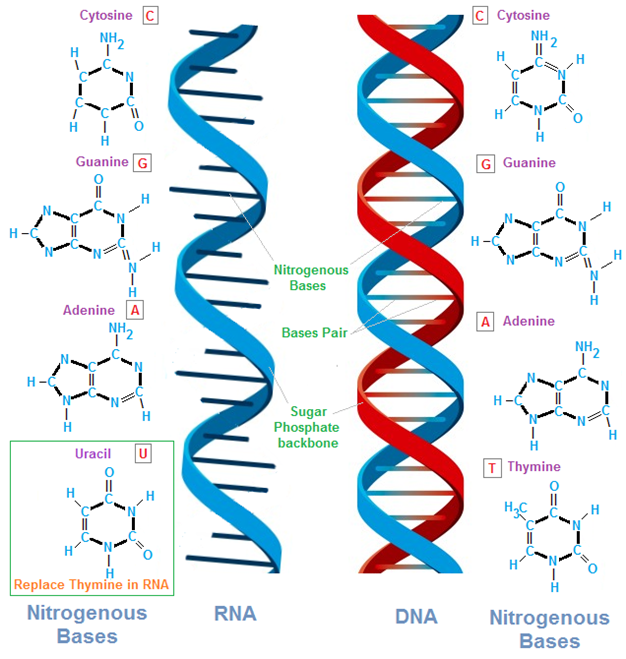
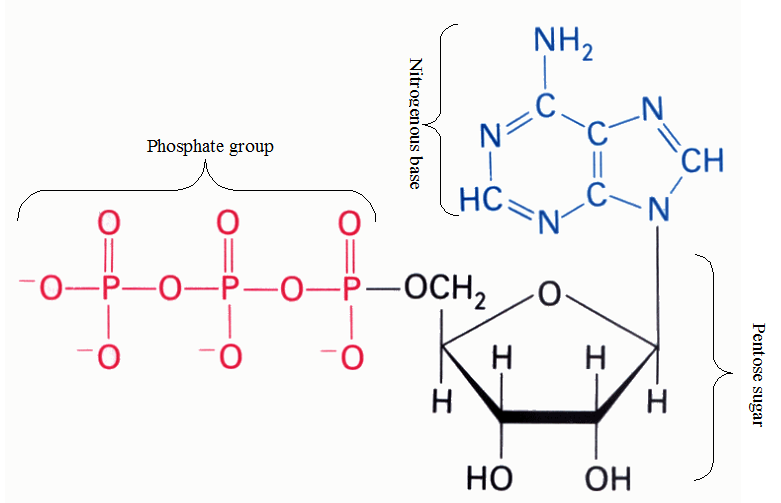
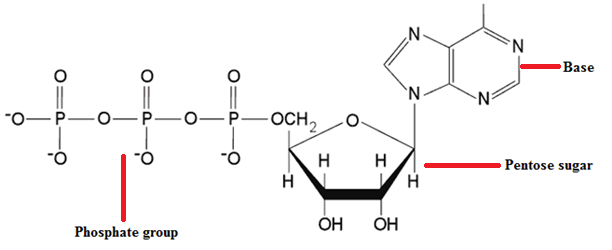
An understanding of the nucleic acid molecules which include deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid […]
Category: Biotechnology
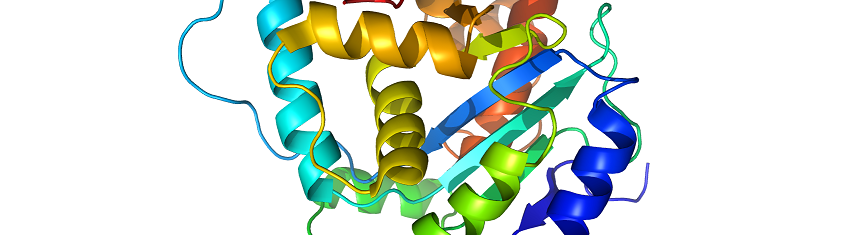
PROTEIN STRUCTURE – types and function
Proteins are a group of polypeptides that form a molecule of specific biological function; and […]
PURINES & PYRIMIDINES
Purines are heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consist of a pyrimidine ring fused to an […]
NUCLEOTIDES
Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more phosphate groups covalently attached to the 3′ or […]
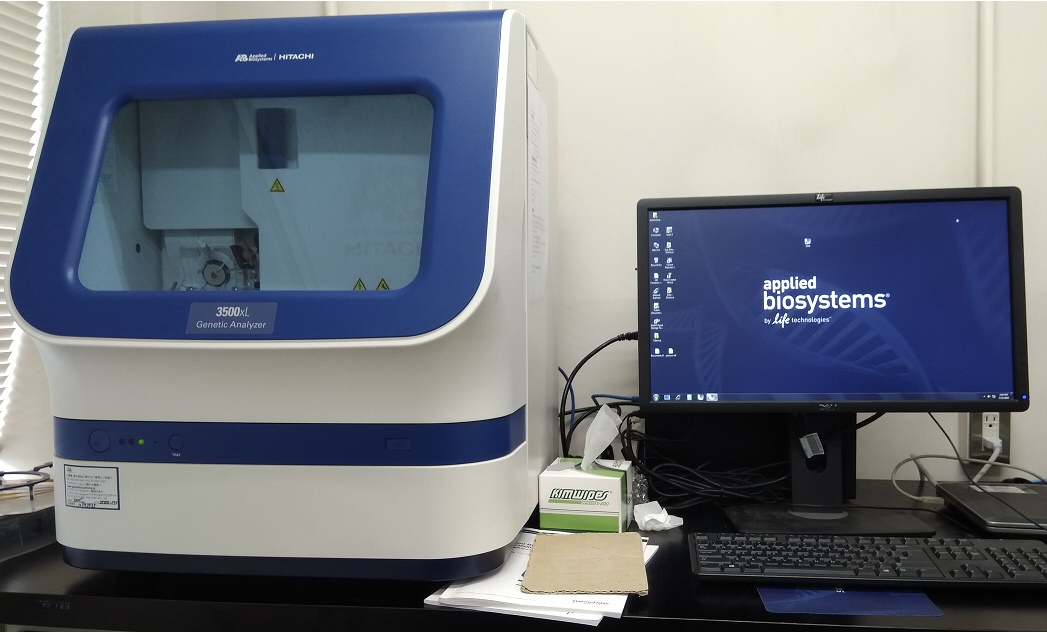
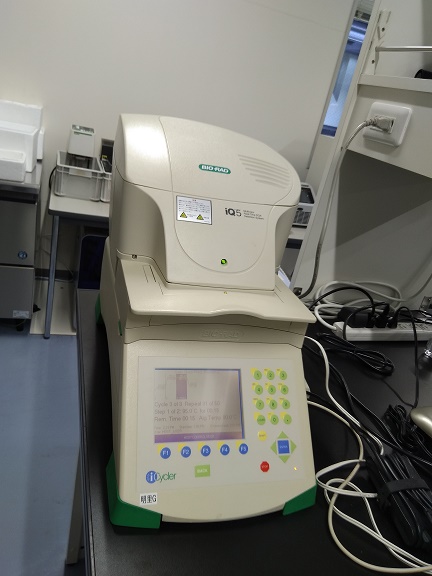
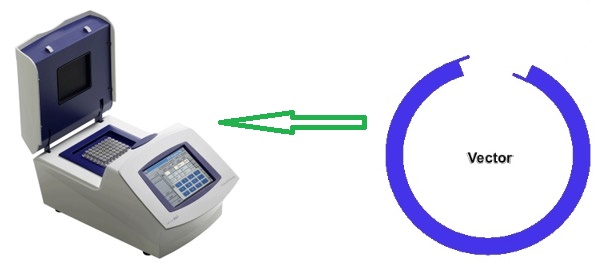
THERMOCYCLER (PCR Machine)
Thermocycler or thermal cycler is a piece of equipment is used for the copying or […]
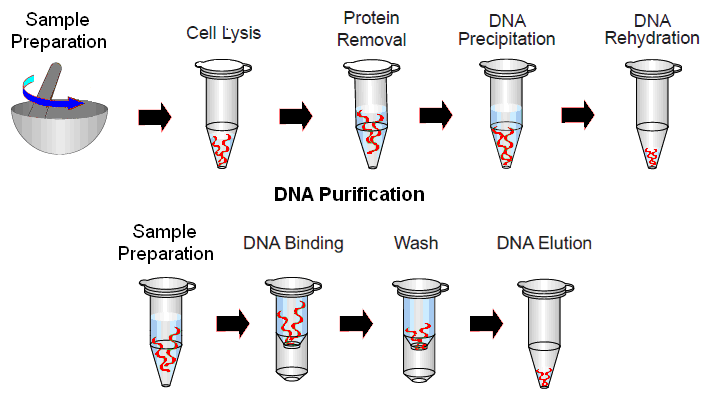
GENOMIC DNA ISOLATION
The Isolation of Genomic DNA from the bacterium, Escherichia coli is explained in this section […]
