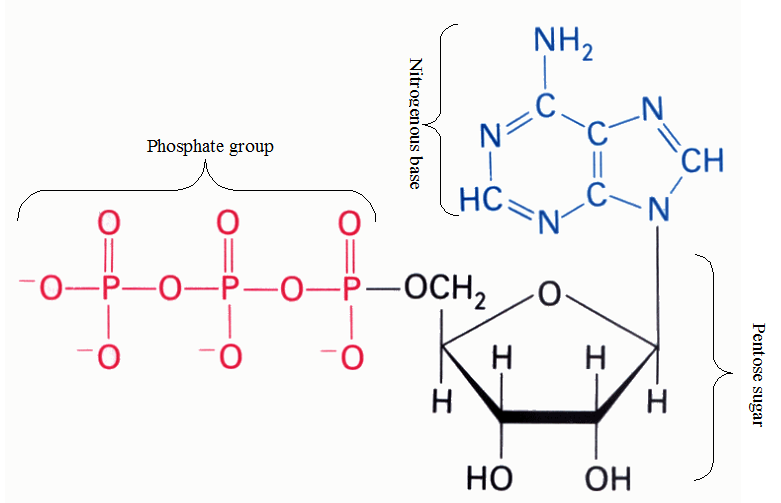
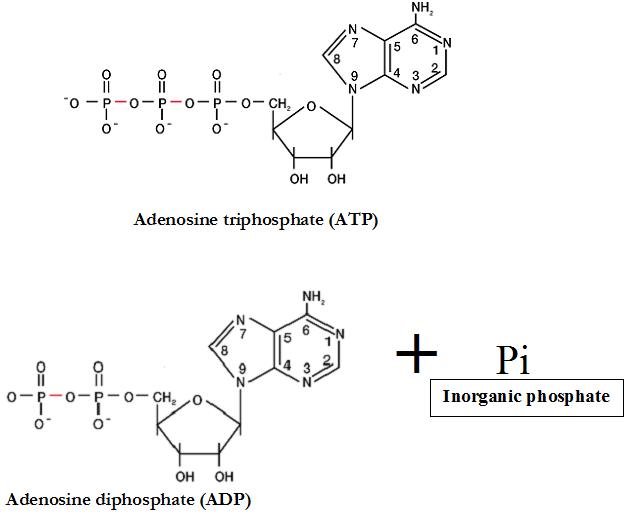
Metabolic reactions help to maintain a state of balance or equilibrium in the cell. And […]
METABOLISM
Metabolism is simply defined as the summation of the chemical reactions that occurs in the […]
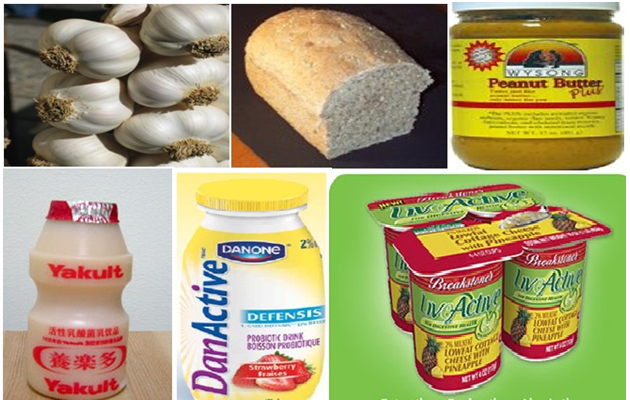
PROBIOTICS
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the […]
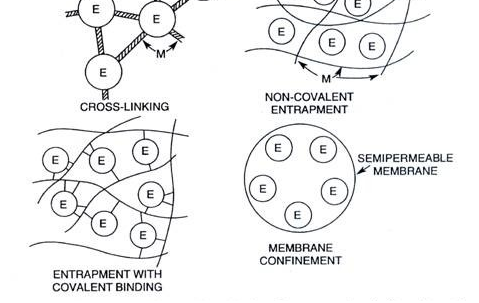
CELL IMMOBILIZATION
Cell immobilizationis the process of fixing the cells of living organisms including plants, animals, […]
INNATE IMMUNITY
Innate immunity is the body’s natural inborn resistance to infection and it is quick in […]
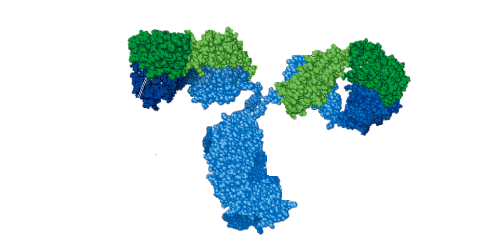
SIGNIFICANCE OF MONOCLONAL AND POLYCLONAL ANTIBODIES
The two basic forms in which antibodies can be produced in purified forms in the […]
How to write a COVER LETTER – Faculty, Postgraduate, Postdoc – sample attached
How to write a COVER LETTER – Faculty, Postgraduate, Postdoc – sample attached A cover […]
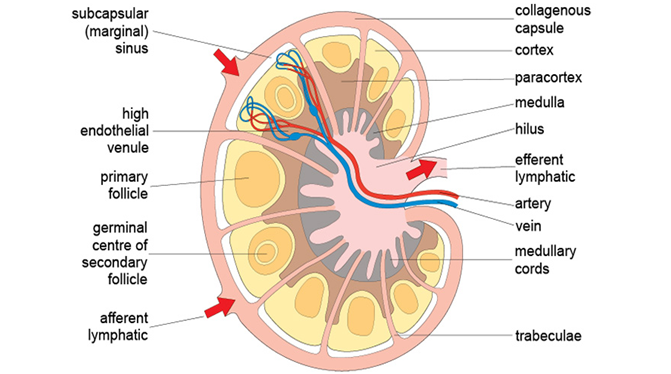
ORGANS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM AND THEIR FUNCTION
The organs of the immune system are generally divided into two major groups: the primary […]
