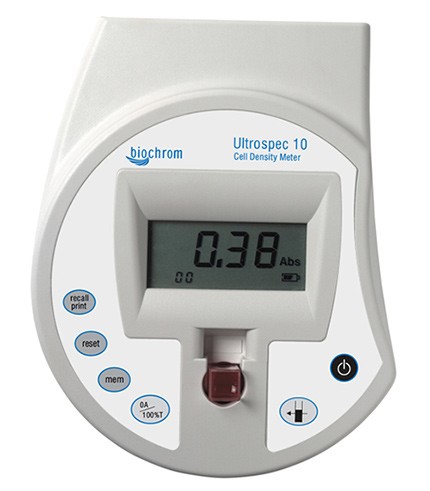
Cell density meter is an instrument that is used for measuring of the density of […]
Category: Techniques in Microbiology Lab
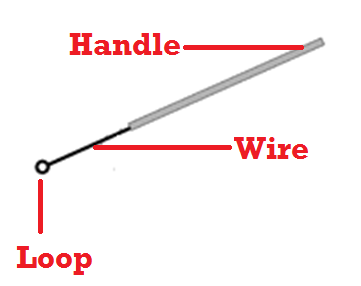
Glass Plating Beads for spreading bacteria/fungi on culture plate
Glass Plating Beads are reusable beads which helps to spread suspensions of microorganisms (bacteria or […]
FTA CARDS
The acronym FTA stands for “Flinders Technology Association”. FTA CARDS are chemically treated Whatman filter […]
Assessing RNA Purity, Concentration and Integrity
The integrity, purity and concentration of the RNA so isolated should be confirmed before proceeding […]
INOCULATION TECHNIQUE
Inoculation is a microbiology technique which is used to introduce or place specimens and microbial […]
BUNSEN BURNER FLAME
Bunsen burner is practically a tube or hosepipe that is connected directly to a steady […]
GRAM STAINING TECHNIQUE
Gram staining is a general purpose bacteriological identification technique used in the bacteriology section of […]
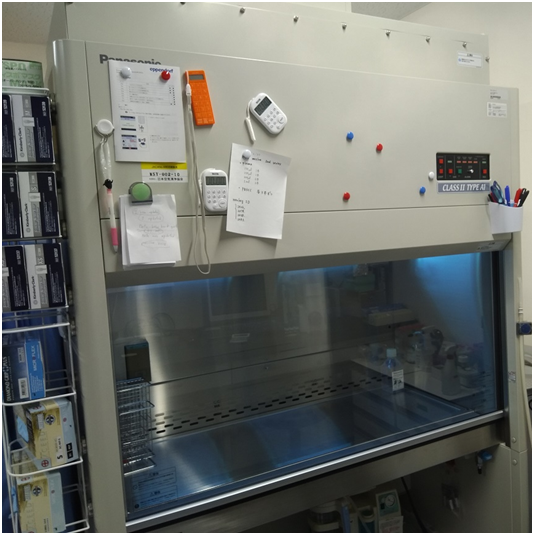
LAMINAR FLOW BIOLOGICAL SAFETY CABINET
Laminar flow biological safety cabinet is an air filtration system which protects a laboratory worker […]
ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE
