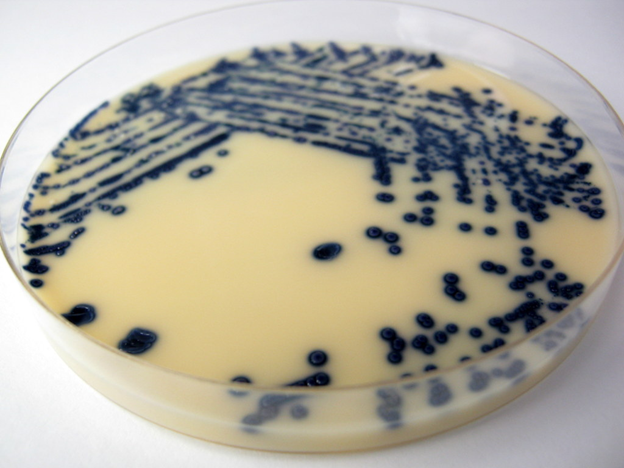
Desoxycholate Citrate Agar (DCA)
Desoxycholate Citrate Agar (DCA) is a selective medium for the isolation of Salmonella and Shigella organisms. It is ideal for the investigation of pathogenic Enterobacteria. The Gram-positive organisms are totally inhibited by the sodium citrate and sodium desoxycholate in the medium. Proteus and coliforms are also highly inhibited. Salmonella typhi, S. paratyphi and Shigella species […]
Desoxycholate Citrate Agar (DCA) Read More »
Culture media