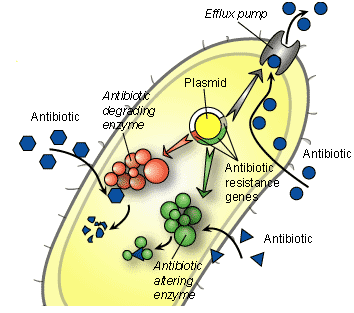
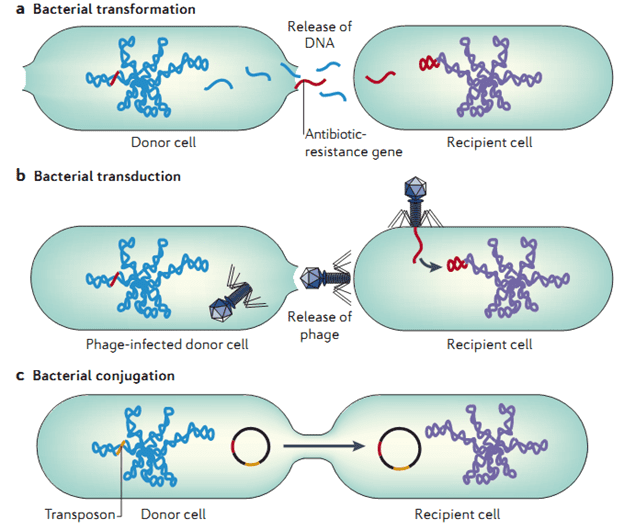
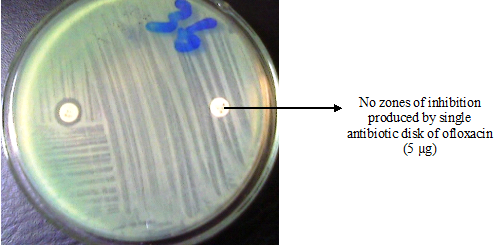
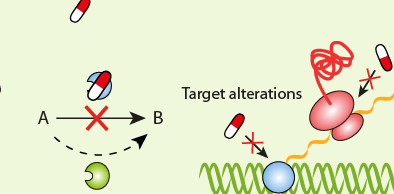
IMPACT AND COST OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE ON PUBLIC HEALTH AND THE ECONOMY OF A NATION
Antimicrobial agents (antibiotics in particular) have helped countless numbers of people worldwide owing to their invaluable role in fighting microbial related infections/diseases; but the effectiveness of these agents and their usefulness for therapy is gradually being tested and deteriorated by the emergence and spread of drug-resistant forms of pathogenic microorganisms that has extended across the […]
IMPACT AND COST OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE ON PUBLIC HEALTH AND THE ECONOMY OF A NATION Read More »
Antibiotic Resistance / Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR), Pharmaceutical Microbiology