Air quality is defined as the degree to which the ambient air in a particular […]
Category: Pharmaceutical Microbiology
RULES OF GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE (GMP)
GMP encompasses the rules governing the manufacture of a safe and efficacious pharmaceutical product, drug […]
CRITICAL ASPECTS OF GMP (sources of microbial contamination)
Some of the main sources of contamination in the course of production in a food […]
PRINCIPLES OF GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE (GMP)
GMP guidelines are not prescriptive instructions on how to manufacture any product including food, drugs, […]
GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE (GMP)
Good manufacturing practice (GMP) is simply defined as those general rules that govern the manufacture […]
Quality Assurance: System Design and Implementation in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Clinical Laboratory Practice
Quality Assurance (QA) is a structured, systematic, and documented framework designed to ensure that products […]
Quality Control in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Principles, Microbial Testing, Practical Implementation & GMP Compliance
Introduction Quality control (QC) is a systematic monitoring and verification framework used to detect, measure, […]
Limulus Amoebocyte Lysate (LAL) Test
The LAL test is applied in the testing of pharmaceuticals, medical devices, water, food, and […]
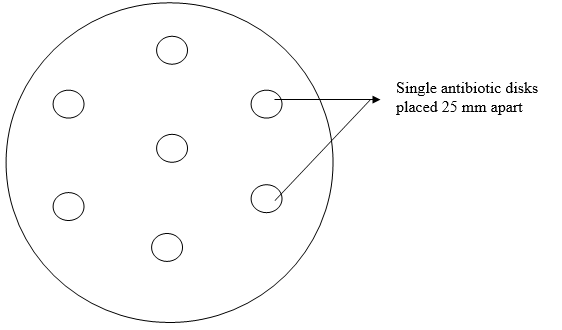
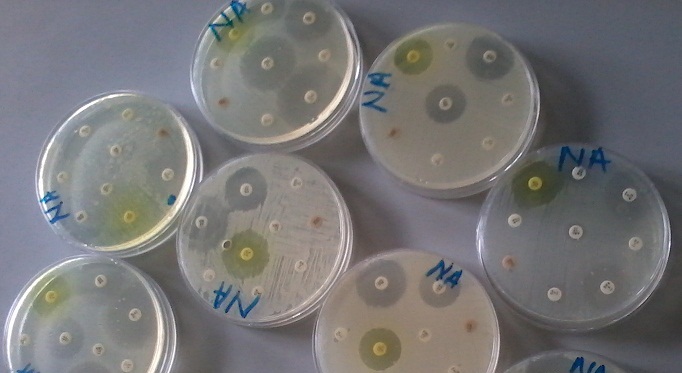
PHENOTYPIC DETECTION METHODS OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE (AMR) IN PATHOGENIC BACTERIA
The expression “phenotypic” is from the word phenotype, which means “the observable characteristics of an […]
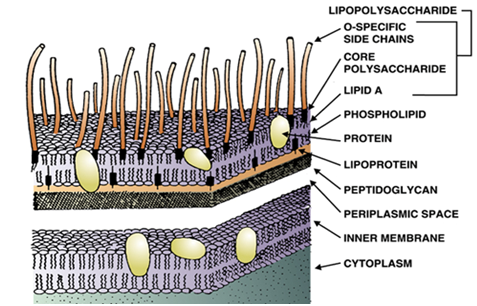
OTHER BETA-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS AND NON-BETA-LACTAMS THAT INTERFERE WITH CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Aside penicillins and cephalosporins, other beta-lactam antibiotics used for clinical applications also exist. These beta-lactam […]
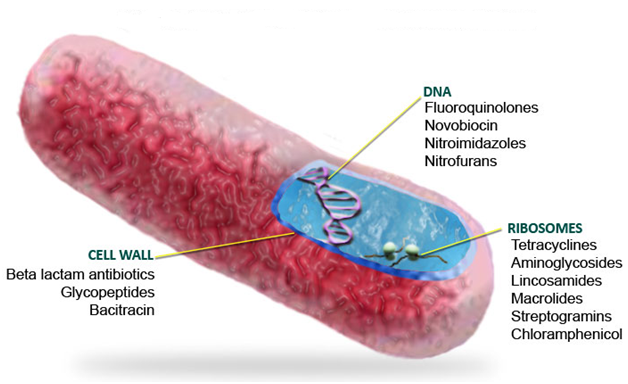
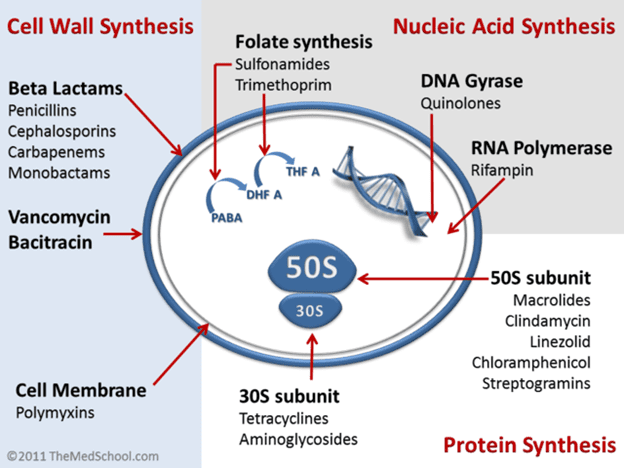
MECHANISM OF ACTION OF ANTIBIOTICS: Antibacterial Agents
The antibiotics described above including those not described in this work are used to treat […]
PYROGEN TEST
A pyrogen is simply defined as a fever-causing (inducing) agent that includes toxins of microorganisms. […]
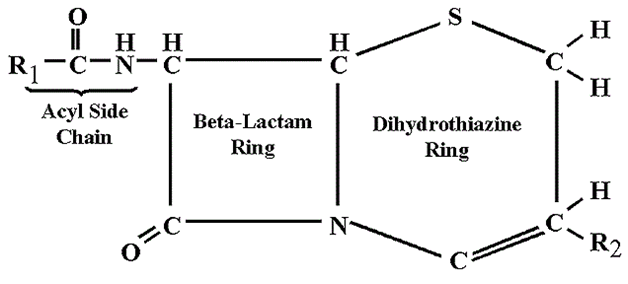
CEPHALOSPORINS
