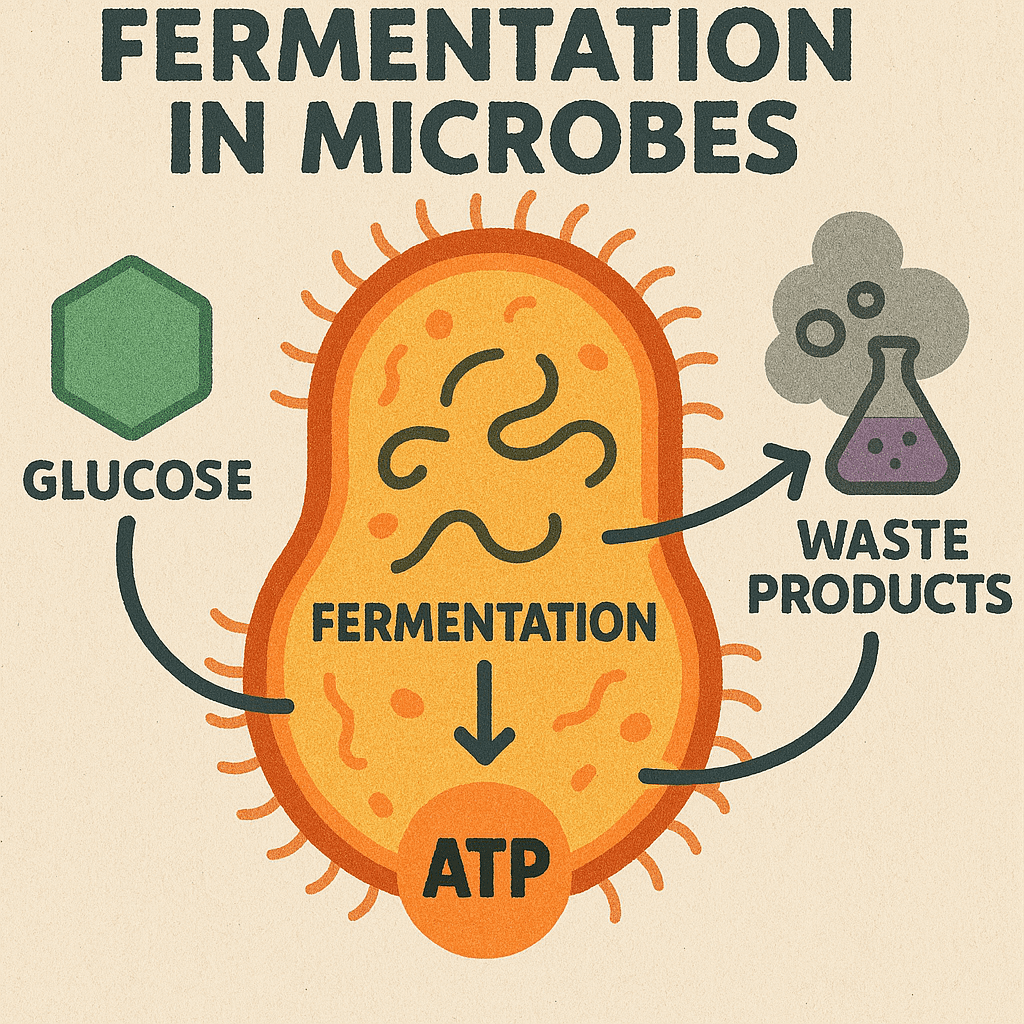
Fermentation is a metabolic process that enables cells to extract energy from organic molecules in […]
Tag: fermentation
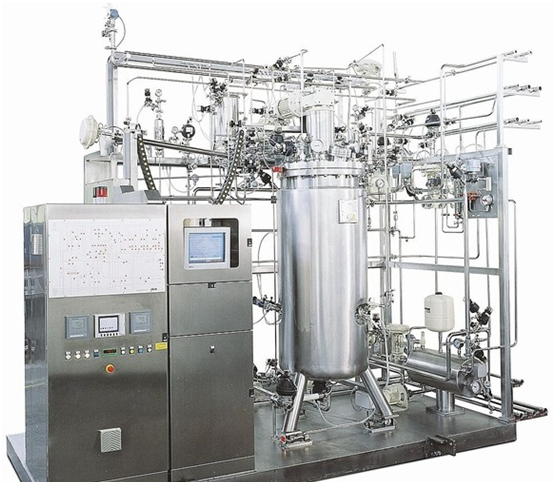
Design and Operation of Fermenters: Engineering Optimal Environments for Microbial Cultivation and Industrial Bioproduction
Introduction Fermentation stands as a fundamental and versatile process across multiple scientific and industrial disciplines, […]
Benefits of Fermentation: A Comprehensive Exploration
Fermentation is one of the oldest and most fundamental biotechnological processes known to mankind, with […]
Fermentation and Its Importance
The term fermentation is one of the oldest in the history of biological and chemical […]
MICROBIAL METABOLITES: PRIMARY METABOLITES AND SECONDARY METABOLITES
Microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes, are among nature’s most prolific chemists. They are capable […]
LOUIS PASTEUR (1822-1895)
Louis Pasteur, a French scientist was the first to report the role of microorganisms in […]
Introduction to Industrial Microbiology
Microorganisms have long been central to the development and sustenance of human civilization. They play […]