CENTRAL DOGMA (FRAMEWORK) OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
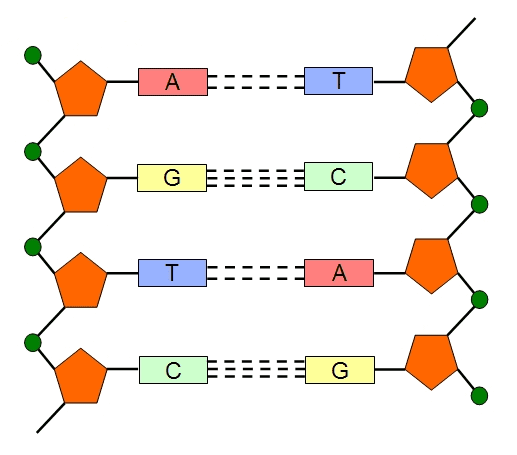
The central framework of molecular biology otherwise known as the “central dogma” is the starting point for the actual course of movement of genetic information within the cell’s nucleus of an organism. The transfer of genetic information within the cell of an organism (i.e. in the nucleus) from deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) to ribonucleic acid (RNA) […]
CENTRAL DOGMA (FRAMEWORK) OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Read More »
Biotechnology, Molecular Microbiology