Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, is a debilitating water-borne disease caused by parasitic blood flukes […]
Category: Public Health & Parasitology
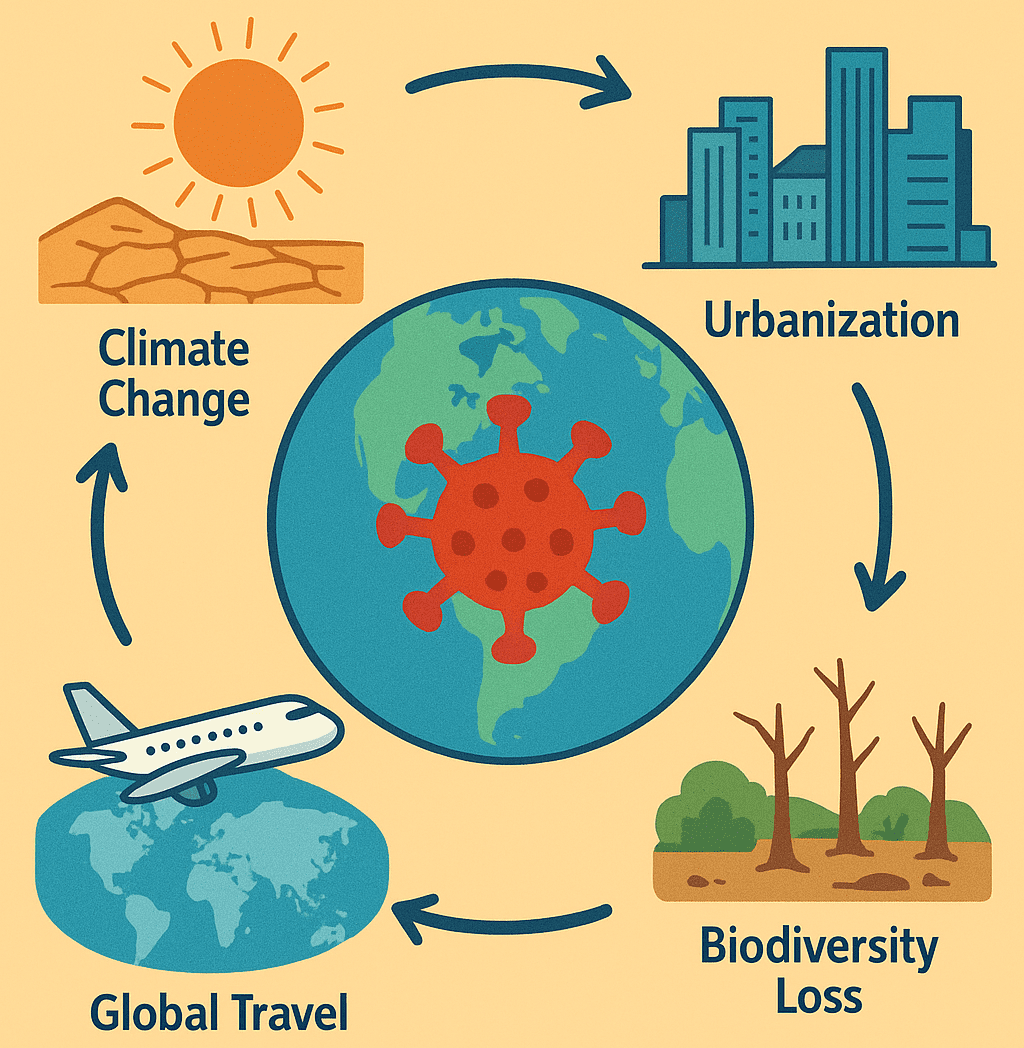
How Global Change Contributes to the Spread of Infectious Diseases
The dynamics of infectious disease transmission are shaped by a complex interplay of environmental, biological, […]
Hand Washing: when and how to wash your hands
Hand washing is one of the best ways to protect yourself and your family from […]
HEALTHY HABITS TO HELP PREVENT FLU
Preventing Flu at Work and School At School At Work Source: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/actions-prevent-flu.htm
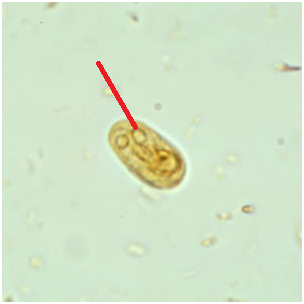
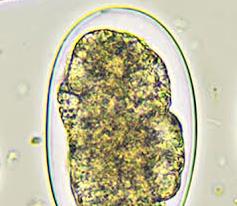
GIARDIASIS
Giardiasis is a water-borne protozoal diarrheal-disease that is cause by parasites in the genus Giardia. […]
LEISHMANIASIS
Leishmaniasis is the parasitic disease caused by the protozoal organism, Leishmania. The disease affects the […]
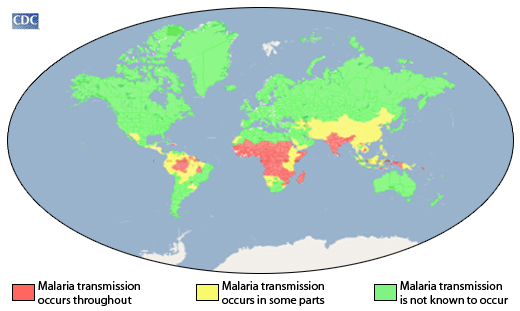
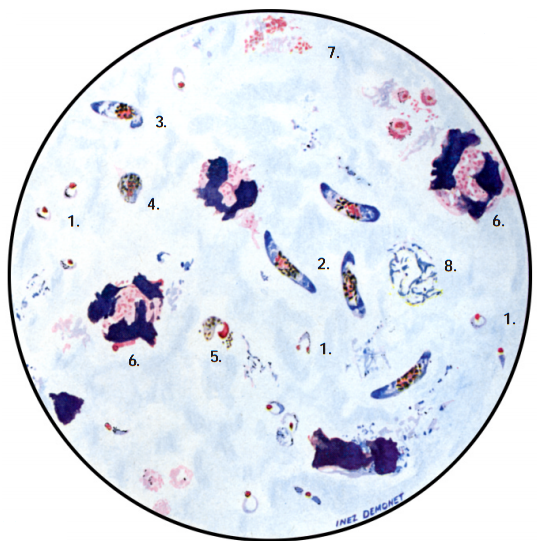
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MALARIA
Malaria is increasing at a worrying rate compared to the other blood and tissue parasitic […]
FACTORS THAT AFFECT TRANSMISSION OF MALARIA
Environmental factors greatly enhances the spread and transmission of malaria because these climatic factors which […]
