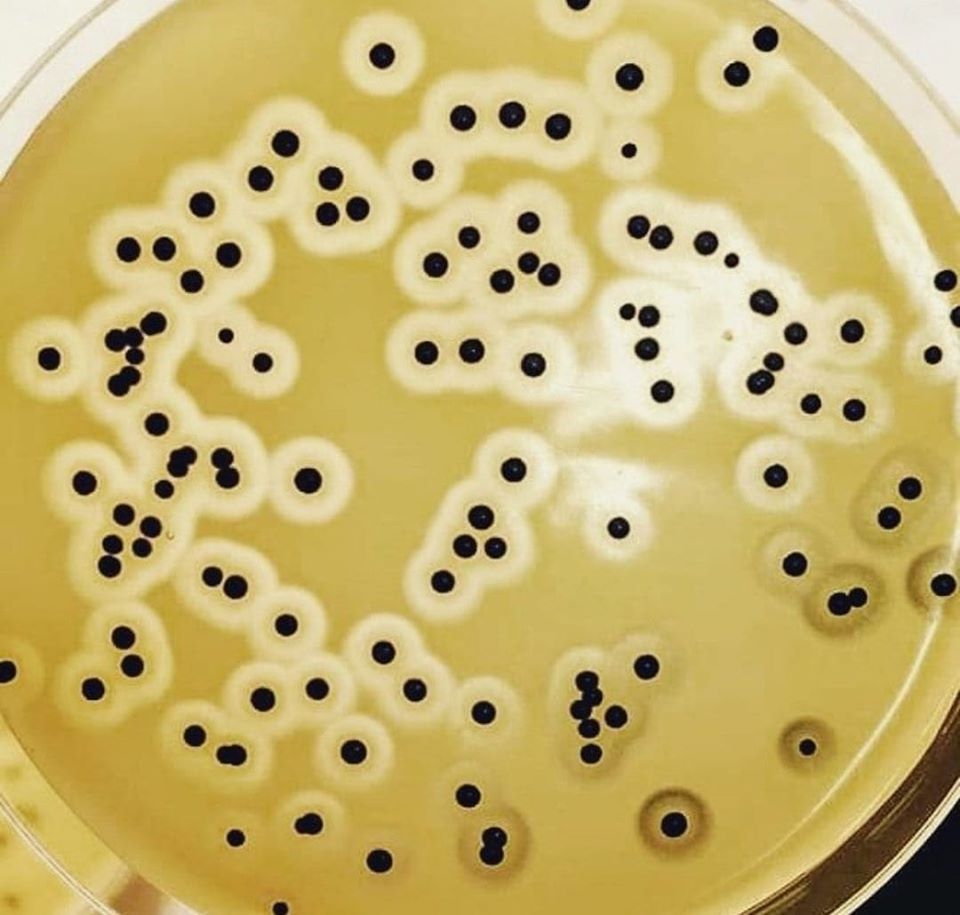
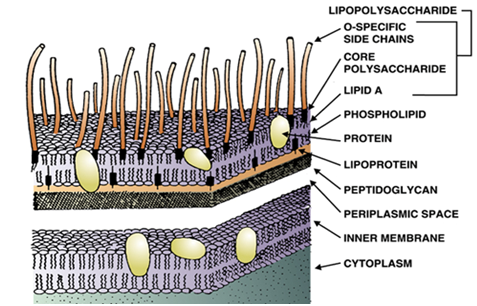
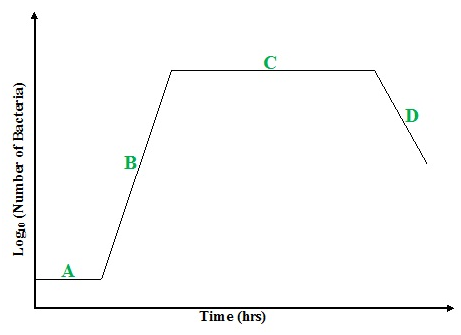
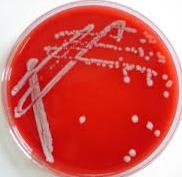
QUALITY CONTROL
Quality control (QC) is defined as a monitoring system that is used for detecting and correcting analytical errors by establishing performance limits. QC is a procedure or set of procedures intended to ensure that a manufactured product including pharmaceutical and medical products or performed services adheres to a defined set of quality criteria or meets […]