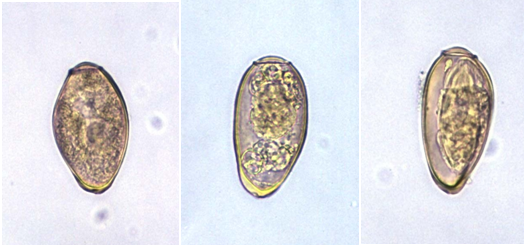
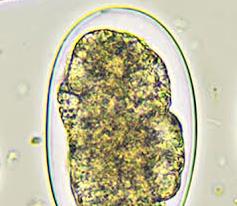
PARAGONIMIASIS
Paragonimiasis or lung-fluke infection is a protozoan lung disease that resembles bacterial tuberculosis in humans; and it is caused by trematodes or flukes. It is a lung-fluke disease that has a worldwide distribution but more prevalent in parts of Asia including China, Taiwan, Indonesia and Japan. The disease has also been reported in some parts […]