Overview of Molecular Biology
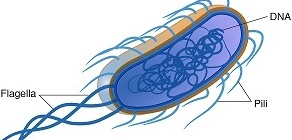
Molecular biology is the study of the genetic makeup of organisms at the level of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). It encompasses the study of the ways in which diseases and traits can be passed through the genes especially via from parents to their offspring’s. Genes are the hereditary unit or genetic material that is transmitted from […]
Overview of Molecular Biology Read More »
Molecular Microbiology