WAYS TO SEPARATE DNA FROM OTHER CELLULAR MATERIALS: BINDING AND WASHING
When phenol or a mixture of phenol:chloroform is mixed with a cell Lysate, two phases […]
Assessing RNA Purity, Concentration and Integrity
The integrity, purity and concentration of the RNA so isolated should be confirmed before proceeding […]
TOOLS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY
Biotechnology uses the tools of molecular biology (i.e. genetic engineering) to produce novel products through […]
Significance and Applications of Microorganisms
Microorganisms, often referred to as microbes, are tiny life forms that are invisible to the […]
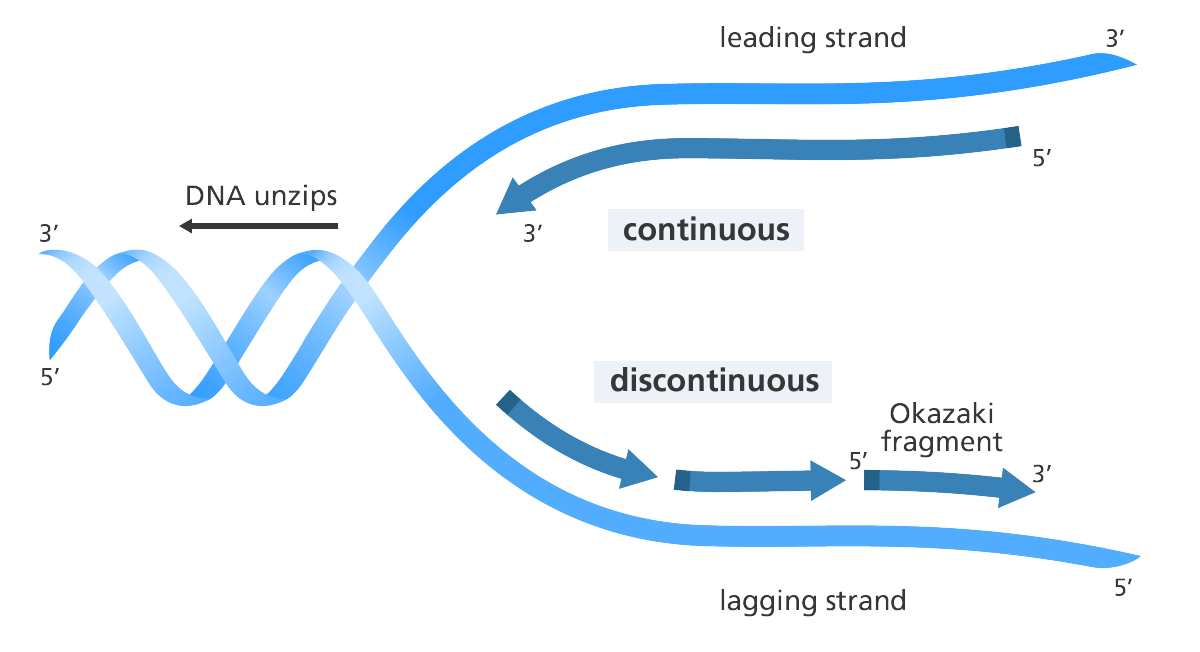
DNA REPLICATION
DNA replication is simply defined as the genetic process of duplicating the genome of a […]
Fermentation and Its Importance
The term fermentation is one of the oldest in the history of biological and chemical […]
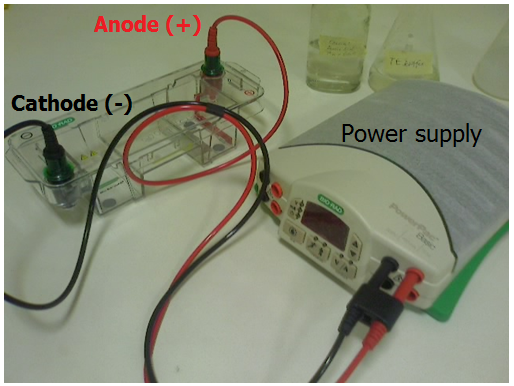
STEPS OF PERFORMING GEL ELECTROPHORESIS
