MYCOSES – fungal infections
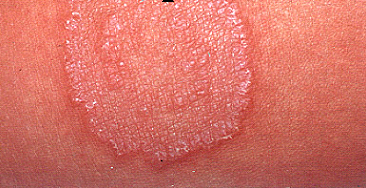
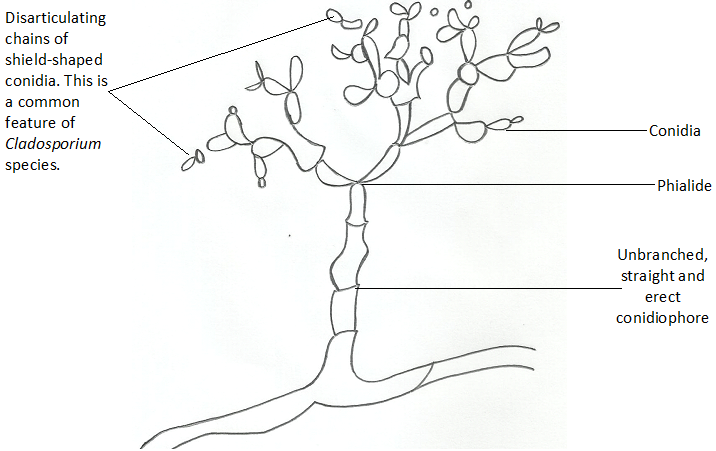
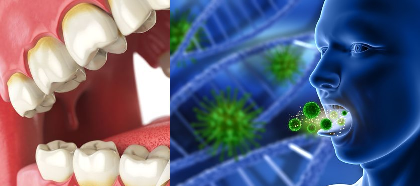
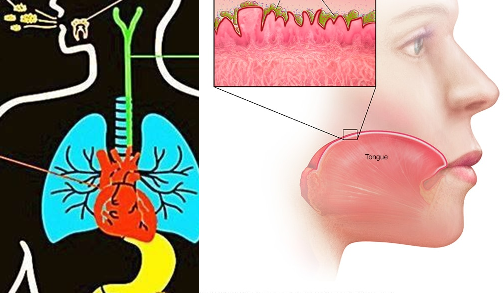
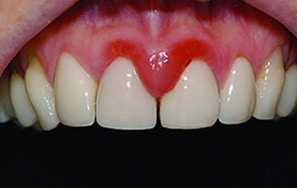
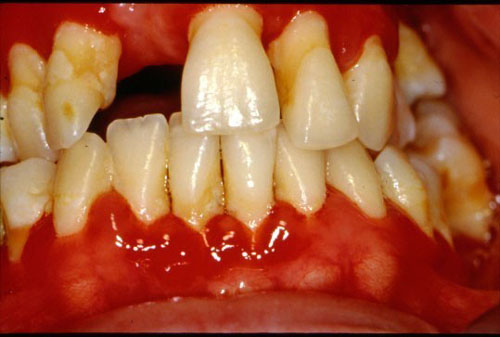
Mycoses are infections caused by pathogenic fungi. And they include superficial mycoses, cutaneous mycoses, subcutaneous mycoses, systemic or deep-seated mycosis and opportunistic mycoses depending on the affected tissue or parts of the body. However, other forms of fungal infections which are not directly caused by pathogenic fungi but their toxic products and the untoward reactions […]
MYCOSES – fungal infections Read More »
Mycology