Cetrimide selective agar
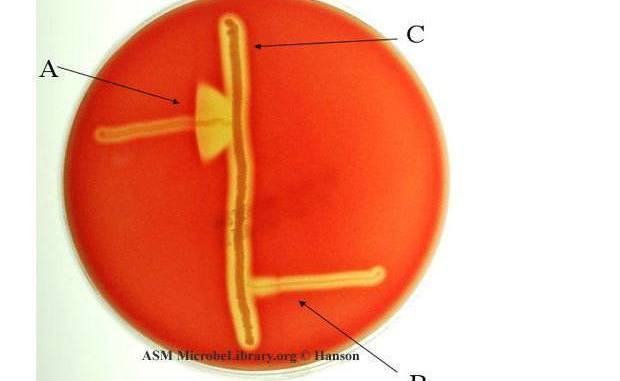
Cetrimide selective agar is used for the selective cultivation and isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from clinical and non-clinical samples. The preparation of cetrimide selective agar is elaborated in this section. P. aeruginosa is a pigment-producing bacterium. The organism produces certain types of pigments including pyocyanin (blue-green pigment), pyomelanin (black pigment) and pyoverdine (yellow-green and fluorescent pigment) [Figure […]
Cetrimide selective agar Read More »
Culture media