Aseptic technique refers to all the quality control and precautionary measures taken by microbiologists in […]
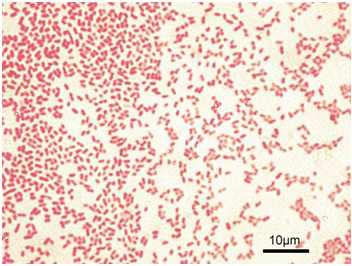
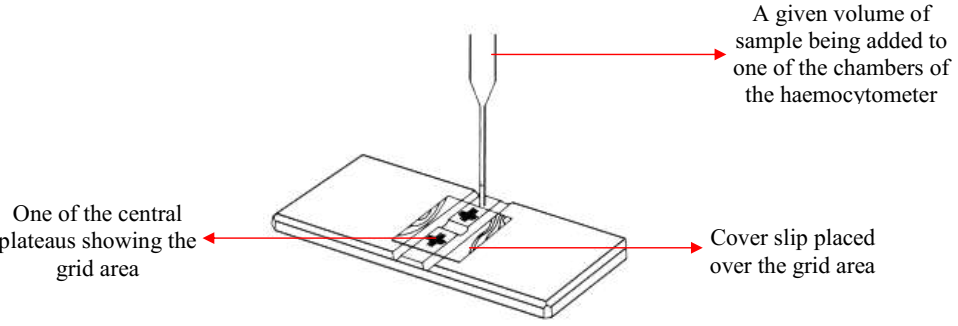
MICROBIAL COUNT: Total Count & Viable Count
Viable cell count: Viable cell count gives an estimate of the total number of living […]
SLIDE RACK & STAINING RACK
Slide rack is a piece of vessel used for packing and storing clean glass slides […]
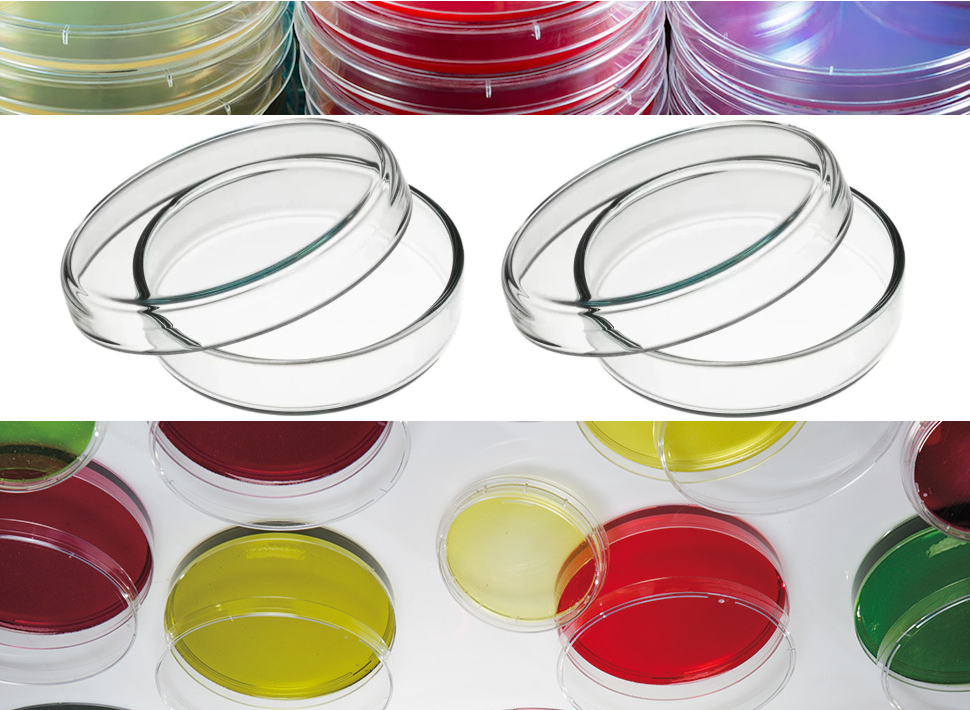
PETRI DISHES
Petri dishes are shallow glass or plastic plates that are cylindrical in shape, and which […]
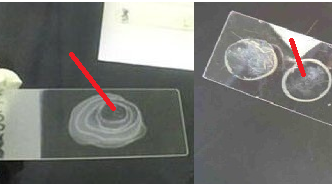
PREPARATION OF BACTERIAL SMEAR & HEAT FIXING
Bacterial smear is defined as a dehydrated or dried preparation of a bacterial suspension (cells) […]
PRECAUTIONARY MEASURES TO OBSERVE WHILE WORKING IN THE MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY
REFERENCES Atlas R.M (2010). Handbook of Microbiological Media. Fourth edition. American Society of Microbiology Press, […]
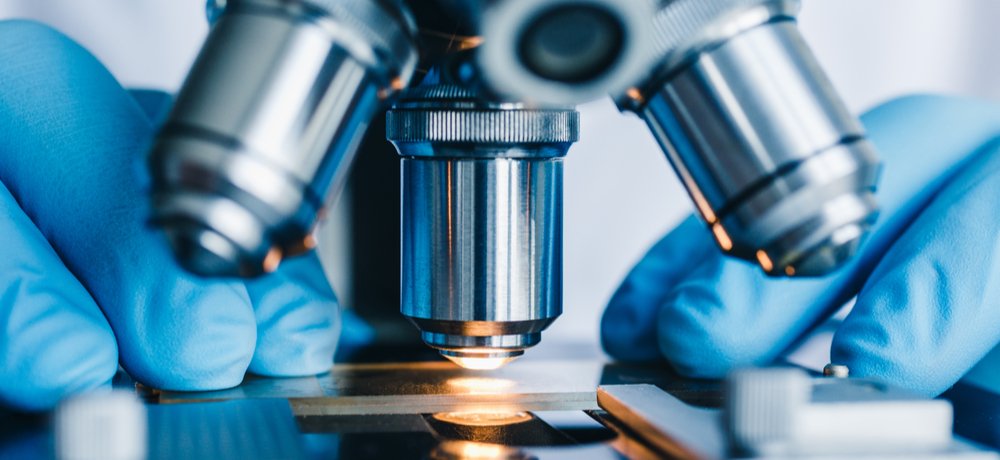
Introduction to Microscopy and Microscope
The history of microbiology will be incomplete without first mentioning the discovery and development of […]
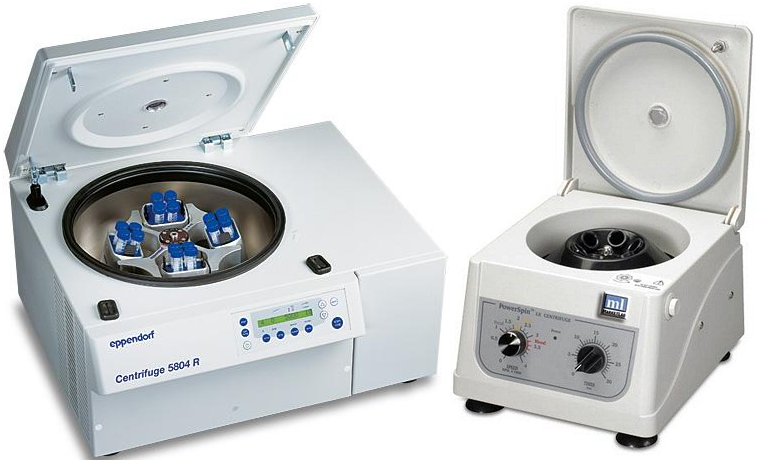
Centrifuge
Centrifuge is an instrument is used to separate suspensions or particulate matter in a liquid […]