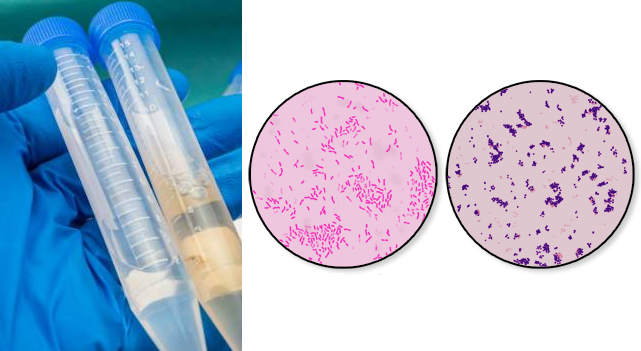
GRAM SMEAR OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF) SAMPLE
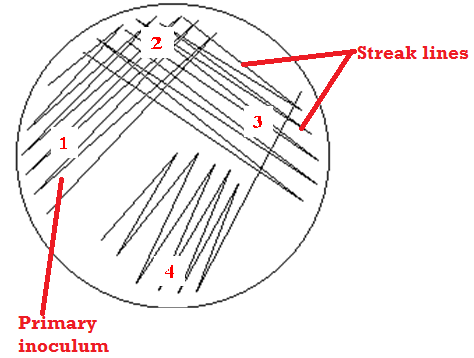
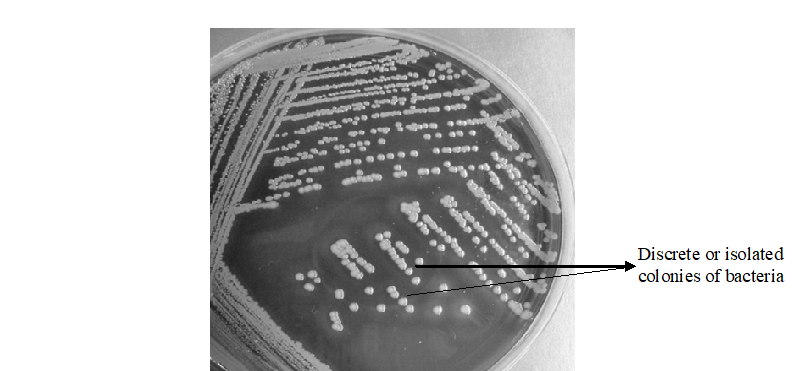
AIM: To detect the presence of pus cells and bacteria in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimen. MATERIAL/APPARATUS: CSF specimen, Gram staining reagents, microscope, glass slide, immersion oil, Bunsen burner. METHOD/PROCEDURE FOR CSF GRAM STAINING REPORTING OF THE RESULT Look for Gram negative intracellular diplococcic, Gram negative rods, Gram positive diplococci, and pus cells and report same. […]
GRAM SMEAR OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF) SAMPLE Read More »
Microbe Lab, Techniques in Microbiology Lab