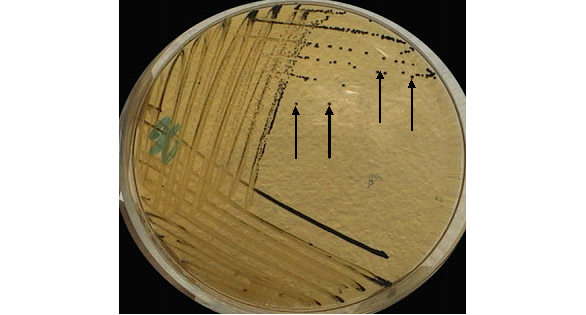
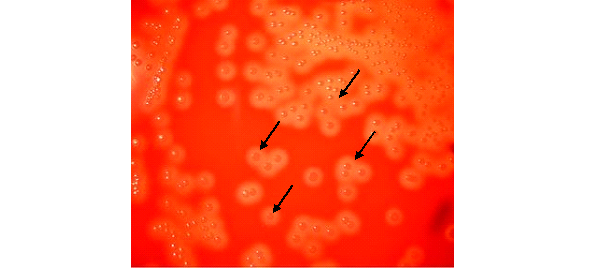
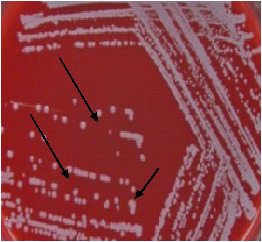
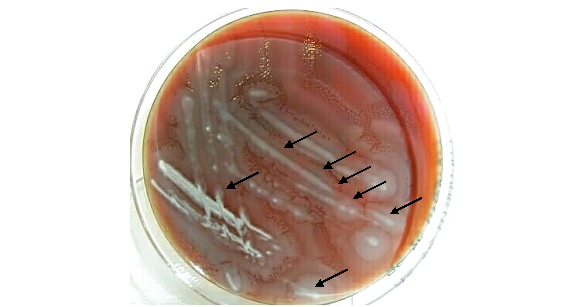
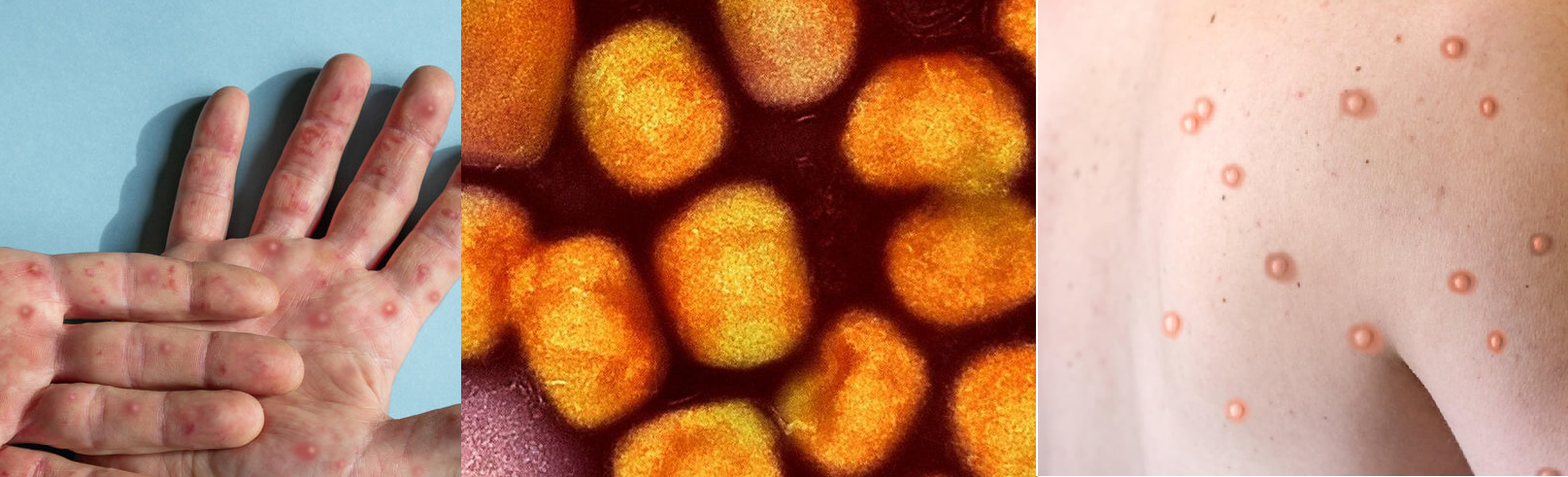
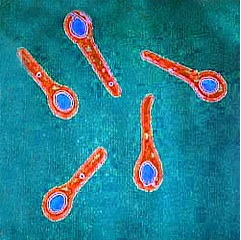
Shigella dysenteriae is a Gram-negative, non-motile bacterium causing bacillary dysentery. It’s transmitted primarily through the fecal-oral route, requiring a low dose to initiate infection. Symptoms include bloody diarrhea and abdominal cramps. Diagnosis involves stool cultures, and treatment may include antibiotics for severe cases. Prevention focuses on hygiene and clean water.