Gel electrophoresis is one type of electrophoresis technique, and its procedure is highlighted below. The […]
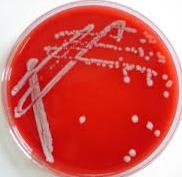
CHARACTERISTICS OF MICROORGANISMS USED FOR BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PROCESSES
As one of the world’s most research-intensive industry, biotechnology corporations are high-profit making enterprises that […]
CENTRAL DOGMA (FRAMEWORK) OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
The central framework of molecular biology otherwise known as the “central dogma” is the starting […]
MICROBIAL METABOLITES: PRIMARY METABOLITES AND SECONDARY METABOLITES
Microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes, are among nature’s most prolific chemists. They are capable […]
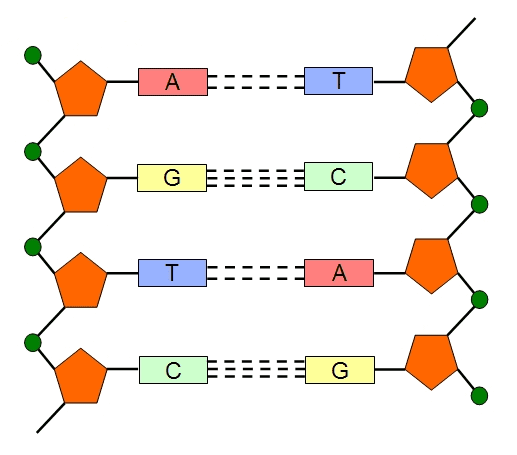
GENOMIC DNA
Genomic DNA is a double helix structure that is composed of several components including purines […]
Microorganisms Used in Biotechnological Processes
Biotechnology, the application of biological systems or organisms to develop products and technologies for human […]
