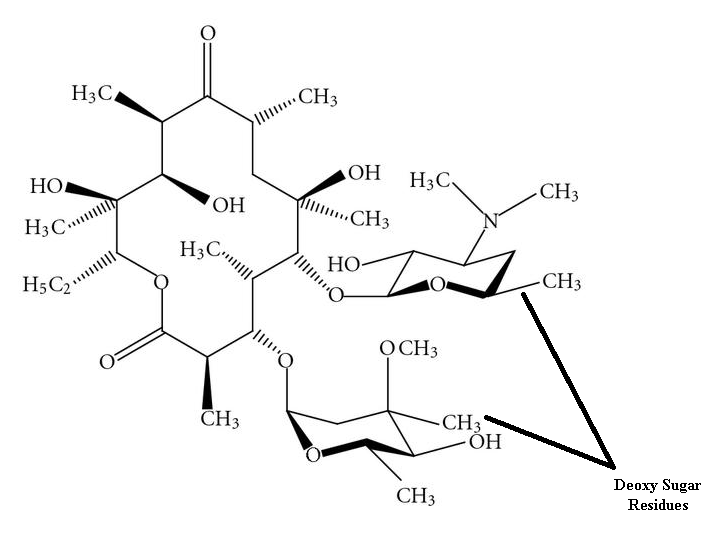
FERMENTATION
The phrase fermentation is derived from the Latin word “fevere” – which means “to boil”. It was first coined and used by Louis Pasteur – who used it to describe the bubbling of sugar solutions especially due to the microbial activity occurring in them. The bubbling action of the sugar (a substrate) was due to […]