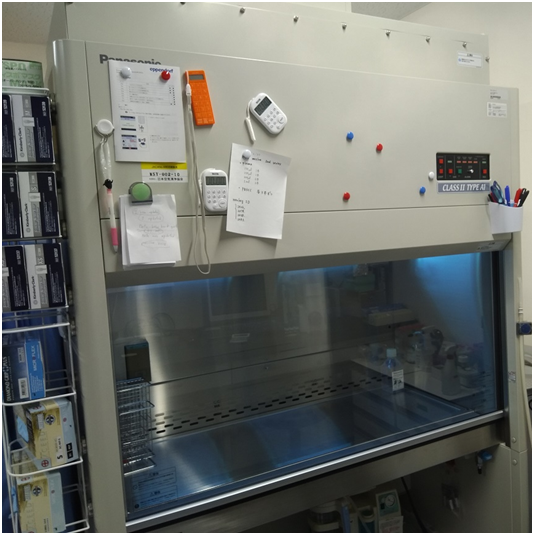
Biosafety laminar flow cabinet or hood is used to maintain a clean environment when performing microbiological investigations. The hood also protects the worker or scientist from a direct contamination with the organisms or materials they are working with.
It provides the perfect environment for the handling of pathogenic microorganisms or infectious specimens; and the hood excludes all forms of contamination during experimentation in the laboratory.
Biosafety laminar flow cabinet or hood (Figure 1) is an immovable piece of equipment, and fragile laboratory equipment, and thus it should be sited in places within the laboratory where they will not be moved from one point to another.
The hood provides a secure environment for conducting experiment and for the manipulation of microorganisms (especially pathogenic microbes). Working in the hood minimizes infection of the researcher and the escape of pathogens to the environment and/or laboratory room.
MAINTENANCE/CARE OF THE HOOD
- Users of the hood should always read the owner’s manual before usage.
- The hood should be properly cleaned and disinfected after use.
- The UV light in the hood should only be put on when no work is being performed in the biosafety laminar flow cabinet.
- Microbiologists working in the biosafety laminar flow cabinet must always ensure that the glass covering in the hood is kept at the recommended levels during experimentation.
- The hood should be properly covered after experimentation.

REFERENCES
Cheesbrough, M (2006). District Laboratory Practice in Tropical countries Part I Cambridge
Chung K.T, Stevens Jr., S.E and Ferris D.H (1995). A chronology of events and pioneers of microbiology. SIM News, 45(1):3–13.
Dictionary of Microbiology and Molecular Biology, 3rd Edition. Paul Singleton and Diana Sainsbury. 2006, John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Canada.
Goldman E and Green L.H (2008). Practical Handbook of Microbiology, Second Edition. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, USA.
Madigan M.T., Martinko J.M., Dunlap P.V and Clark D.P (2009). Brock Biology of microorganisms. 12th edition. Pearson Benjamin Cummings Publishers. USA.
Nester E.W, Anderson D.G, Roberts C.E and Nester M.T (2009). Microbiology: A Human Perspective. Sixth edition. McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc, New York, USA.
Prescott L.M., Harley J.P and Klein D.A (2005). Microbiology. 6th ed. McGraw Hill Publishers, USA.
Willey J.M, Sherwood L.M and Woolverton C.J (2008). Harley and Klein’s Microbiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Higher Education, USA.
Discover more from #1 Microbiology Resource Hub
Subscribe to get the latest posts to your email.