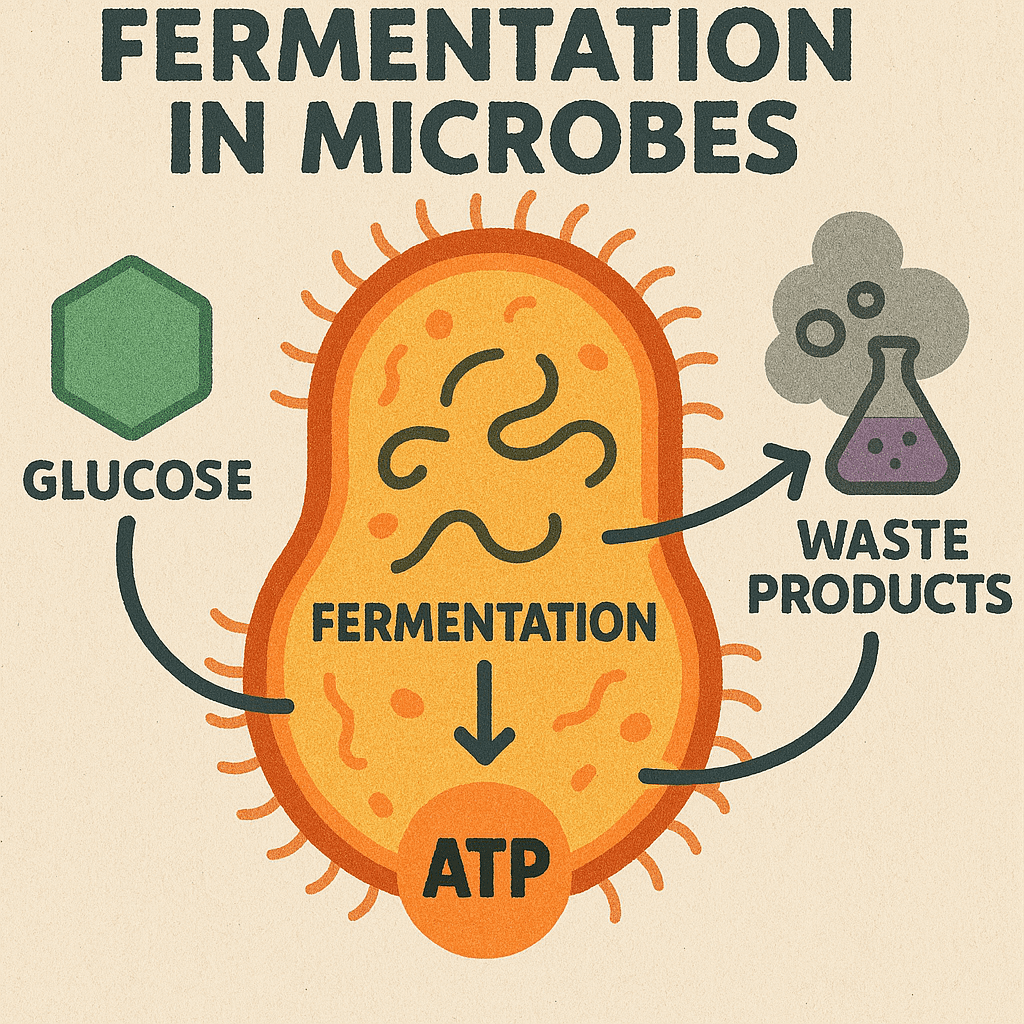
Fermentation is a metabolic process that enables cells to extract energy from organic molecules in […]
Category: Food Microbiology
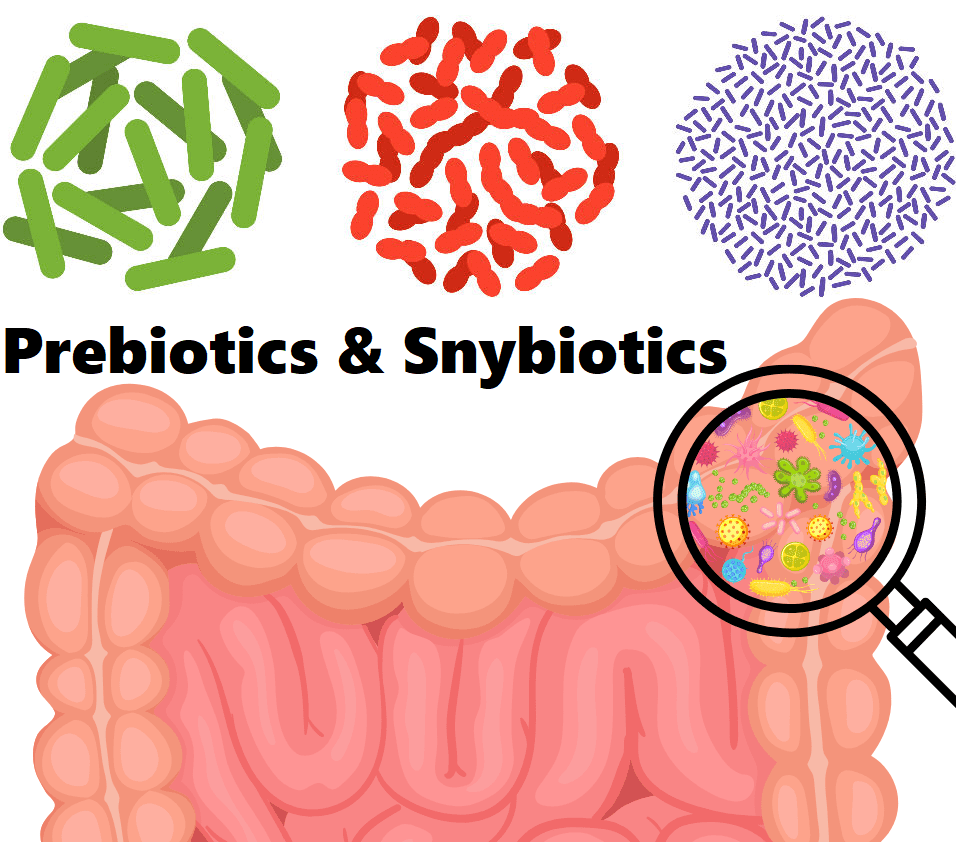
Harnessing the Power of Prebiotics and Synbiotics: A New Frontier in Gut Health and Beyond
IntroductionIn recent decades, scientific interest in gut health has intensified significantly, driven by a growing […]
LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES
Listeria monocytogenes is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive, non-spore forming, aerobic or anaerobic intracellular rod bacterium in […]
Features of probiotics & reported modes of action of probiotics
Microorganisms must meet stringent criteria to be used as probiotics, including being non-pathogenic, non-toxic, and able to survive stomach acid and pancreatic secretions. Probiotics confer health benefits such as enhancing the immune system, producing vitamins, preventing GI infections, and aiding in lactose digestion, potentially treating conditions like IBS and eczema.
Design and Operation of Fermenters: Engineering Optimal Environments for Microbial Cultivation and Industrial Bioproduction
Introduction Fermentation stands as a fundamental and versatile process across multiple scientific and industrial disciplines, […]
MICROBIAL ENUMERATION OF FOOD PRODUCTS
Food meant for human or animal consumption should be certified safe and hygienically acceptable after […]
The Role and Potential of Microbes in Food Production
Microorganisms, particularly bacteria and fungi, are fundamental to the sustainability and advancement of modern agriculture […]
Principles of Food Hygiene: Sources of Contamination in the Food Industry
Introduction Food hygiene encompasses all conditions and measures necessary to ensure the safety and suitability […]
HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP): Building Effective Food Safety Control Systems for Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) is an internationally recognized, science-based food safety management […]
