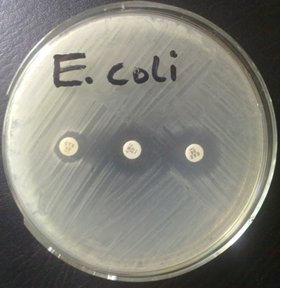
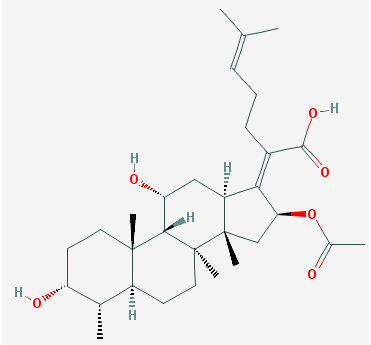
HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP)
Hazard analysis critical control point (HACCP) is an internationally recognized food safety system that is employed in the production line of food and food products in food processing industries to ensure food safety, food hygiene and good food quality. It is a quality assurance technique or system that is used especially in food processing and […]
HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) Read More »
Pharmaceutical Microbiology, Food Microbiology