SPECIFIC FUNCTIONS OF LICHEN ACIDS (SECONDARY METABOLITES)
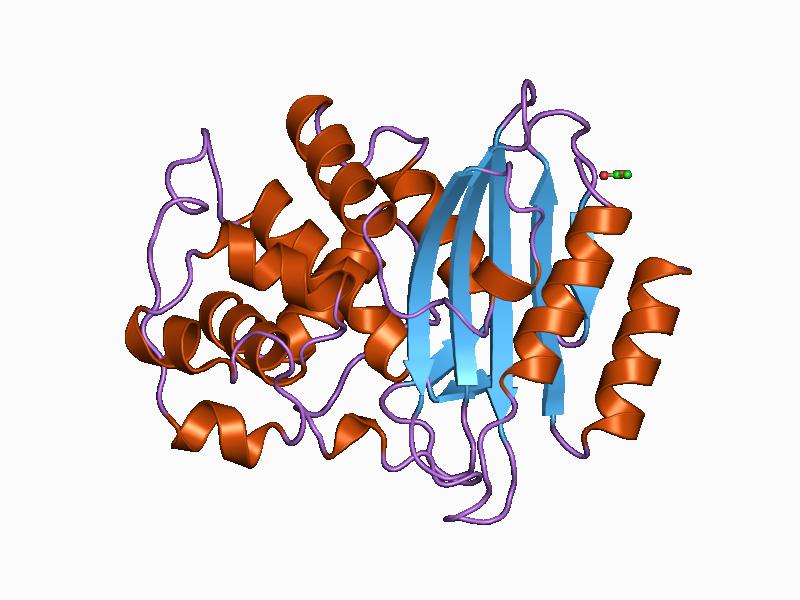
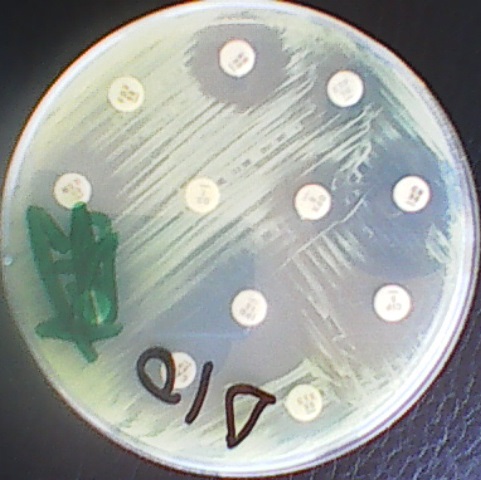
Lichens produce two types of metabolites: primary metabolites (e.g. carbohydrates and amino acids) and secondary metabolites (e.g. alkaloids and lichen acids). Primary metabolites (which are intracellularly secreted) are critical to the survival of the lichens while secondary metabolites are rarely involved in the metabolism or growth of the lichenized fungi. Secondary metabolites of lichens are […]
SPECIFIC FUNCTIONS OF LICHEN ACIDS (SECONDARY METABOLITES) Read More »
Mycology