INDICATOR ORGANISMS
Indicator organisms are microorganisms that signify the possible contamination of food or food products as […]
Feeding the Future: How Single Cell Proteins Can Help Solve Global Malnutrition
As the global population races past 8 billion and continues to rise, the urgency to […]
FOOD POISONING
Food poisoning/food infection is defined as the microbial infection or disease that is caused by […]
FOOD BORNE DISEASES
Food borne diseases are diseases caused by the ingestion of food borne pathogens. They are […]
SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINATION OF FOOD
Microbial contamination of food is almost inevitable owing to the ubiquity of microorganisms – which […]
EXTRINSIC FACTORS OF FOOD SPOILAGE
Extrinsic factors of food spoilage are the non-substrate factors that affect the spoilage of foods […]
INTRINSIC FACTORS OF FOOD SPOILAGE
Intrinsic factors of food spoilage are those inherent factors that are associated with the food […]
FOOD SPOILAGE
What is food spoilage? Food spoilage is simply defined as the change in the overall […]
Botulism – a public health menace
Key facts Foodborne botulism is a serious, potentially fatal disease. However, it is relatively rare. […]
MONITORING OF WATER QUALITY
Water quality is defined as the suitability of water to sustain various uses or processes […]
ACTIVE AIR MONITORING
Active air monitoring also involve the use of settle plates or sedimentation culture plates (as […]
PASSIVE AIR MONITORING
Passive air monitoring is usually done using special type of Petri dish plates known as […]
MONITORING OF AIR QUALITY
Air quality is defined as the degree to which the ambient air in a particular […]
Quality Assurance: System Design and Implementation in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Clinical Laboratory Practice
Quality Assurance (QA) is a structured, systematic, and documented framework designed to ensure that products […]
