AMYLASE (STARCH HYDROLYSIS) TEST
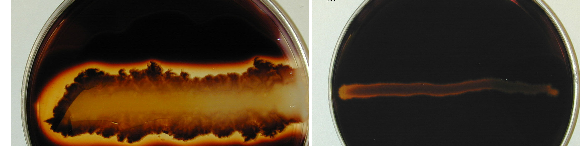
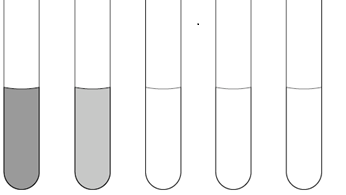
Amylase (Starch hydrolysis) test is used to identify bacteria that hydrolyze starch (including amylopectin and amylose) with the help of the enzyme amylase. Amylase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes starch into maltose, glucose, and dextrin’s. Some bacterial isolates including Bacillus and Clostridium have the ability to produce α-amylase and other enzymes that degrade starch molecules […]
AMYLASE (STARCH HYDROLYSIS) TEST Read More »
Biochemical Tests in Microbiology Lab