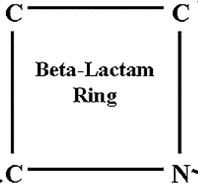
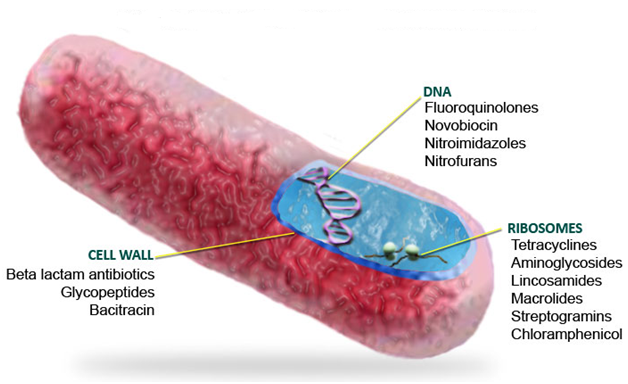
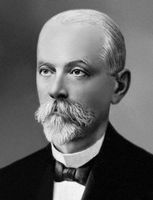Aside penicillins and cephalosporins, other beta-lactam antibiotics used for clinical applications also exist. These beta-lactam […]
MECHANISM OF ACTION OF ANTIBIOTICS: Antibacterial Agents
The antibiotics described above including those not described in this work are used to treat […]
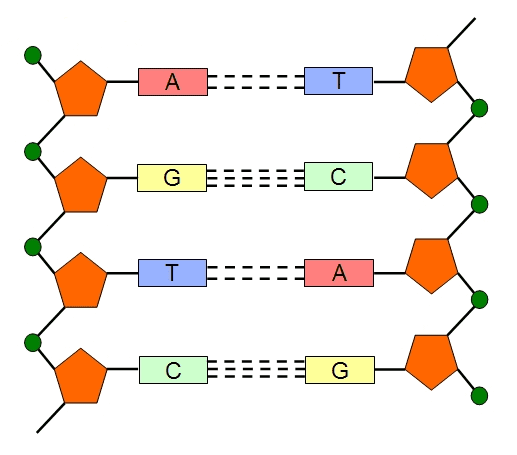
GENOMIC DNA
Genomic DNA is a double helix structure that is composed of several components including purines […]
REASONS FOR THE HIGH FREQUENCY OF PARASITES & PARASITIC DISEASES IN TROPICAL & SUBTROPICAL REGIONS
Parasitic diseases are usually common in rainforest parts of the world (the tropical and subtropical […]
PYROGEN TEST
A pyrogen is simply defined as a fever-causing (inducing) agent that includes toxins of microorganisms. […]
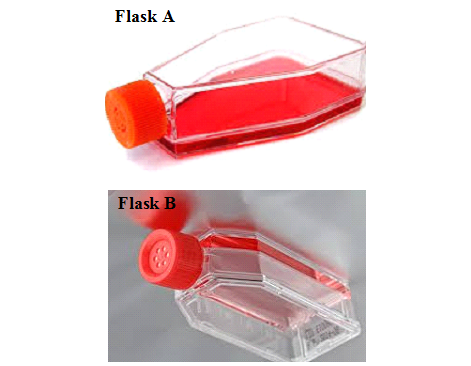
CELLS THAT CAN BE CULTURED IN VITRO USING CELL CULTURE TECHNIQUE
The living cells that are cultured may include: When a whole organ or intact organ […]
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES
An epidemiological study usually involves two important steps that must be put into consideration prior […]
MICROBIOTA OF DENTAL DISEASES: Dental Plaque, Dental Caries, Gingivitis, Periodontitis
The microbiota of dental diseases describes the microorganisms (inclusive of normal flora of the oral […]
PREPARATION OF BACTERIAL SMEAR & HEAT FIXING
Bacterial smear is defined as a dehydrated or dried preparation of a bacterial suspension (cells) […]
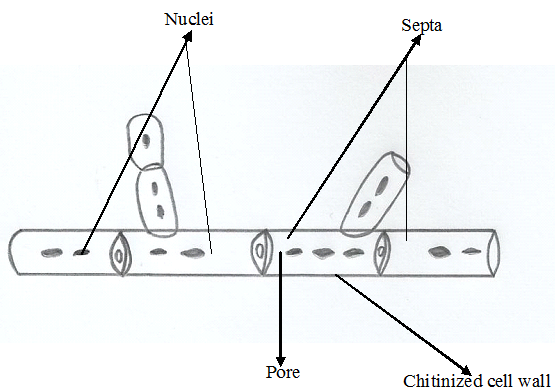
FUNGAL MORPHOLOGY
Fungi unlike other groups of microorganisms possess or have unique structures which distinguish them from […]
PARTS OF A CELL AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
The cells of all living organisms share several structural characteristics together. Some of the many […]
Microorganisms Used in Biotechnological Processes
Biotechnology, the application of biological systems or organisms to develop products and technologies for human […]
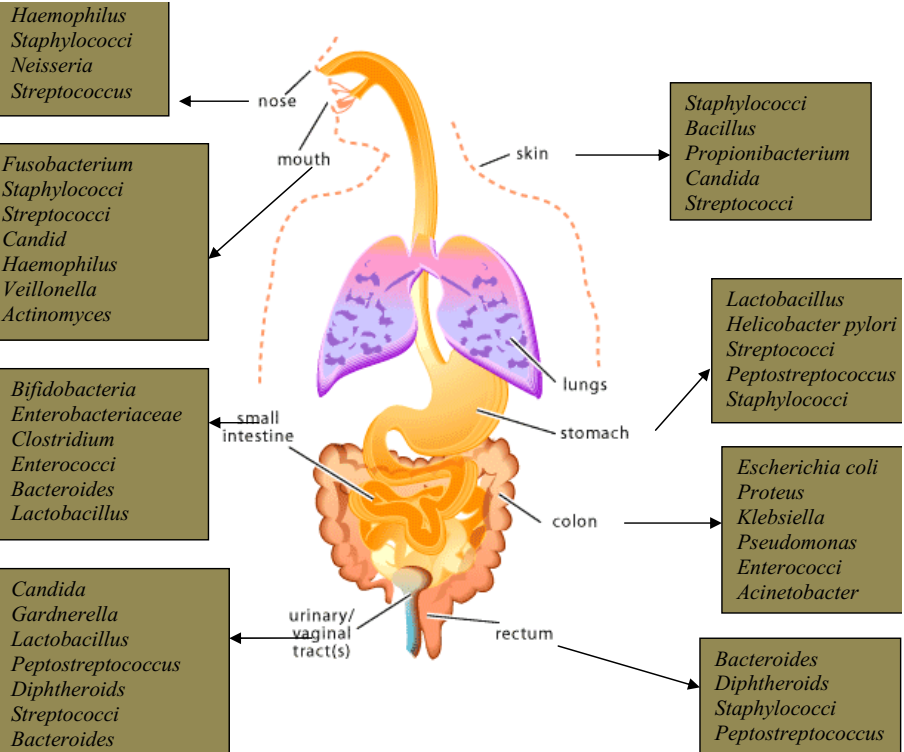
MICROBIOTA (NORMAL MICROFLORA) OF LIVING ORGANISMS
Microbiota which can also be called normal microflora is the totality of microorganisms that are […]
FOOD PRESERVATION
Food preservation is the technique used to prevent food spoilage. It encompass all the methods […]
PRECAUTIONARY MEASURES TO OBSERVE WHILE WORKING IN THE MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY
REFERENCES Atlas R.M (2010). Handbook of Microbiological Media. Fourth edition. American Society of Microbiology Press, […]
SCOPE OF MICROBIOLOGY
The field of Microbiology has tremendous possibilities and a very bright future, and intending or […]
HISTORY OF IMMUNOLOGY
Man’s interest in achieving some level of resistance to diseases and their causative agents (i.e. […]
HISTORY OF THE MICROSCOPE
Before the advent of microscopes and its actual application in viewing and making clear the […]
HISTORY OF VIROLOGY
The field of virology (inclusive of medical virology, plant virology and veterinary virology) blossomed following […]
STAINING TECHNIQUE
Staining is any microbiological process which increases the contrast of organisms when certain dyes or […]
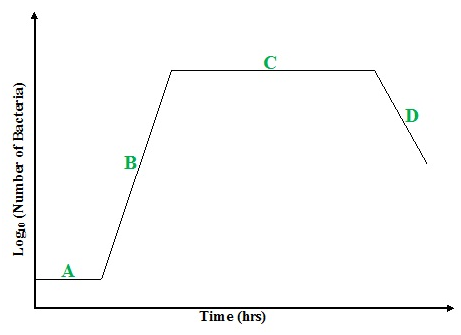
MICROBIAL GROWTH PHASE
Microbial growth is a fundamental biological process that governs the proliferation of microbial cells in […]
Overview of Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the study of the genetic makeup of organisms at the level of […]
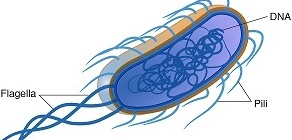
OVERVIEW OF BACTERIA
Bacteria (singular: Bacterium) is one of the two important members of the prokaryotes (i.e. cells […]
Characteristics of Microorganisms Used in Industrial Microbiology
Microorganisms—including bacteria (e.g. Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis), fungi (yeasts like Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris, […]
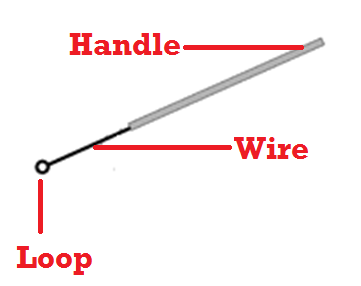
INOCULATING LOOP
Inoculating loop or wire loop is a general purpose piece of instrument that allows microbiologist […]
MICROBIOLOGY KEYWORDS A-Z GLOSSARY OF MICROBIOLOGY YOU NEED TO KNOW
Master these microbiology keywords, terms and definitions with this A-Z Glossary of Microbiology! In this […]
GERM THEORY OF DISEASE
Germ theory of disease is the theory that human infectious diseases are caused by specific […]
SPONTANEOUS GENERATION (ABIOGENESIS)
Spontaneous generation (abiogenesis) is the mistaken hypothesis that living organisms are capable of being generated […]
Milestones in Microbiology
Other landmarks and discoveries in the field of microbiology are summarized in Table 1. Table […]
JAMES WATSON
Born on the 6th of April, 1928, James Watson is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, […]
FRANCIS CRICK (1916-2004)
Francis Crick was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He co-discovered the molecular structure […]