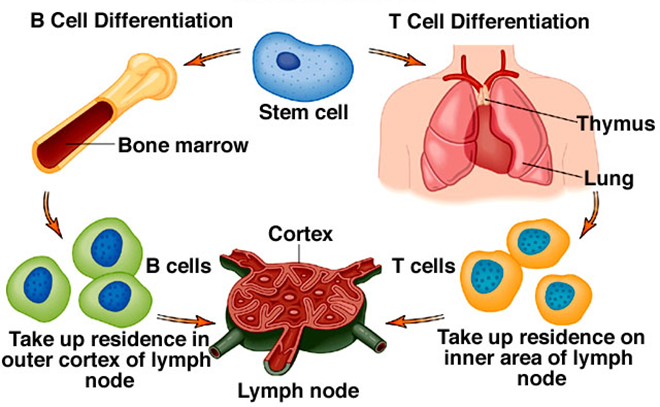
B CELL PRODUCTION
B cells are specialized type of lymphocytes that are responsible for the production of antibodies […]
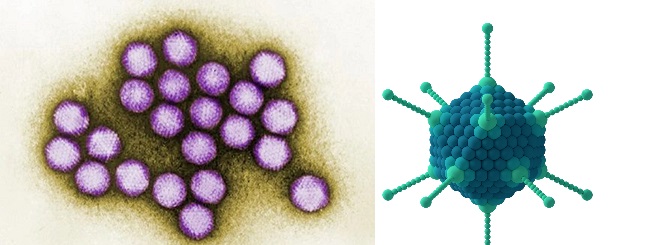
ADENOVIRIDAE FAMILY
Adenoviridae family is made up of two viral genera which are Mastadenoviridae (which contain viruses […]
HEPADNAVIRIDAE FAMILY
Hepadnaviridae family consists of two viral genera which are Orthohepadnavirus (which contain viruses that infect […]
CULTURE (GROWTH) MEDIA
The clinical diagnosis of some infectious diseases (including those caused by bacteria and fungi) in […]
Important techniques in microbiology laboratory
DIRECT PLATE COUNTING Direct plate counting is a microbiological technique used to evaluate the actual […]
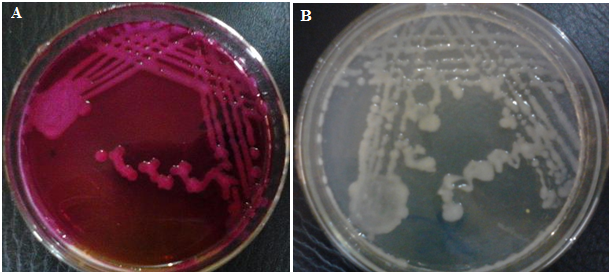
KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a Gram-negative, encapsulated, lactose-fermenting, non-motile, facultative rod in the genus Klebsiella and […]
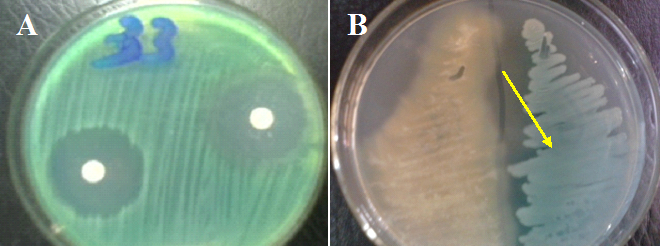
PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a non-enteric, oxidase positive, Gram-negative, motile; obligate aerobic straight or curved rod […]
Sterilization Techniques in Industrial Microbiology: Safeguarding Fermentation Integrity