Author: DrChika
TREPONEMA PALLIDUM
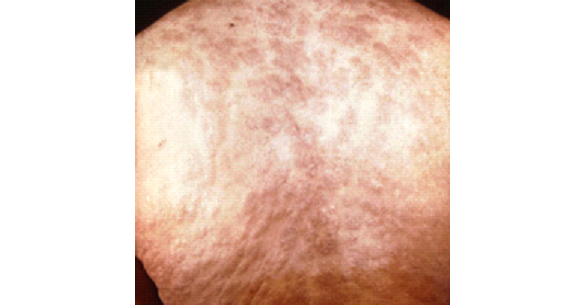
Treponema pallidum, a Gram-negative spirochaete, causes syphilis, a contagious STD spread through direct contact, including mother-to-child transmission. The disease progresses through primary, secondary, and tertiary stages without treatment, potentially causing severe complications. Laboratory diagnosis relies on serological tests, as the bacterium cannot be cultured in vitro. Prevention includes safe sexual practices and treating infected individuals.
Helicobacter pylori
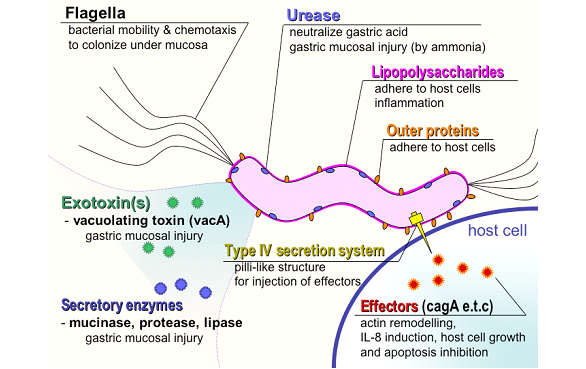
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium causing peptic and gastric ulcers, linked to stomach cancer. It survives stomach acidity by producing urease, creating an alkaline environment. Spread via fecal-oral route, it induces inflammation in the gastric mucosa. Diagnosis involves invasive and non-invasive tests, treatment includes antibiotics and protein-pump inhibitors. Prevention focuses on hygiene.
SALMONELLA (S. TYPHI)
Salmonella Typhi, a Gram-negative rod, causes typhoid fever in humans, transmitted through contaminated food and water. Non-typhoid strains, like S. Typhimurium, cause gastrointestinal infections. Infections primarily spread via the fecal-oral route, and effective prevention includes good hygiene, proper food handling, and clean water. Treatment involves antibiotics and hydration.
RICKETTSIA PROWAZEKII
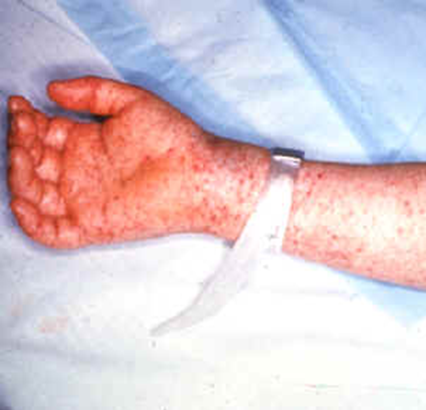
Rickettsia prowazekii is an obligate intracellular parasite causing epidemic typhus, primarily transmitted via lice bites. Symptoms include vasculitis, thrombosis, and systemic infections. Diagnosis involves serological tests and cell culture. Treatment includes chloramphenicol and tetracyclines; prevention focuses on vector control and hygiene. RMSF and Q fever are related rickettsial diseases.
STREPTOCOCCUS PYOGENES
Streptococcus pyogenes, a Group A Streptococcus, is a Gram-positive bacterium causing pharyngitis and various streptococcal diseases like scarlet fever, cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis. It produces numerous virulence factors including streptolysins and exotoxins. Diagnosis involves cultural, microscopic, and serological tests. Treatment includes antibiotics like penicillin, and no vaccines exist currently.
STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
Staphylococcus aureus, a Gram-positive bacterium, is often found in the nose and skin of humans. It causes various infections including pneumonia, gastroenteritis, and toxic shock syndrome, aided by its production of toxins and enzymes. Resistant strains like MRSA are prevalent. Prevention relies on hygiene practices, as vaccines are unavailable.
