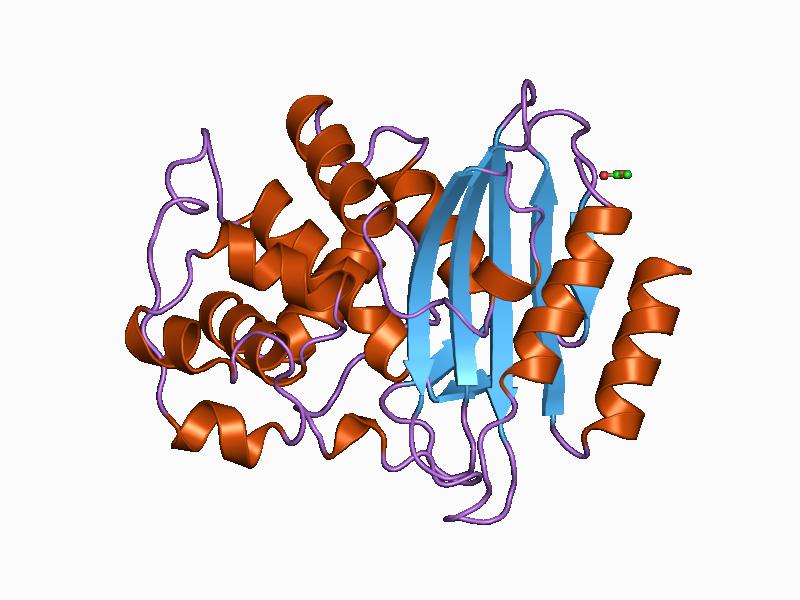
BETA-LACTAMASE: an important resistance mechanism in bacteria
Beta-lactamases are enzymes secreted by both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria, and which have the ability to hydrolyze (breakdown) beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactamases are responsible for bacterial resistance to broad class of-beta-lactam antibiotics, including the penicillins, cephalosporins and carbapenems. They provide antibiotic resistance in pathogenic bacteria by breaking the antibiotic structure, thereby leaving a molecule […]
BETA-LACTAMASE: an important resistance mechanism in bacteria Read More »
Antibiotic Resistance / Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR), Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST) & Antibiogram, Pharmaceutical Microbiology