Introduction Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) constitute a diverse and functionally significant group of Gram-positive, non-sporulating, […]
Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB): Key Microorganisms in Fermentation and Food Biotechnology
Introduction Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) constitute a diverse and functionally significant group of Gram-positive, non-sporulating, […]
Factors that affect microbial population in the soil
The population of microorganisms in the soil are affected or influenced by many factors […]
Importance of microbial population in the soil
The soil is that part of the earth crust or earth that supports plant life. […]
STANDARD QUALITY CONTROL STRAINS FOR ANTIBIOGRAM
Quality control strains (or reference strains)are typed cultures of microorganisms with known antimicrobial susceptibility patterns […]
PREPARATION OF 0.5 McFARLAND TURBIDITY STANDARDS
McFarland Turbidity Standard is an important technique performed in the microbiology laboratory especially when carrying […]
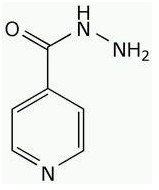
ISONIAZID – anti-tuberculosis (TB) drug
Isoniazid or isonicotinyl hydrazine (INH) is a first-line antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis […]
CHLORAMPHENICOL
Chloramphenicol is a protein synthesis inhibitor but the antibiotic unlike other drugs that interfere with […]
MECHANISMS OF TRANSFER OF RESISTANCE GENES IN BACTERIA
Below are some of the major ways through which bacteria pass on their antibiotic […]
GENETIC BASIS OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Genetic resistance of microbes to antibiotics is due to a chromosomal mutation in the bacterial […]
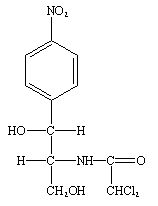
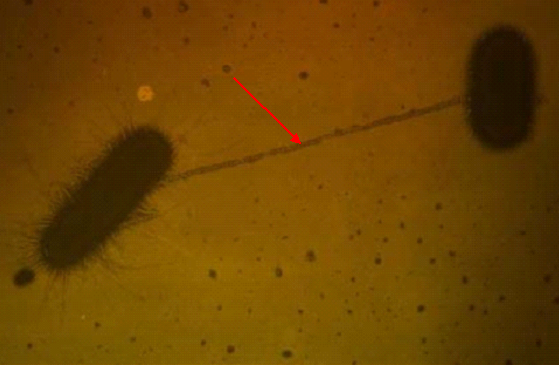
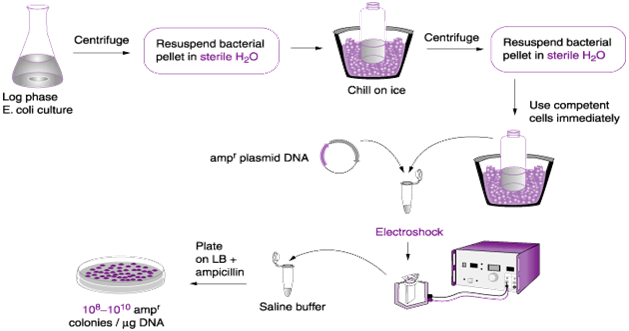
STEPS INVOLVED IN TRANSFORMING BACTERIAL CELLS
There are different types of steps involved in the transformation of a bacterial cell in […]
GENE CLONING
Cloning is a molecular biology technique which is used to make millions of copies of […]
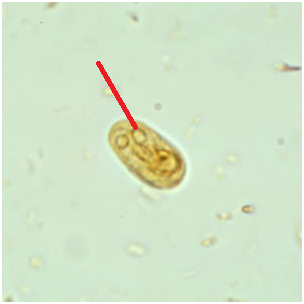
GIARDIASIS
Giardiasis is a water-borne protozoal diarrheal-disease that is cause by parasites in the genus Giardia. […]
LEISHMANIASIS
Leishmaniasis is the parasitic disease caused by the protozoal organism, Leishmania. The disease affects the […]
UNDERSTANDING MBL MICROBIOLOGY
