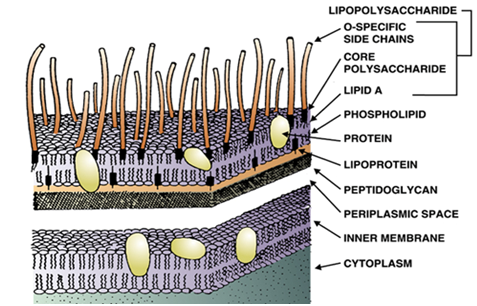
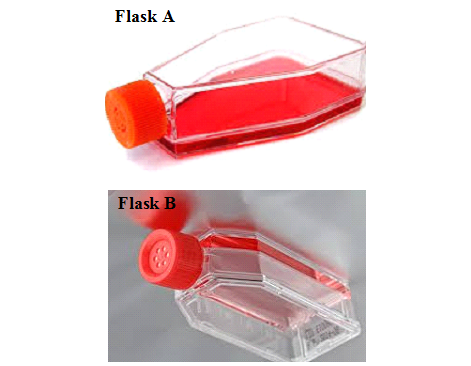
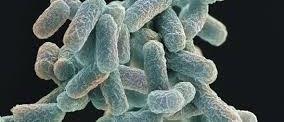
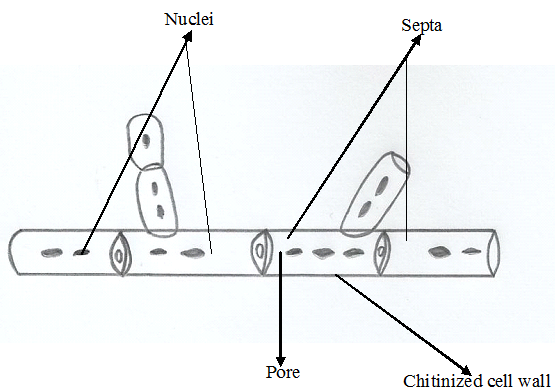
GENOMIC DNA
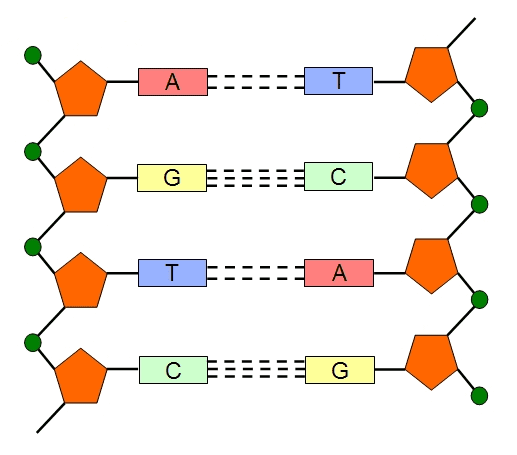
Genomic DNA is a double helix structure that is composed of several components including purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) as nitrogenous bases, deoxyribose sugar (a pentose sugar) and phosphate groups. It is a large nucleic acid molecule composed mainly of two polynucleotide chains or strands that are coiled in a complementary […]