TERMINOLOGIES USED IN PLASMODIUM INFECTION
References Aschengrau A and Seage G.R (2013). Essentials of Epidemiology in Public Health. Third edition. […]
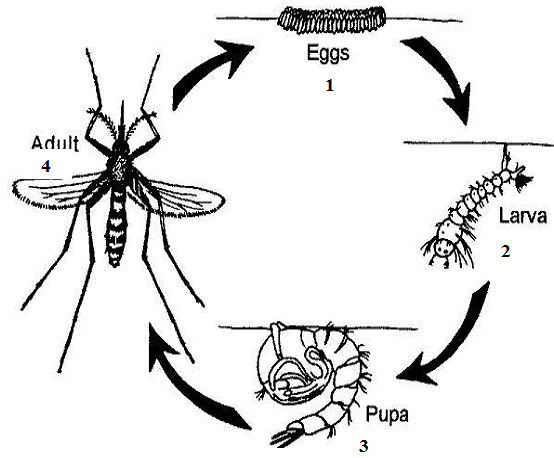
LIFE CYCLE OF MOSQUITO
Mosquito species including those of Anopheles carry out effective breeding and survival in freshwaters (i.e. […]
HUMAN PLASMODIUM SPECIES: causative agents of malaria
Malaria in humans is majorly caused by four (4) species of Plasmodium. Plasmodium species are […]
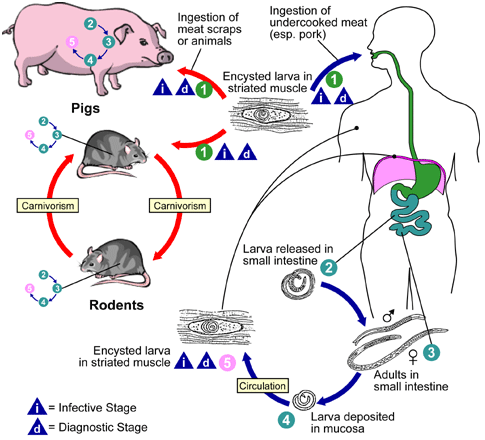
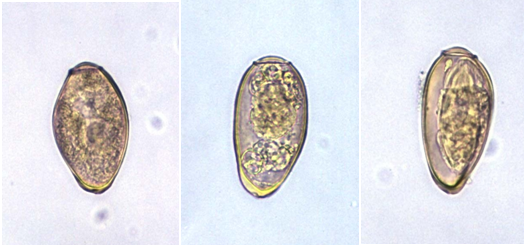
TRICHINELLOSIS
Trichinellosis or trichinosis is a zoonotic parasitic disease caused by tissue nematodes or roundworms after […]
PARAGONIMIASIS
Paragonimiasis or lung-fluke infection is a protozoan lung disease that resembles bacterial tuberculosis in humans; […]
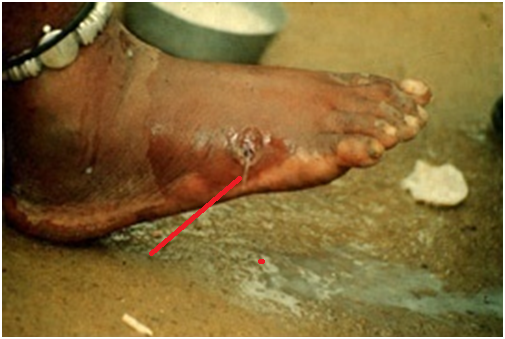
DRACUNCULIASIS
Dracunculiasis is a crippling parasitic disease that is caused by a tissue nematode (roundworm) which […]
Classification of parasites that parasitize humans
Generally, parasites can be classified into two major groups: Endoparasites are parasites that live inside […]
ECHINOCOCCOSIS(HYDATIDOSIS, OR HYDATID DISEASE)
BIOLOGY AND CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF ECHINOCOCOCCUS Human echinococcosis (hydatidosis, or hydatid disease) is caused by […]