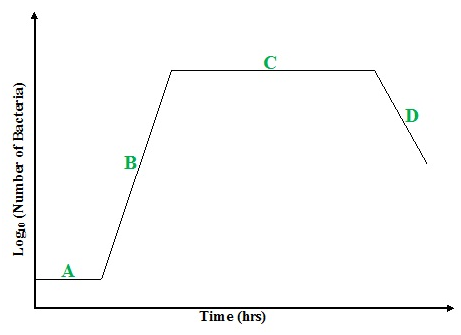
MICROBIAL GROWTH PHASE
Microbial growth is a fundamental biological process that governs the proliferation of microbial cells in […]
Characteristics of Microorganisms Used in Industrial Microbiology
Microorganisms—including bacteria (e.g. Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis), fungi (yeasts like Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris, […]
GEL ELECTROPHORESIS TECHNIQUE
The term “electrophoresis” refers to the movement of a solid particle (e.g. nucleic acids) through […]
Introduction to Recombinant DNA (rDNA) Technology / Genetic Engineering
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology or genetic engineering is the in vitro controlled manipulation of nucleic […]
General Significance and Importance of Fungi
Fungi represent a vast and diverse kingdom of eukaryotic organisms that play indispensable roles in […]
Introduction to Biotechnology
Biotechnology is simply defined as the scientific manipulation of living organisms at the molecular genetics […]