ESCHERICHIA COLI
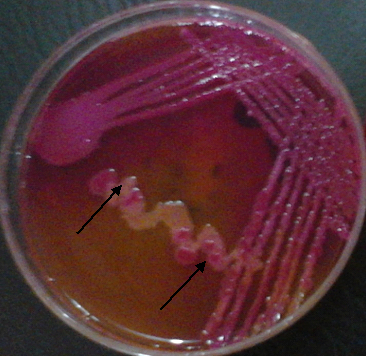
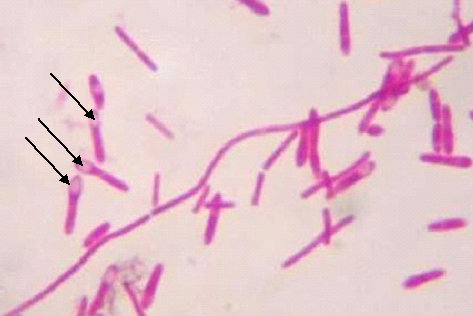
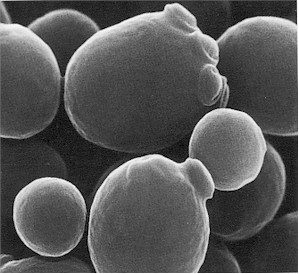
Escherichia coli is a facultative, enteric, Gram-negative, motile/flagellated, and lactose-fermenting rod that occur in the genus Escherichia and family Enterobacteria or Enterobacteriaceae. Enterobacteriaceae are bacteria that naturally exist in the intestinal tract of animals and humans, and also found in water and soil. Because the natural habitat of E. coli is the intestinal tract of […]