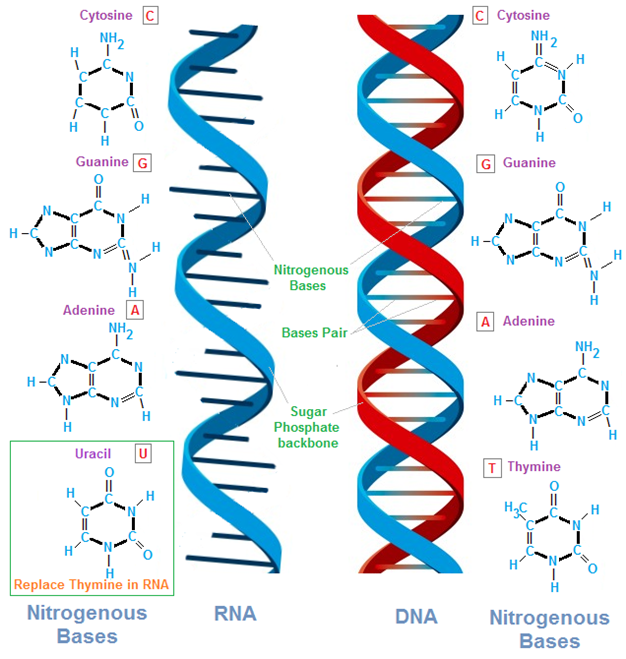
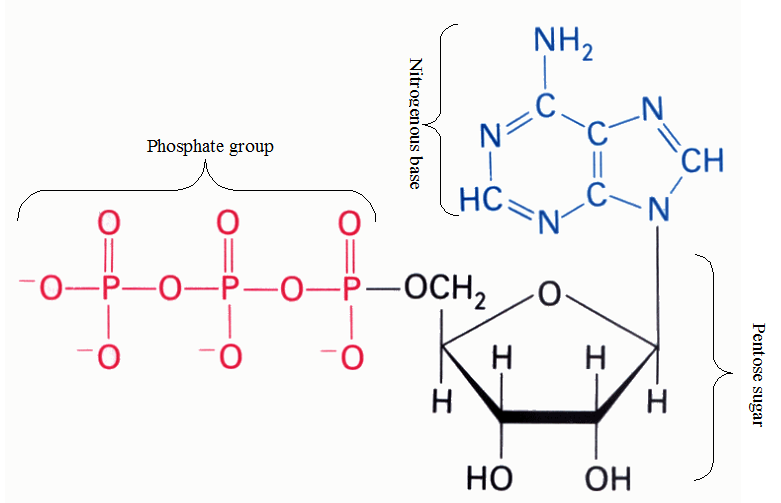
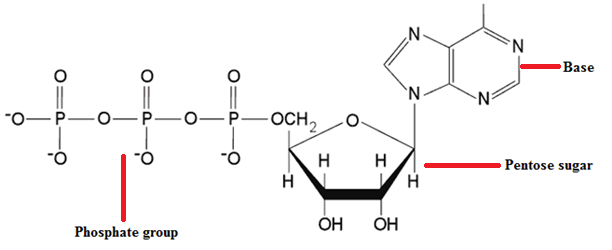
RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA)
An understanding of the nucleic acid molecules which include deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) important for us to understand the molecular and/or genetic basis of life. Nucleic acid molecules are found in all living organisms as the carriers of genetic materials from parent organisms to their offspring’s. With the exception of viruses (which […]
RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA) Read More »
Biotechnology, Molecular Microbiology