PROTEUS MIRABILIS
Proteus mirabilis is a Gram-negative, motile, non-capsulated, facultative anaerobic, non-lactose fermenting and pleomorphic bacillus in […]
Beyond the Bench: Expanding Your Skill Set for a Successful Postdoc
If you’ve reached postdoc level as a life scientist, you’ll almost certainly have a wide […]
Features of probiotics & reported modes of action of probiotics
Microorganisms must meet stringent criteria to be used as probiotics, including being non-pathogenic, non-toxic, and able to survive stomach acid and pancreatic secretions. Probiotics confer health benefits such as enhancing the immune system, producing vitamins, preventing GI infections, and aiding in lactose digestion, potentially treating conditions like IBS and eczema.
Risk group classification of microorganisms
The great majority of microorganisms are beneficial to man, plants, animals and the environment. These […]
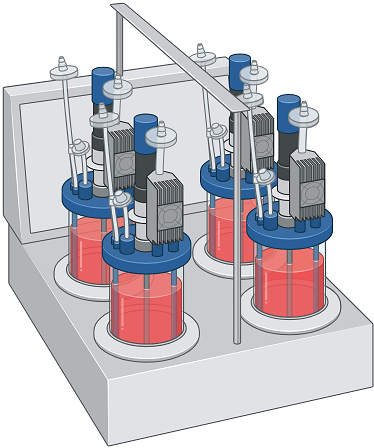
Design and Operation of Fermenters: Engineering Optimal Environments for Microbial Cultivation and Industrial Bioproduction
Introduction Fermentation stands as a fundamental and versatile process across multiple scientific and industrial disciplines, […]
Hand Washing: when and how to wash your hands
Hand washing is one of the best ways to protect yourself and your family from […]
HEALTHY HABITS TO HELP PREVENT FLU
Preventing Flu at Work and School At School At Work Source: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/actions-prevent-flu.htm
Monkeypox (Mpox) infection
Mpox, caused by the monkeypox virus, is a viral infection with symptoms like rash, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. Transmitted through contact with infected individuals, animals, or materials, it can be severe, especially for immunocompromised individuals. Preventive measures include vaccination and avoiding physical contact. Diagnosis involves PCR testing, and treatment includes supportive care.
CLOSTRIDIUM TETANI
CLOSTRIDIUM TETANI Clostridium tetani is a Gram-positive, motile, anaerobic, spore-forming, rod-shaped bacterium found in the […]
Approaches to Microbial Strain Improvement for Industrial Applications
Introduction Microbial strain improvement is a critical process in industrial microbiology and biotechnology, aimed at […]
GARDNERELLA VAGINALIS
GARDNERELLA VAGINALIS Gardnerella vaginalis in association with other bacteria is the causative agent of bacterial […]
Inoculum Development and Preparation for Industrial Fermentation
Introduction Inoculum preparation is a foundational step in the fermentation process and plays a pivotal […]
