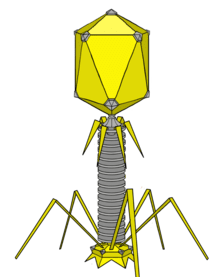
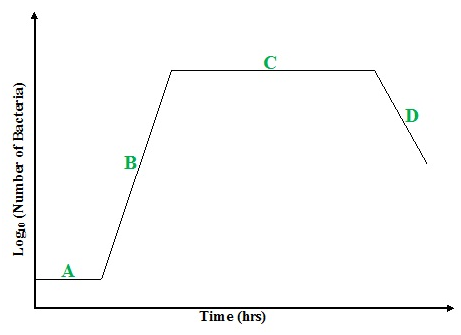
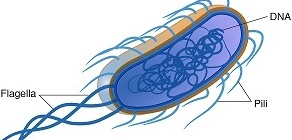
HISTORY OF VIROLOGY
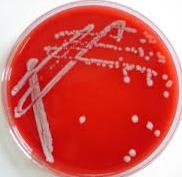
The field of virology (inclusive of medical virology, plant virology and veterinary virology) blossomed following the discovery and development of transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Virology as a field in the biological sciences has spanned over 200 years; and this important discipline has continued to remain relevant to mankind and its environment owing to the varying […]
HISTORY OF VIROLOGY Read More »
Virology