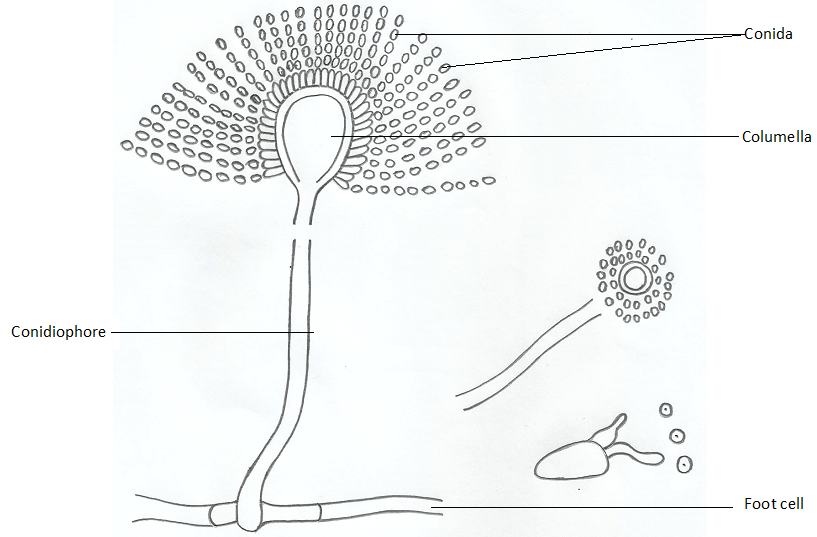
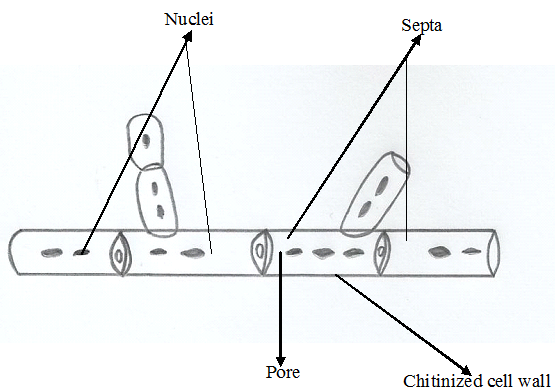
SUPERFICIAL MYCOSES
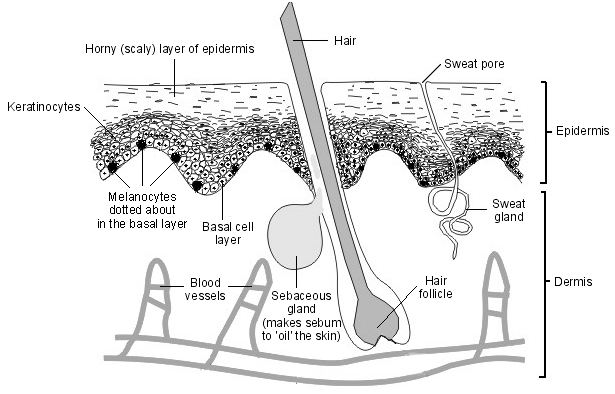
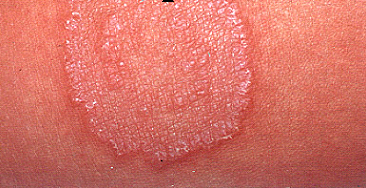
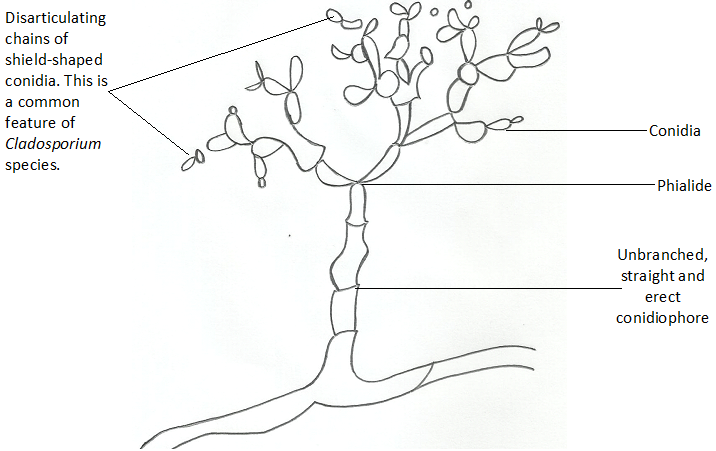
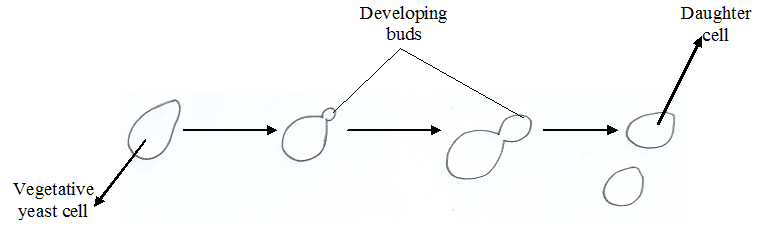
Superficial mycoses are fungal infections which are only limited to the keratinized outer layer of the skin, hair and nails. Superficial mycoses unlike other forms of mycoses rarely result in inflammatory reactions in the host but it is usually characterized by intense itching and peeling or scaling of the affected body sites. They are self-limiting […]
SUPERFICIAL MYCOSES Read More »
Mycology