Metallo-beta-lactamases (MBLs) are beta-lactamase enzymes produced by pathogenic bacteria, and which hydrolyzes the carbapenems (e.g. […]
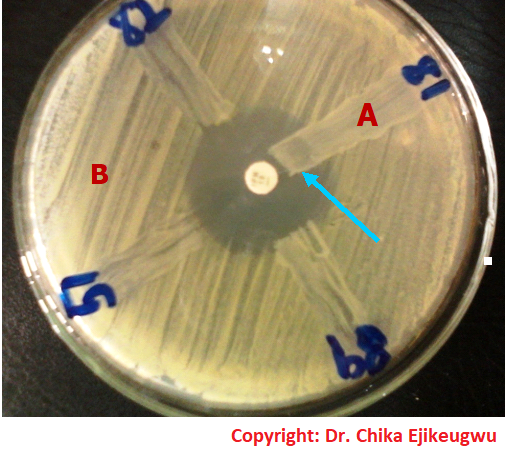
ESBL Positive – Understanding Extended spectrum beta-lactamases tests
What does it mean to be ESBL positive? Learn how to detect these antibiotic-resistant bacteria […]
The 3 Rs (Reduction, Refinement, Replacement): Guiding Principles in the Use of Animals For Biomedical/Scientific Research
The use of laboratory animals including mice, rats, rabbits and primates for scientific/biomedical research is […]
RATIONALE FOR THE CONTINUED USE OF ANIMALS FOR RESEARCH
Animals including (primates, dogs, cats, rabbits, mice) are still being used to conduct scientific/biomedical research […]
Issues Surrounding the Use of Animals in Scientific Research
Animals such as mice, rats, rabbits, monkeys and primates are used in biomedical research to […]
Advantages & disadvantages of cell culture techniques
ADVANTAGES OF CELL CULTURE TECHNIQUES DISADVANTAGES OF CELL CULTURE TECHNIQUES References Alberts B, Bray D, […]
SAFETY IN THE CELL CULTURE LABORATORY
Safety is paramount in any cell culture laboratory. It protects the researcher from possible contamination […]
