IMMUNOGLOBULIN D (IgD)
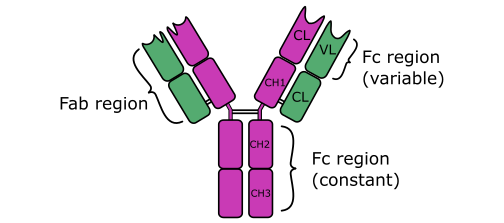
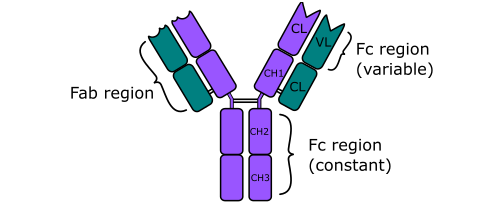
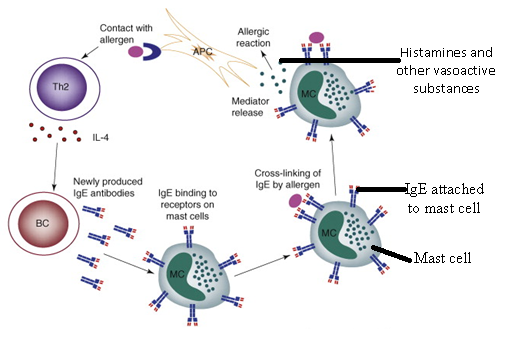
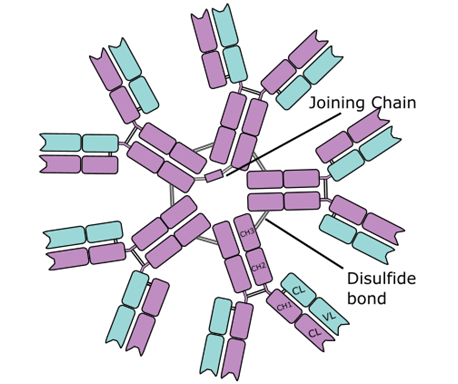
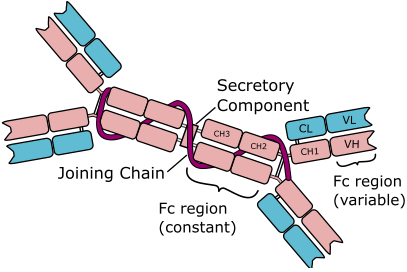
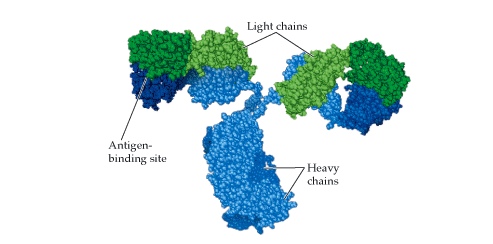
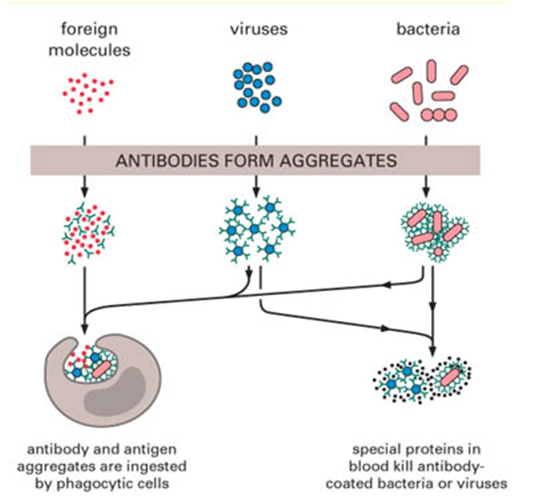
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is an antibody with the basic four polypeptide structure of an immunoglobulin (Figure 1); and IgD is mostly found attached to the membranes of B cell. IgD is a membrane bound immunoglobulin, and it has a molecular weight (MW) of about 180, 000 DA. Immunoglobulin D is present in only trace amounts […]
IMMUNOGLOBULIN D (IgD) Read More »
Immunology & Immune System