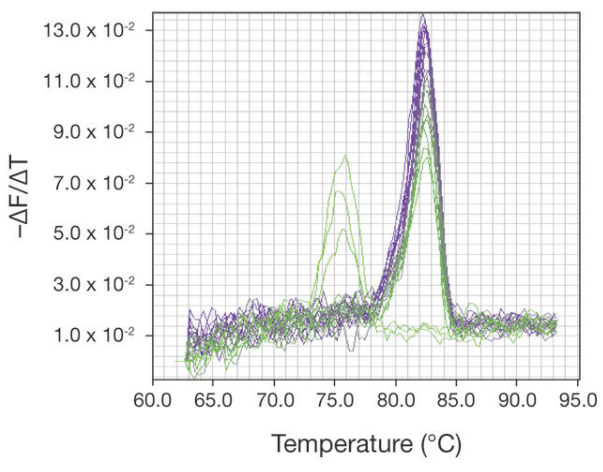
Melting curve analysis in Real-time PCR
Melting curve analysis and detection systems Melting curve analysis can only be performed with realtime […]
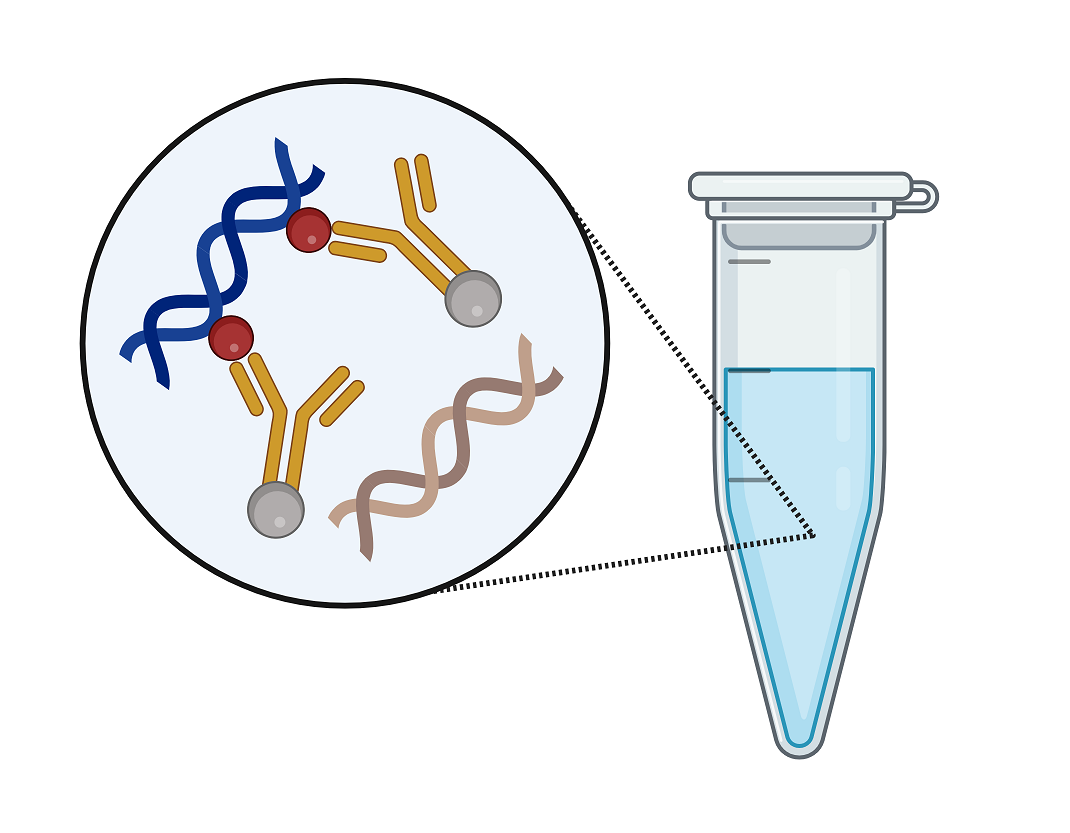
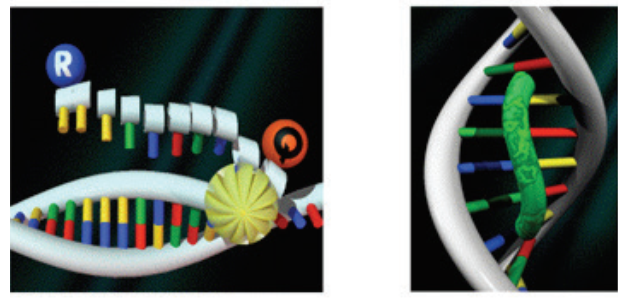
Real-time PCR probes
TaqMan® probe signal production Whether an MGB or non-MGB probe is chosen, both follow the […]
Sample template on how to write your research achievements and results when applying for a fellowship or grant
Sample of my research statement and results below: My Research Goal My research focused on […]
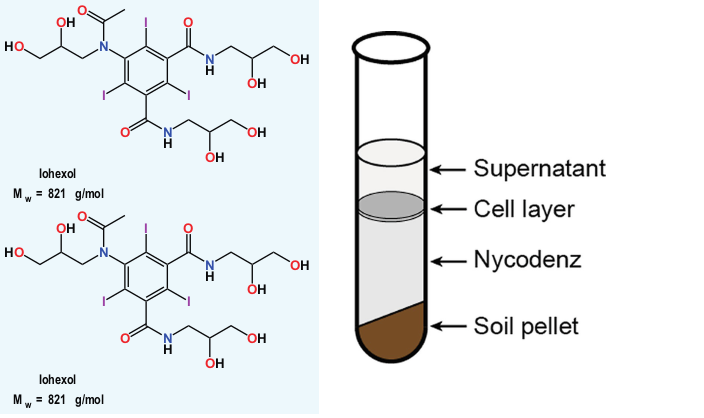
Nycodenz: application and properties
What is Nycodenz Nycodenz is a non-ionic, triiodinated radiopaque substance used primarily in molecular biology […]
Luria Broth (LB) and Luria Agar (LA) Media
Luria-Bertani (LB) broth is the most widely used medium for the growth of bacteria. It […]
Real-time PCR fluorescence detection systems
Real-time PCR fluorescence detection systems Real-time fluorescent PCR chemistries Many real-time fluorescent PCR chemistries exist, […]
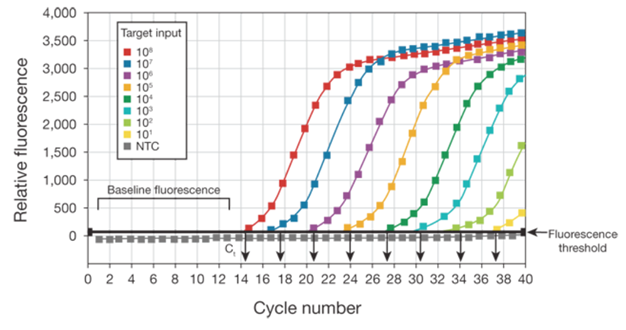
Real-time PCR analysis technology
BaselineThe baseline of the real-time PCR reaction refers to the signal level during the initial […]
Real-time PCR primer design
Good primer design is one of the most important parameters in real-time PCR. This is […]
OPPORTUNISTIC MYCOSES
Opportunistic mycoses are fungal infections caused by opportunistic fungi that only affect people with weakened […]
RESEARCH PROPOSAL TIPS FOR GRANTS & PROJECTS
What is a research proposal? A research proposal is simply defined as a planned and […]
REAL-TIME PCR COMPONENTS
DNA polymerasePCR performance is often related to the thermostable DNA polymerase, so enzyme selection is […]
STEPS INVOLVED IN PERFORMING REAL-TIME PCR
Real-time PCR is a variation of the standard PCR technique that is commonly used to […]
INTRODUCTION TO REAL TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (RT PCR)
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is one of the most powerful technologies in molecular biology. […]
Practical Tips for Resolving Conflict as a Scientist, Research Leader, Scholar
Conflict Resolution: Practical Tips for STEM Leaders These tips presented here was adapted from the […]
Clinical and pharmacological significance of synergism, antagonism and additive effects of drugs or pharmacological compounds
The terms synergistic effect (synergism), antagonistic effect (antagonism) and additive effect are all clinical and […]
HOW TO DESIGN PRIMERS FOR YOUR PCR EXPERIMENT