APPLICATIONS OF CELL CULTURE TECHNIQUE
Cell culture technique is defined as the process by which prokaryotic, eukaryotic or plant cells […]
TERMINOLOGIES USED IN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Such drift or subtle changes in the antigenic surfaces of pathogens are a setback for […]
ANTIMICROBIAL PROPERTIES OF LICHEN SECONDARY METABOLITES
Lichens possess varying antimicrobial properties; and they have been shown to be active against a […]
MACROMOLECULES OF LIFE
Macromolecules are large biological molecules that are made up of repeating smaller biological units generally […]
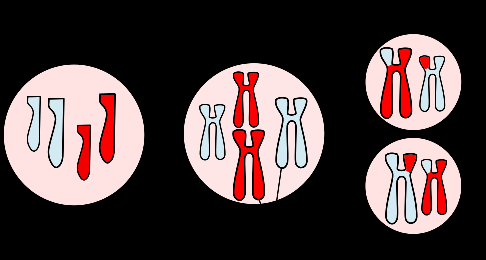
MEIOSIS
Meiosis unlike mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs during the formation of […]
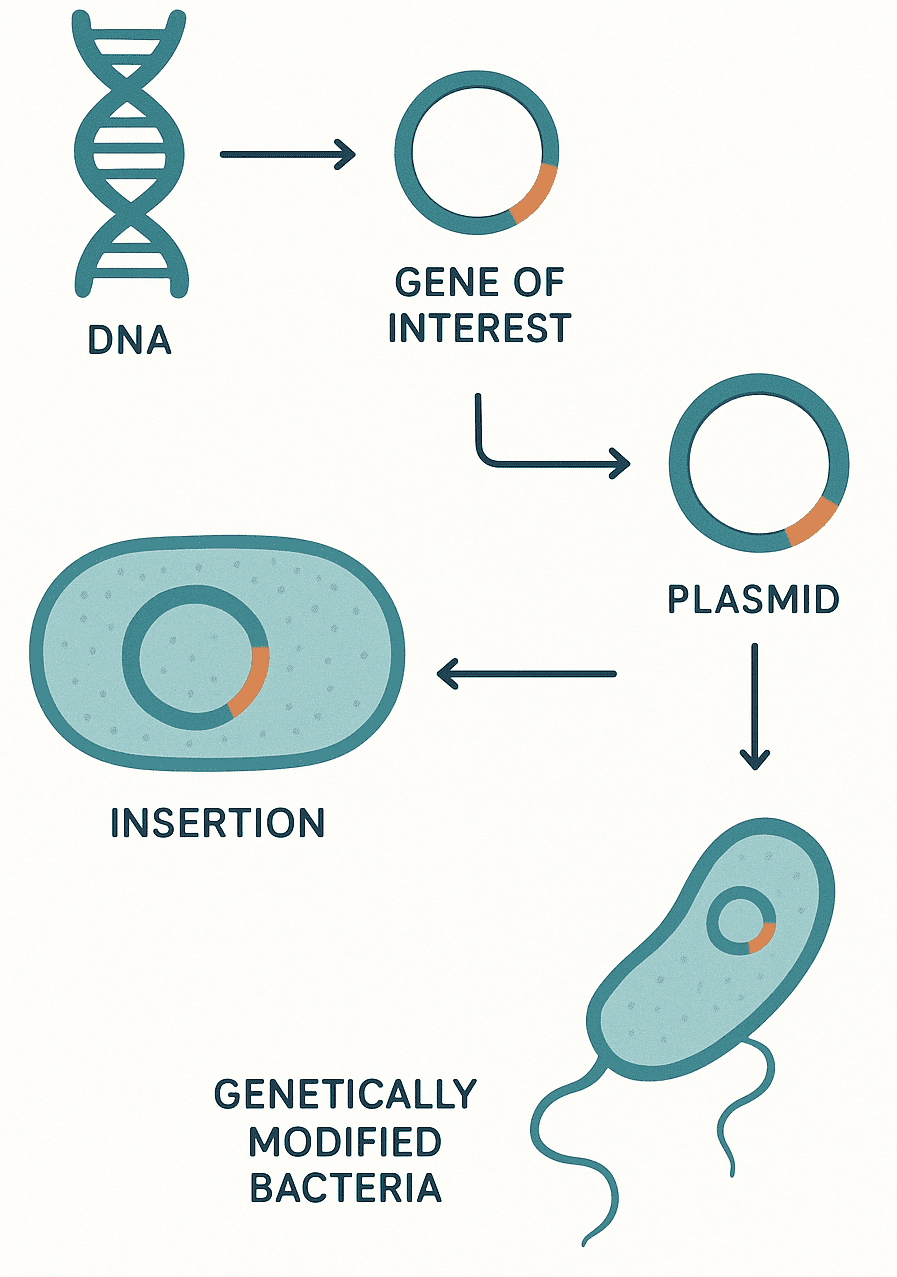
Application of genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
The field of medicine has in the past decades seen the production of many biotherapeutics […]
GENETICALLY MODIFIED ORGANISMS (GMOs)
Genetically modified organisms(GMOs) are living organisms including plants and microorganisms whose genetic material has been […]
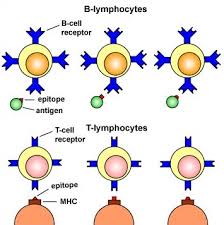
MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX (MHC) MOLECULES
