IMPORTANCE OF IMMUNIZATION
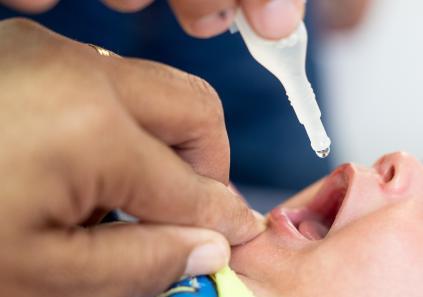
Immunization is the process whereby a person is made immune or resistant to an infectious disease, typically by the administration of a vaccine. Vaccines stimulate the body’s own immune system to protect the person against subsequent infection or disease. Another word that can be used for immunization is vaccination. Immunization is a proven tool for […]
IMPORTANCE OF IMMUNIZATION Read More »
Immunology & Immune System, Virology