Primers are short stretches of DNA that target unique sequences of a DNA molecule and […]
Epidemiology, control, prevention, and public health concern of biowarfare
Chemical agents and biological agents are very exceptional from other conventional warfare tools including nuclear/atomic […]
Mode of delivery/transmission of biological and chemical agents
Biological agents used for bioterrorism can be delivered or trasmissted in human or animal population […]
Other categories of hazardous chemicals used as agents of mass destruction
Other categories of hazardous chemicals used as agents of chemical warfare according to the Center […]
Category C Biological Agents
Category “C” Biological Agents are the third highest priority biological agents that present no […]
Category B Biological Agents
Category “B” Biological Agentsare the second highest priority biological agents that have lesser public alertness […]
Access to scholarship and funding opportunities for conferences, study (B.Sc., M.Sc., Ph.D.), postdoctoral fellowships and research grants
As an academic, researcher or student, attending conferences or doing research can be a herculean […]
Category A Biological Agents
Category “A” Biological Agents are high-priority agents which pose the greatest security and health […]
MICROORGANISMS USED AS BIOLOGICAL WEAPONS
Agents of bioterrorism are usually found in the hands of terrorists, scientists, and most of […]
BIOTERRORISM – Brief History
Bioterrorism is an archaic and primitive practice of warfare that predates the development of the […]
BIOTERRORISM – Definition & Attributes of Biological Agents used for Biowarfare
Bioterrorism is simply defined as the unauthorized, threatened, and deliberate use of microbes (including bacteria, […]
ZOONOTIC INFECTIONS
The phrase ‘Zoonosis’ is a Greek word that comes from zoon (which means animal) and […]
FDA Approves First Gene Therapies to Treat Patients with Sickle Cell Disease
Today, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved two milestone treatments, Casgevy and Lyfgenia, representing […]
MEASUREMENT OF DISEASE OCCURRENCE IN A POPULATION
Statistically, the measures and/or determination of disease occurrence in a given population are usually expressed […]
SOURCES OF INFORMATION FOR EPIDEMIOLOGICAL DATA
In describing the health status of any population, useful data (in terms of health-related issues) […]
HOW TO CREATE YOUR EUROPASS CV AND EUROPASS COVER LETTER FOR EU APPLICATIONS (JOBS, RESEARCH, EDUCATION)
When applying for a scholarship for further studies abroad (in this case the European Union […]