FREDERICK GRIFFITH (1879-1941)
Frederick Griffith was a British bacteriologist who performed transformation experiments that suggested that DNA was […]
SERGEI WINOGRADSKY (1856-1953)
Sergei Winogradsky was a Ukrainian-Russian microbiologist, ecologist and soil scientist who was among the first […]
MARTINUS BEIJERINCK (1851-1931)
Martinus Beijerinck was a Dutch microbiologist and botanists who like Sergei Winogradsky began examining the […]
GERHARD DOMAGK (1895-1964)
Gerhard Domagk was a German pathologist and bacteriologist who reported in 1935 that prontosil (a […]
PAUL EHRLICH (1854-1915)
Systematic work on antimicrobial drugs was first initiated by the Germanphysician Paul Ehrlich. Ehrlich worked […]
DMITRI IWANOVSKI (1864-1920)
Dmitri Iwanovski was a Russian botanist, and one of the discoverer of filterable nature of […]
JOSEPH LISTER (1827-1912)
Joseph Lister, an English surgeon is the father of antiseptic surgery. He was aware of […]
IGNAZ SEMMELWEIS (1818-1865)
Ignaz Semmelweisis regarded as the father of infection control because of his discovery of the […]
ELIE METCHNIKOFF (1845-1916)
Elie Metchnikoff was a Russian biologist, zoologist and protozoologist who is best remembered for his […]
ABBE LAZZARO SPALLANZANI (1729-1799)
Lazzaro, an Italian naturalist criticized John Needham’s work on spontaneous generation. In 1769, he performed […]
GIROLAMO FRACASTORO (1478-1553)
While the issue of spontaneous generation lasted as at the time, some other scientist like […]
FRANCESCO REDI (1626-1697)
Francesco Redi, an Italian scientist was the first scientist to challenge the theory of spontaneous […]
NICOLAS APPERT (1749-1841)
Nicolas Appert, a French chef and a confectioner is the “father of canning”, and was […]
FERDINAND J. COHN (1828-1898)
Ferdinand Cohn, a German biologist was born in Breslau (now in Poland). Cohn was the […]
EDWARD JENNER (1749-1823)
Edward Jenner was the pioneer of the dreaded smallpox vaccination and also the father of […]
LOUIS PASTEUR (1822-1895)
Louis Pasteur, a French scientist was the first to report the role of microorganisms in […]
JOHN TYNDALL (1820-1883)
One of the traditional arguments against abiogenesis was the claim that the heat used to […]
ALEXANDER FLEMMING (1881-1955)
Alexander Flemming, a Scottish born physician who spent most of his time studying bacteria discovered […]
AVERY OSWALD (1877-1955)
Avery Oswald was a Canadian-born American physician and medical researcher who provided the molecular explanation […]