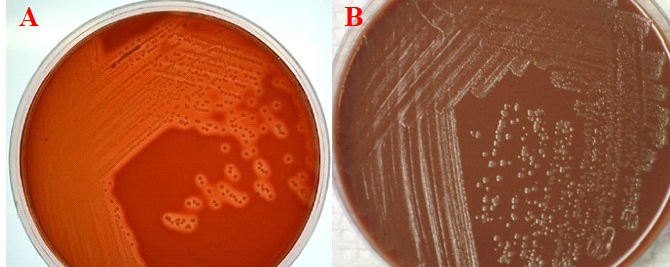
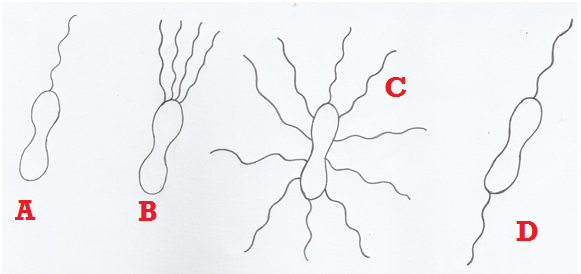
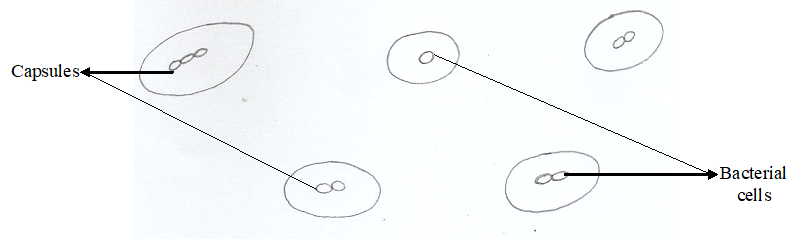
Selenite F broth
In the microbiology laboratory, pure cultures of microorganisms (e.g., bacteria) are critical to the success of the next stages of the experiment to be undertaken. Thus, selective isolation of bacteria from samples (especially those suspected to contain mix bacteria) is usually performed in two steps: The discovery of selenite F broth as an enrichment medium […]