Cephalosporins are beta-lactam antibiotics that are penicillinase-resistant, and with related mode of action to the […]
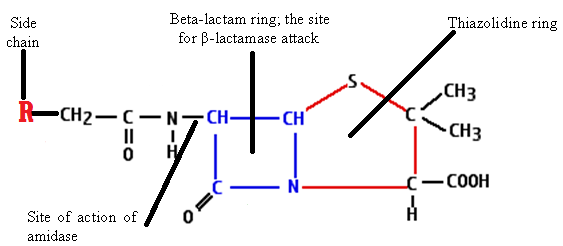
PENICILLINS
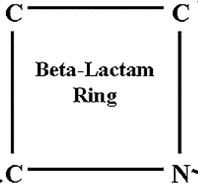
Penicillins are beta-lactam drugs that inhibit the cross-linking of N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG) and N-acetyl muramic […]
CLASSIFICATION OF ANTIBIOTICS BASED ON SPECTRUM AND MECHANISM OF ACTION
Antibiotics can also be classified into different categories depending on their mode of action and/or […]
ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS
Antibacterial agents are specifically chemical agents that kill or inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria. […]
SPECTRUM OF ACTIVITY OF ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS
The growth of pathogenic microorganisms is usually accompanied by the synthesis of new molecules including […]
Overview of antimicrobial agents (antibiotics)
Ever since their discovery some decadesago, antimicrobial agents particularly antibiotics have saved mankind from the […]
Chromogenic culture media for detecting antimicrobial resistance mechanisms
Chromatic Super CAZ/AVI Chromogenic medium for detecting Ceftazidime-avibactam resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Chromatic Super CAZ/AVI is […]
CLASSES OF ANTIBIOTICS
There are several classification/types of antibiotics today, which is based on bacterial spectrum of activity […]
SOURCES OF ANTIBIOTICS
Before the advent of conventional medicine used in clinical medicine today for the treatment of […]
BRIEF HISTORY OF ANTIBIOTICS
Antibiotic history dates back to 1928 when Sir Alexander Fleming discovered the antibacterial effects of […]
DEFINITION OF AN ANTIBIOTIC
There is no consensus to the definition of antibiotics. But it is very important that […]
Introduction to Antibiotic Resistance
In recent times, antibiotic resistance of pathogens to drugs (antibiotics) directed towards the degrading properties […]
STERILITY TESTS OF BIOLOGICAL PRODUCTS
The phrase sterility simply means the absence of living organisms including bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa […]
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Microbiology
Pharmaceutical microbiology is the branch of microbiology that focuses on all aspects of pharmacy especially […]
Exploring Careers in Microbiology: What Microbiologists Do and Where They Work!
A guide to discovering diverse career paths through the world of microbes—from healthcare to climate […]