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) moleculesalso known as human leukocyte antigens (HLA) complex are a large […]
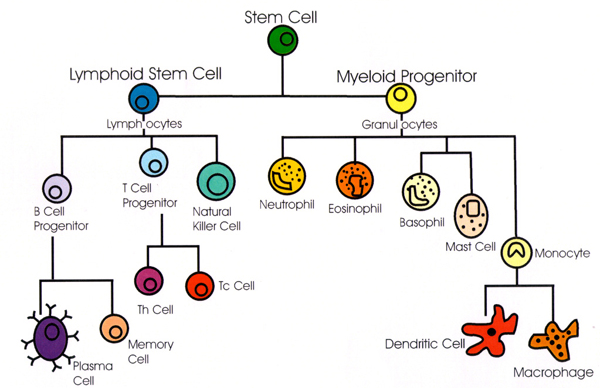
IMMUNE SYSTEM CELLS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
All the cells of the immune system inclusive of blood cells originate from the bone […]
POLYOMAVIRIDAE FAMILY
Polyomaviridae family contains DNA tumourviruses like the Papillomaviridae family. Polyomavirus is the only viral genera […]
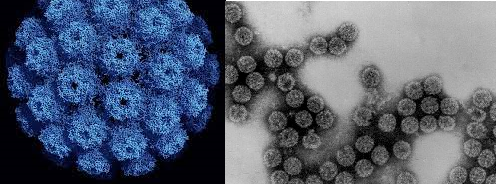
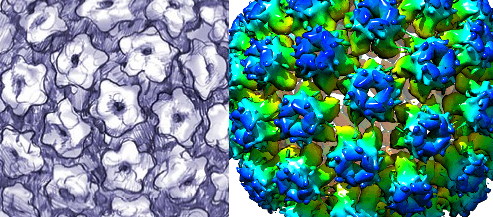
PAPILLOMAVIRIDAE FAMILY
Theviral family Papillomaviridae comprises of papillomaviruses (abbreviated as PVs); and they were previously classified together […]
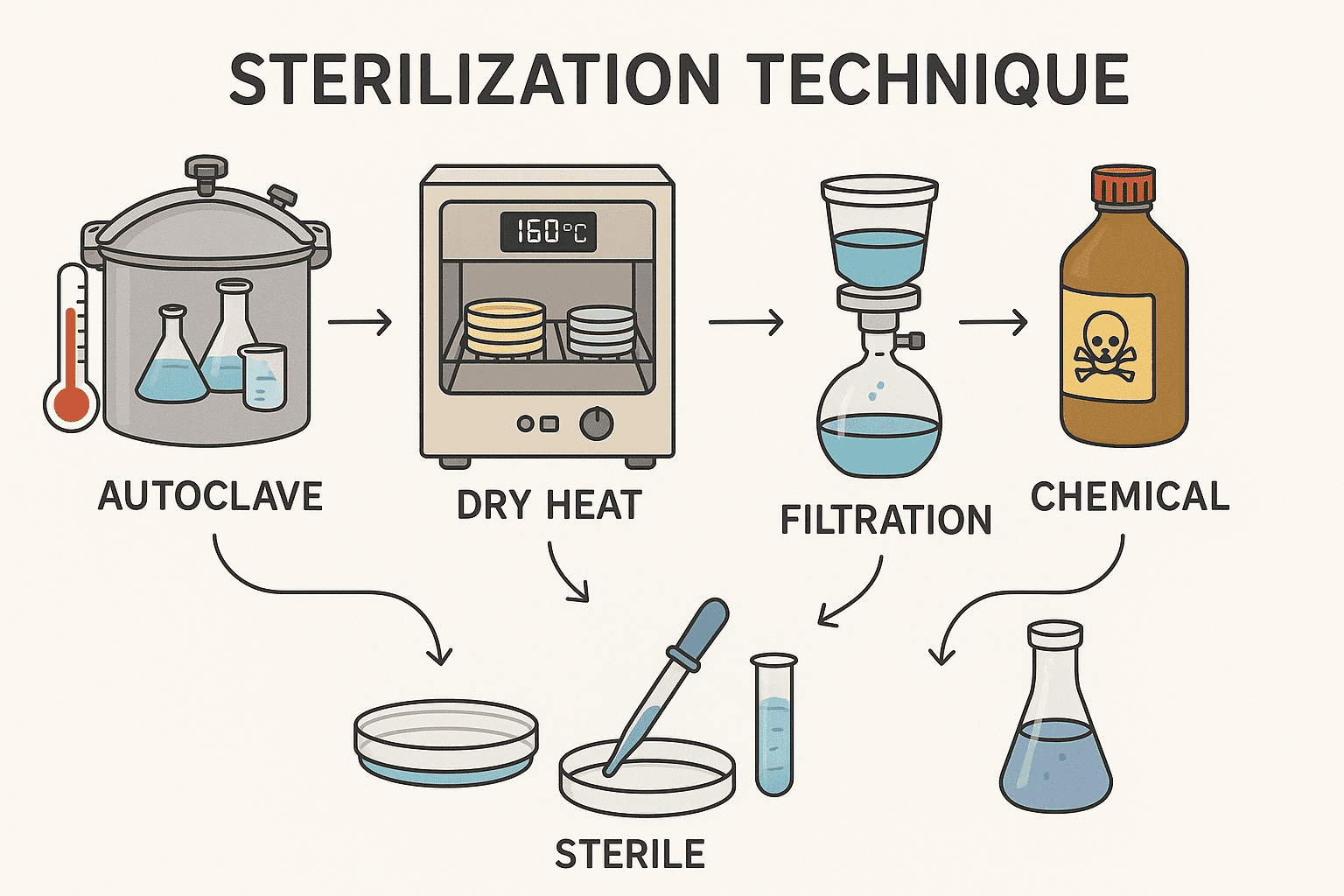
INCUBATION & STERILIZATION TECHNIQUE
Microorganisms are incubated in the incubator at different temperatures and time interval depending on the […]
CULTURING TECHNIQUE
Culturing technique is used for the propagation of microorganisms in the microbiology laboratory; and it […]
ESCHERICHIA COLI
Escherichia coli is a facultative, enteric, Gram-negative, motile/flagellated, and lactose-fermenting rod that occur in the […]