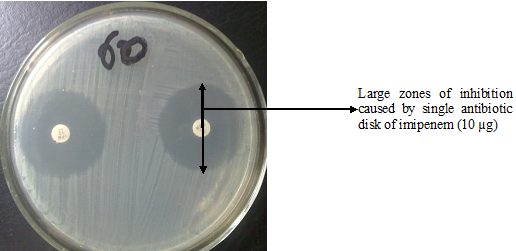
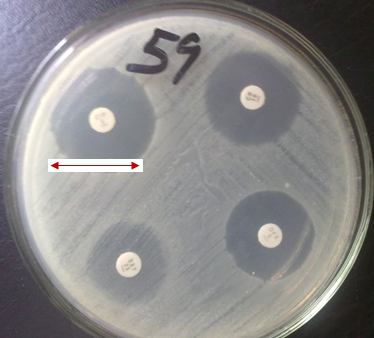
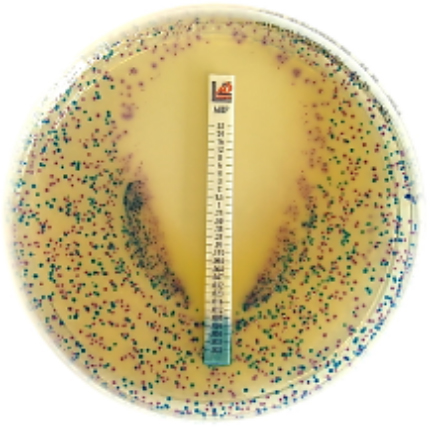
TYPES OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
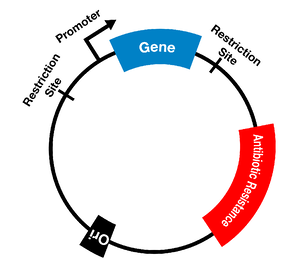
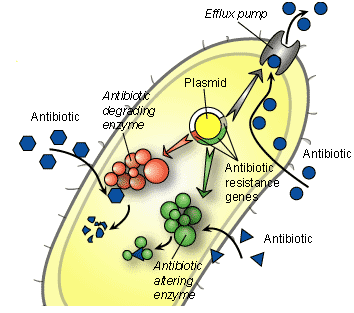
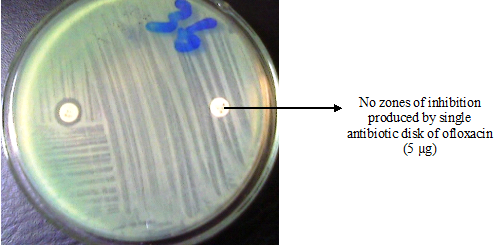
Bacteria have evolved to survive in diverse environments. They survive exposure to harsh chemicals including antibiotics, and they also survive difficult growth conditions. They have learned to “detoxify” harmful substances e.g. antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance can either be intrinsic or acquired. INTRINSIC (INNATE) RESISTANCE Some bacteria are said to possess innate/intrinsic resistance against antibacterial action put […]
TYPES OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE Read More »
Antibiotic Resistance / Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR), Antimicrobial Agents & Antibiotics, Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST) & Antibiogram, Pharmaceutical Microbiology