Botulism – a public health menace
Key facts Foodborne botulism is a serious, potentially fatal disease. However, it is relatively rare. […]
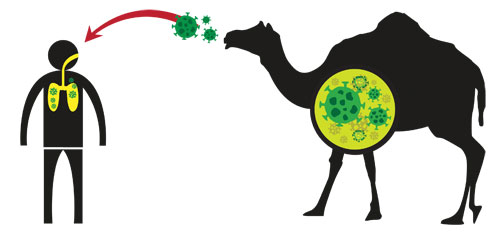
MIDDLE EAST RESPIRATORY SYNDROME (MERS)
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) is an illness caused by a virus (more specifically, a […]
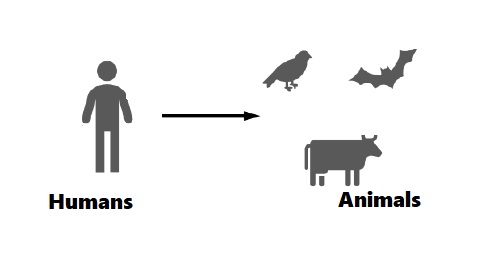
Anthroponotic Disease (Anthroponosis) & Sapronoses
An anthroponotic disease, or anthroponosis, is an infectious disease in which a disease causing agent […]
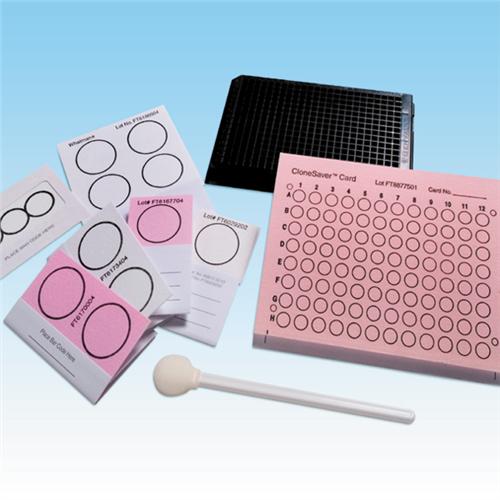
FTA CARDS
The acronym FTA stands for “Flinders Technology Association”. FTA CARDS are chemically treated Whatman filter […]
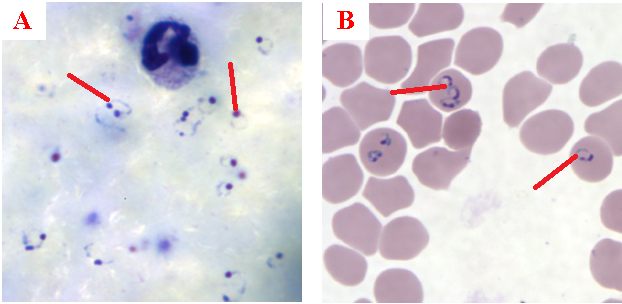
MALARIA
Malaria is an insect-transmitted parasitic disease characterized by recurrent episodes of fever and anaemia (loss […]
REASONS FOR THE HIGH FREQUENCY OF PARASITES & PARASITIC DISEASES IN TROPICAL & SUBTROPICAL REGIONS
Parasitic diseases are usually common in rainforest parts of the world (the tropical and subtropical […]
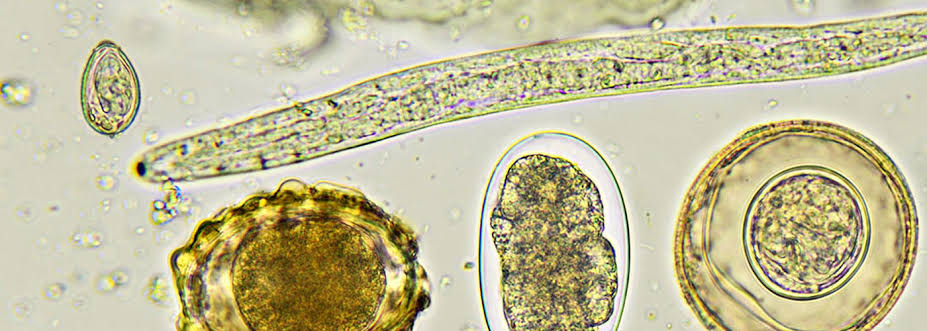
Introduction to Parasitology
Parasitology is the study of parasites and their interaction with other organisms (i.e. their hosts). […]
PUBLIC HEALTH AND PARASITIC DISEASES
Public health is a branch of medical sciences that primarily deals with the surveillance, control, […]