NITRATE REDUCTION TEST
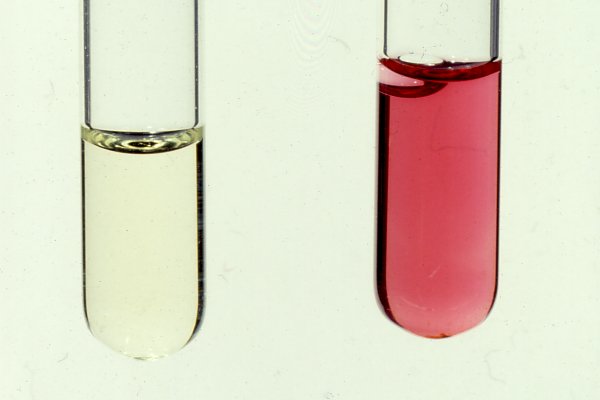
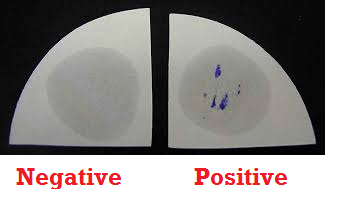
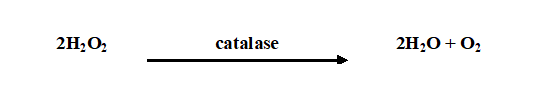
Nitrate reduction test is used to identify pathogenic bacteria that have the ability to convert nitrate (NO3–) to nitrite (NO2–). Nitrate reduction test is used for the differentiation of members of Enterobacteriaceae on the basis of their ability to produce nitrate reductase enzyme – that hydrolyze nitrate (NO3–) to nitrite (NO2–), which may then again be […]
NITRATE REDUCTION TEST Read More »
Biochemical Tests in Microbiology Lab