copying or […]
TECHNIQUES OF REVIVING MICROBIAL CULTURES
The procedures described below are guidelines of the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). They are […]
TRYPAN BLUE & HAEMOCYTOMETER
Trypan blue is defined as a dye or stain that enables us to distinguish between […]
CEFTAZIDIME-IMIPENEM ANTAGONISM TEST (CIAT)
Ceftazidime-imipenem antagonism test (CIAT) is one of the phenotypic confirmation tests that can be used […]