Quality Control in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Principles, Microbial Testing, Practical Implementation & GMP Compliance
Introduction Quality control (QC) is a systematic monitoring and verification framework used to detect, measure, […]
BAIRD–PARKER AGAR
Baird–parker agar is a selective medium for the enumeration of Staphylococcus aureus in foods and […]
APPERTIZATION
Appertization is simply defined as the heat-treatment of food at certain temperature levels that inhibit […]
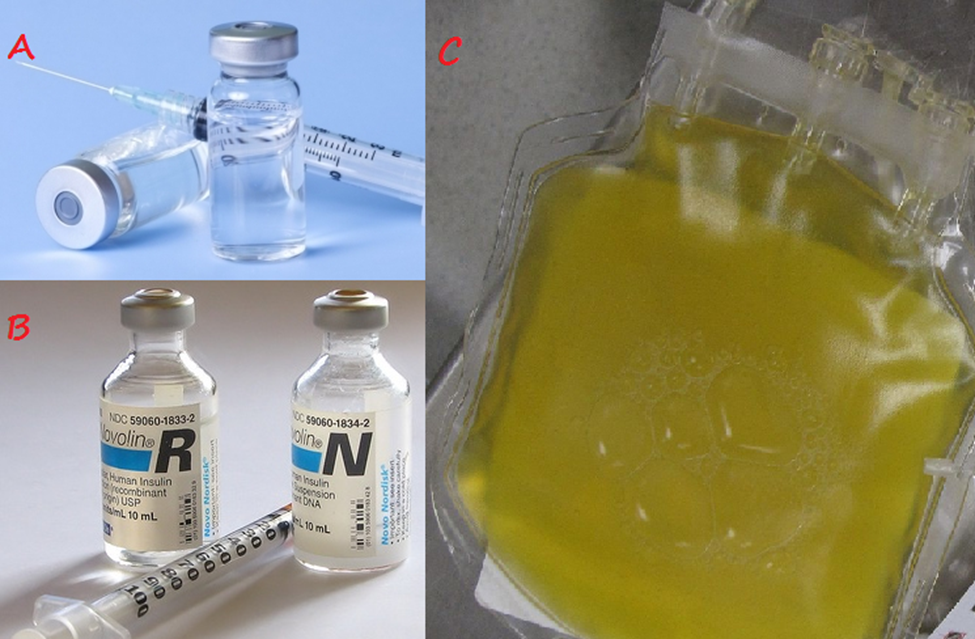
Limulus Amoebocyte Lysate (LAL) Test
The LAL test is applied in the testing of pharmaceuticals, medical devices, water, food, and […]
PASTEURIZATION
Pasteurization is simply defined as the process of heating food during its production in order […]
PYROGEN TEST
A pyrogen is simply defined as a fever-causing (inducing) agent that includes toxins of microorganisms. […]
FOOD PRESERVATION
Food preservation is the technique used to prevent food spoilage. It encompass all the methods […]
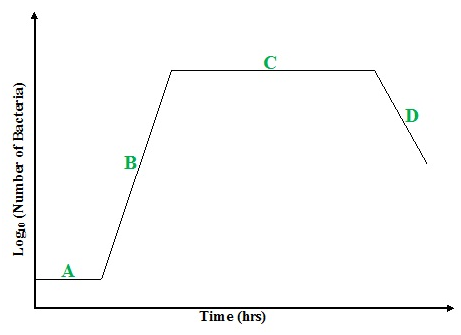
MICROBIAL GROWTH PHASE
Microbial growth is a fundamental biological process that governs the proliferation of microbial cells in […]
Characteristics of Microorganisms Used in Industrial Microbiology
Microorganisms—including bacteria (e.g. Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis), fungi (yeasts like Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris, […]
STERILITY TESTS OF BIOLOGICAL PRODUCTS
The phrase sterility simply means the absence of living organisms including bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa […]
General Significance and Importance of Fungi
Fungi represent a vast and diverse kingdom of eukaryotic organisms that play indispensable roles in […]
Introduction to Food Microbiology
Food microbiology is the branch of microbiology that deals with methods for keeping microorganisms (especially […]
Exploring Careers in Microbiology: What Microbiologists Do and Where They Work!
A guide to discovering diverse career paths through the world of microbes—from healthcare to climate […]