STRUCTURES OF FUNGI
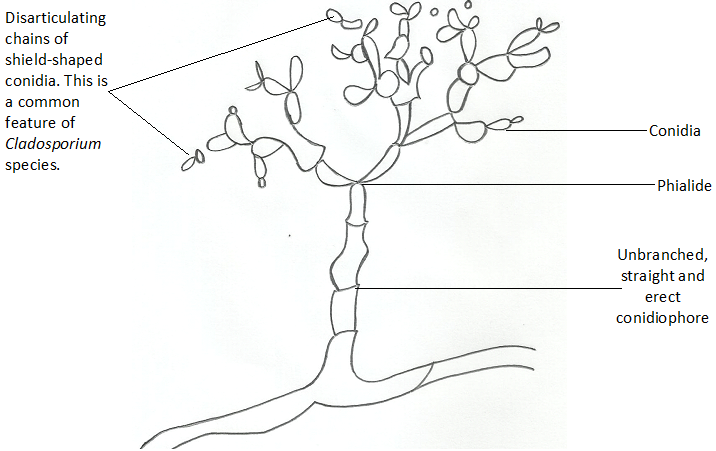
The spores (conidia) are produced in dry chains from the tips of the phialides, with the youngest spore at the base of the chain (Figure 1). Penicillium is found in the soil, decaying vegetation, air and they are common contaminants on various substances. Penicillium causes food spoilage, and it colonizes leather objects. It is an […]
STRUCTURES OF FUNGI Read More »
Mycology