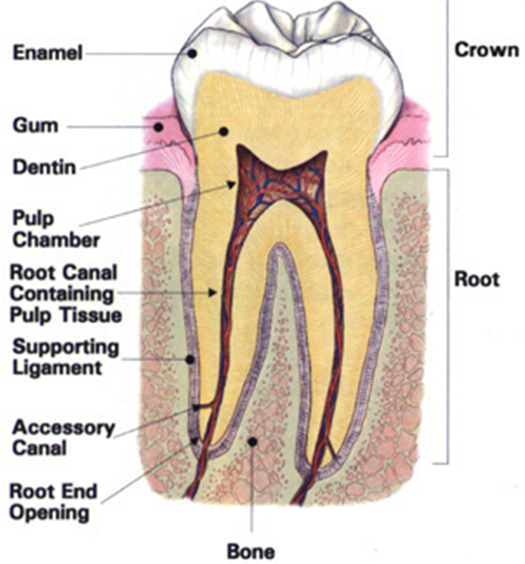
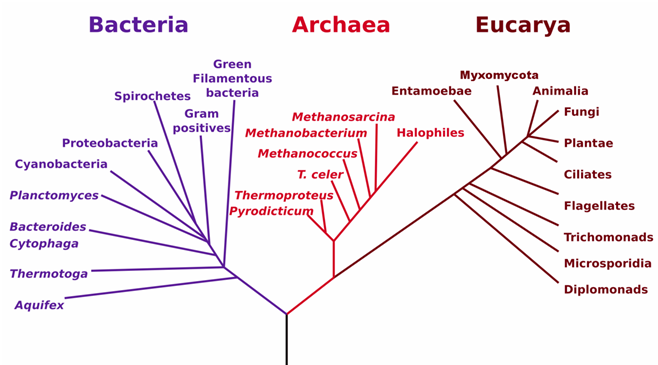
Introduction to Cell Culture
Cell culture is the laboratory technique of growing and maintaining the cells of multicellular organisms (plants and animal cells inclusive) in a favourable artificial environment conducive for growth. It is the maintenance of animal cells (inclusive of plant and human cell lines) in vitro.Such an artificial environment or growth medium mimics the internal environment of […]
Introduction to Cell Culture Read More »
Cell Culture Notes