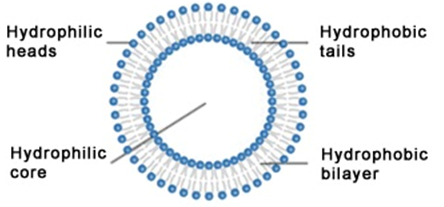
MUTATION: definition, types and causes
The term mutation is derived from the Latin word “mutare” – which means “to change”. Thus, mutation is simply defined as the change in genetic makeup (genotype) of an organism which results in the transformation of the phenotype of the organism. Mutation is an inheritable change in the base sequence of the genome of an […]
MUTATION: definition, types and causes Read More »
Biotechnology